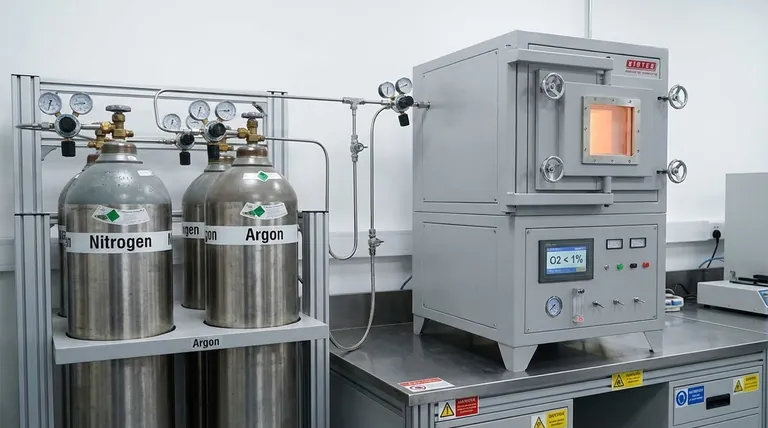
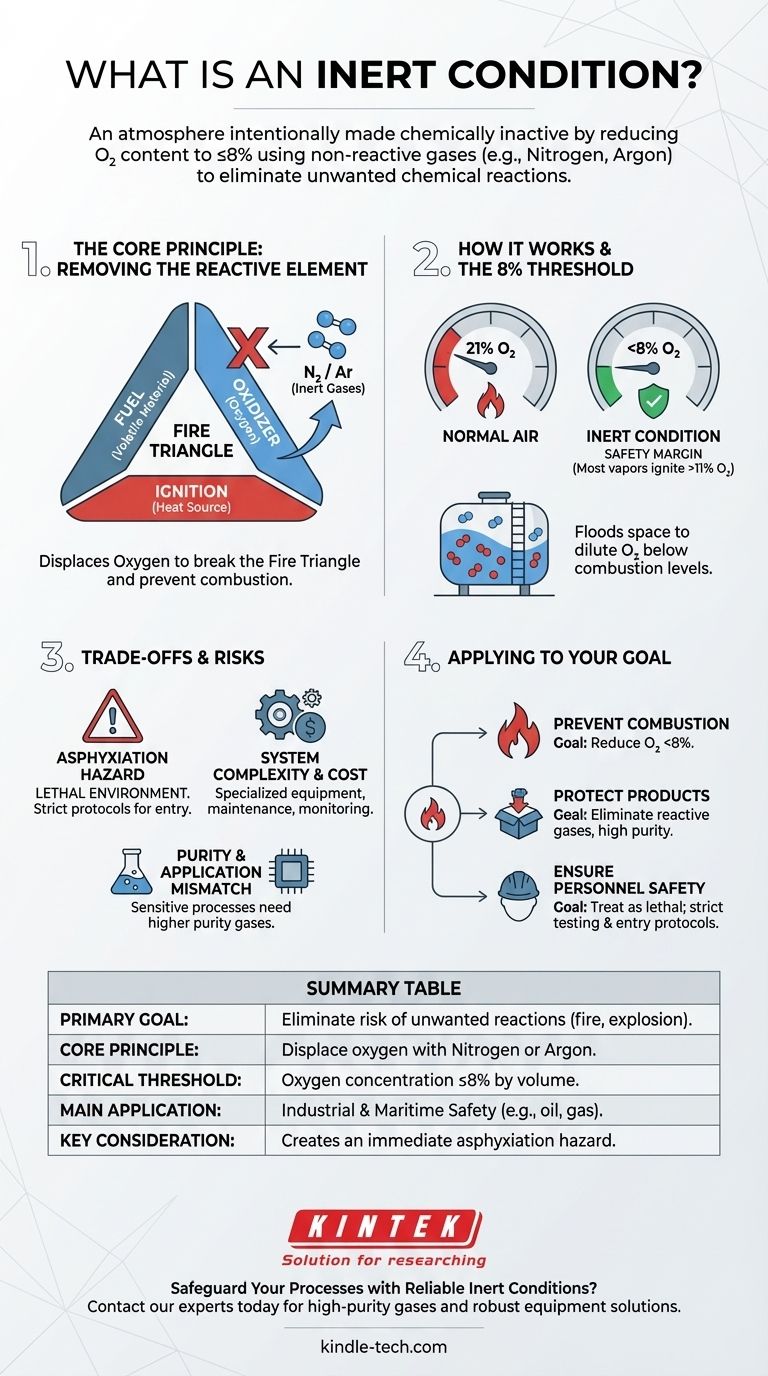
An inert condition describes an atmosphere that has been intentionally made chemically inactive. In industrial and maritime safety contexts, this is achieved by reducing the oxygen content to 8% or less by volume through the addition of a non-reactive gas, such as nitrogen or argon.
The core purpose of creating an inert condition is to eliminate the risk of unwanted chemical reactions. By displacing reactive gases like oxygen, you can prevent fires, explosions, or the degradation of sensitive materials.

The Core Principle: Removing the Reactive Element
An inert condition is fundamentally a form of engineered safety. It works by removing one of the key ingredients required for hazardous chemical reactions, most commonly combustion.
Why Oxygen is the Primary Target
Many dangerous industrial incidents, like fires and explosions, require three things: fuel, an ignition source (heat), and an oxidizer. This is often called the fire triangle.
While fuel and ignition sources can be managed, the oxygen in normal air (about 21%) is a powerful and readily available oxidizer. The most effective way to render a volatile atmosphere safe is to break the fire triangle by removing the oxygen.
How Inert Gases Work
Inert gases, such as nitrogen and argon, are chemically stable and do not readily react with other substances. They don't neutralize oxygen; they physically displace it.
By flooding an enclosed space like a storage tank with an inert gas, you dilute the concentration of oxygen. Once the oxygen level drops below the threshold required to support combustion, the environment becomes inert.
The Significance of the 8% Threshold
The specific value of 8% oxygen or less is a critical safety standard in many industries, particularly those handling flammable hydrocarbons like oil and gas.
Most hydrocarbon vapors cannot ignite when the oxygen concentration is below approximately 11%. The 8% limit provides a crucial safety margin to account for measurement inaccuracies or small fluctuations in the atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While creating an inert condition is a powerful safety measure, it introduces its own set of critical considerations that must be managed.
The Immediate Danger to Human Life
The most significant risk is asphyxiation. An atmosphere with 8% oxygen cannot support human life and is considered immediately dangerous.
Any inert space is a confined space hazard. No personnel should ever enter an inerted tank or vessel without following strict safety protocols, which include thoroughly ventilating the space and verifying a safe oxygen level (typically 19.5% to 23.5%).
System Complexity and Cost
Achieving and maintaining an inert condition requires specialized equipment. This can include inert gas generators, high-pressure storage cylinders for nitrogen or argon, and continuous atmospheric monitoring systems.
These systems add cost, complexity, and maintenance requirements to an operation. They are not "set and forget" solutions and demand constant vigilance.
Purity and Application Mismatch
The required purity of the inert gas depends on the application. For preventing a fire in a crude oil tank, cooled and cleaned exhaust gas from a ship's engine might suffice.
However, for sensitive processes like manufacturing electronics or packaging food, even trace amounts of contaminants can be unacceptable. These applications require high-purity inert gases, which are more costly to produce or procure.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Understanding the purpose behind inerting is key to implementing it correctly. Your primary objective dictates your operational focus.
- If your primary focus is preventing combustion in volatile environments: Your goal is to reliably reduce and maintain oxygen levels below the 8% safety threshold through inert gas displacement.
- If your primary focus is protecting sensitive products or processes: Your goal is to eliminate reactive gases to prevent oxidation or contamination, which may demand higher-purity inert gases.
- If your primary focus is ensuring personnel safety: An inert condition must always be treated as a lethal environment, requiring strict atmospheric testing and entry protocols before any human access is permitted.
Ultimately, creating an inert condition is a deliberate engineering control designed to master chemical reactivity and ensure operational safety.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Eliminate risk of unwanted chemical reactions (fire, explosion, degradation). |
| Core Principle | Displace reactive oxygen with non-reactive gases like Nitrogen or Argon. |
| Critical Threshold | Oxygen concentration reduced to 8% or less by volume. |
| Main Application | Industrial & maritime safety for volatile materials (e.g., oil, gas). |
| Key Consideration | Creates an immediate asphyxiation hazard for personnel. |
Need to Safeguard Your Processes with Reliable Inert Conditions?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-purity gases and robust equipment necessary to create and maintain precise inert atmospheres. Whether your goal is to prevent combustion in volatile environments or protect sensitive materials from oxidation, our solutions are designed for safety and performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you implement a safe and effective inerting strategy for your laboratory or industrial needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting



















