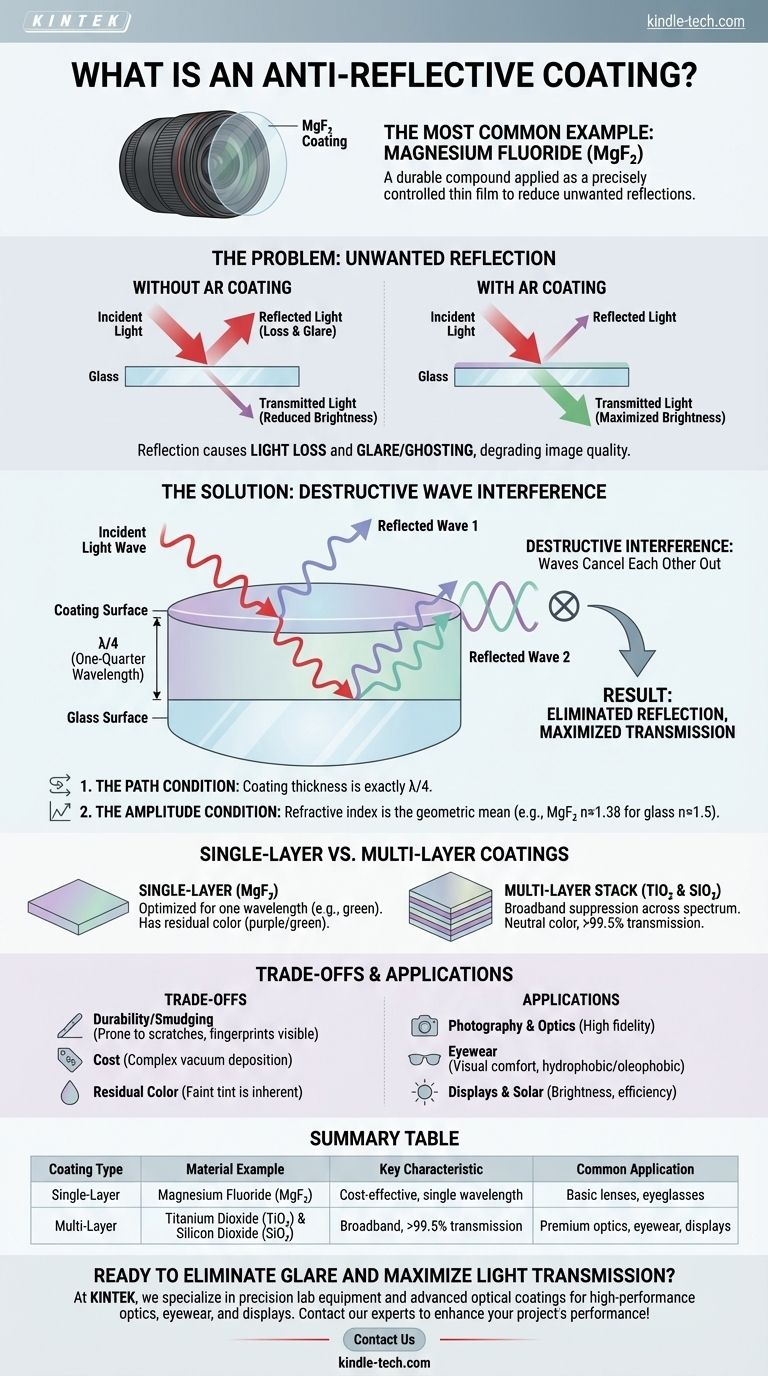
The most common example of an anti-reflective (AR) coating material is Magnesium Fluoride (MgF₂). For decades, this durable compound has been applied in a precisely controlled thin layer to surfaces like camera lenses and eyeglasses to reduce unwanted reflections. It works not by being inherently "non-reflective," but by using the physics of light waves to create cancellation.
An anti-reflective coating is not a material that absorbs light, but rather a carefully engineered thin film that causes reflected light waves to interfere with and cancel each other out. The goal is to maximize light transmission through a surface, not to simply make the surface look less shiny.

How Anti-Reflective Coatings Fundamentally Work
To understand why a material like Magnesium Fluoride is used, you first need to understand the problem it solves and the principle behind the solution.
The Problem: Unwanted Reflection
Whenever light passes from one medium to another (like from air to a glass lens), a portion of that light reflects off the surface. This reflection causes two primary problems:
- Loss of Light: The light that reflects is light that doesn't pass through the lens or sensor. For a complex camera lens with many elements, this can add up to a significant loss of brightness.
- Glare and Ghosting: Reflected light can bounce around inside an optical system, creating flare, haze, and "ghost" images that degrade image quality. For eyeglasses, it creates distracting glare.
The Solution: Destructive Wave Interference
The solution is to apply a transparent, ultra-thin coating to the surface. This creates a new system with two reflective surfaces: the top of the coating and the top of the glass itself.
The coating's thickness is precisely controlled to be one-quarter of the wavelength of a target color of light (typically green, in the middle of the visible spectrum).
When a light wave hits the lens, some of it reflects off the coating's surface. The rest enters the coating, reflects off the glass surface beneath, and travels back out. Because it had to travel down and back up through the coating, this second reflected wave is now perfectly out of sync with the first one.
This is called destructive interference. The two reflected waves cancel each other out, effectively eliminating the reflection.
The Two Critical Conditions
For this cancellation to work, two conditions must be met:
- The Path Condition: The coating thickness must be one-quarter of the light's wavelength (λ/4). This ensures the reflected waves are perfectly misaligned.
- The Amplitude Condition: The amount of light reflected from each surface must be equal. This is achieved when the coating's refractive index is the geometric mean of the two surrounding materials (e.g., air and glass).
Magnesium Fluoride (n≈1.38) has a refractive index that is conveniently close to the ideal value for coating common glass (n≈1.5), making it a simple and effective choice for a single-layer coating.
From Single-Layer to Multi-Layer Coatings
While a single layer of MgF₂ is effective, modern technology has improved upon it significantly.
The Limitation of a Single Layer
A single-layer coating is optimized for only one specific wavelength (color) of light. It is less effective for other colors.
This is why you can often see a faint residual color, typically purplish or greenish, when you look at a coated lens from an angle. You are seeing the colors of light that are not being perfectly canceled.
The Modern Solution: Multi-Layer Stacks
High-performance AR coatings used today are far more advanced. They consist of a stack of multiple, alternating layers of different materials with high and low refractive indices, such as **Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) and Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) **.
By carefully designing the thickness and material of each layer in the stack, engineers can suppress reflections across the entire visible spectrum. This results in a coating that is more neutral in color and transmits over 99.5% of light.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, AR coatings are not without their compromises.
Durability and Smudging
AR coatings are microscopically thin and can be more prone to scratching than bare glass. Modern coatings include a hard, protective topcoat, but care is still required.
Furthermore, because they eliminate reflections, they make fingerprints and smudges much more visible. The oil from your skin stands out because there is no background glare to obscure it.
Cost
Applying multiple layers of material with nanometer-level precision using vacuum deposition technology is a complex and expensive process. This is why high-quality multi-coated optics and eyeglasses command a higher price.
Residual Color
Even the best broadband AR coatings have a slight residual reflection, which gives the surface a faint color tint. While this is a sign the coating is working, it is an inherent characteristic of the technology.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The principles of AR coatings are applied differently depending on the final application.
- If your primary focus is photography or professional optics: You need a multi-layer broadband AR coating to maximize light transmission and eliminate ghosting, ensuring the highest possible image fidelity.
- If your primary focus is eyewear: The goal is to reduce distracting glare for visual comfort and to make your eyes more visible to others, which is achieved with a durable multi-layer coating that includes hydrophobic (water-repellent) and oleophobic (oil-repellent) properties.
- If your primary focus is displays or solar panels: You need a coating that maximizes light throughput to improve screen brightness or energy conversion efficiency, prioritizing function over perfect color neutrality.
By manipulating light at the wavelength scale, we can transform a reflective surface into one that is almost perfectly transparent.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Material Example | Key Characteristic | Common Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Layer | Magnesium Fluoride (MgF₂) | Reduces reflection for a single wavelength; cost-effective | Basic camera lenses, standard eyeglasses |
| Multi-Layer | Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) & Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) | Broadband suppression across visible spectrum; high light transmission (>99.5%) | High-performance optics, premium eyewear, displays |
Ready to eliminate glare and maximize light transmission in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment and consumables, including advanced optical coatings. Whether you're developing high-performance optics, eyewear, or energy-efficient displays, our solutions ensure superior light control and durability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our anti-reflective coating technologies can enhance your project's performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What are the materials used in physical Vapour deposition coating? A Guide to Metals, Nitrides & More
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- How is carbon nanotubes structured? From Graphene Sheets to 1D Cylinders
- What is thin film in semiconductor? The Layered Foundation of Modern Microchips
- How do you make a sputtering target? The Complete Guide to Manufacturing High-Performance Targets
- What are the advantages of diamond coating? Boost Durability and Performance
- What is the substrate for thin film deposition? A Guide to Choosing Your Foundation
- What are the advantages of thin film technology? Achieve Breakthroughs in Electronics, Energy, and More



















