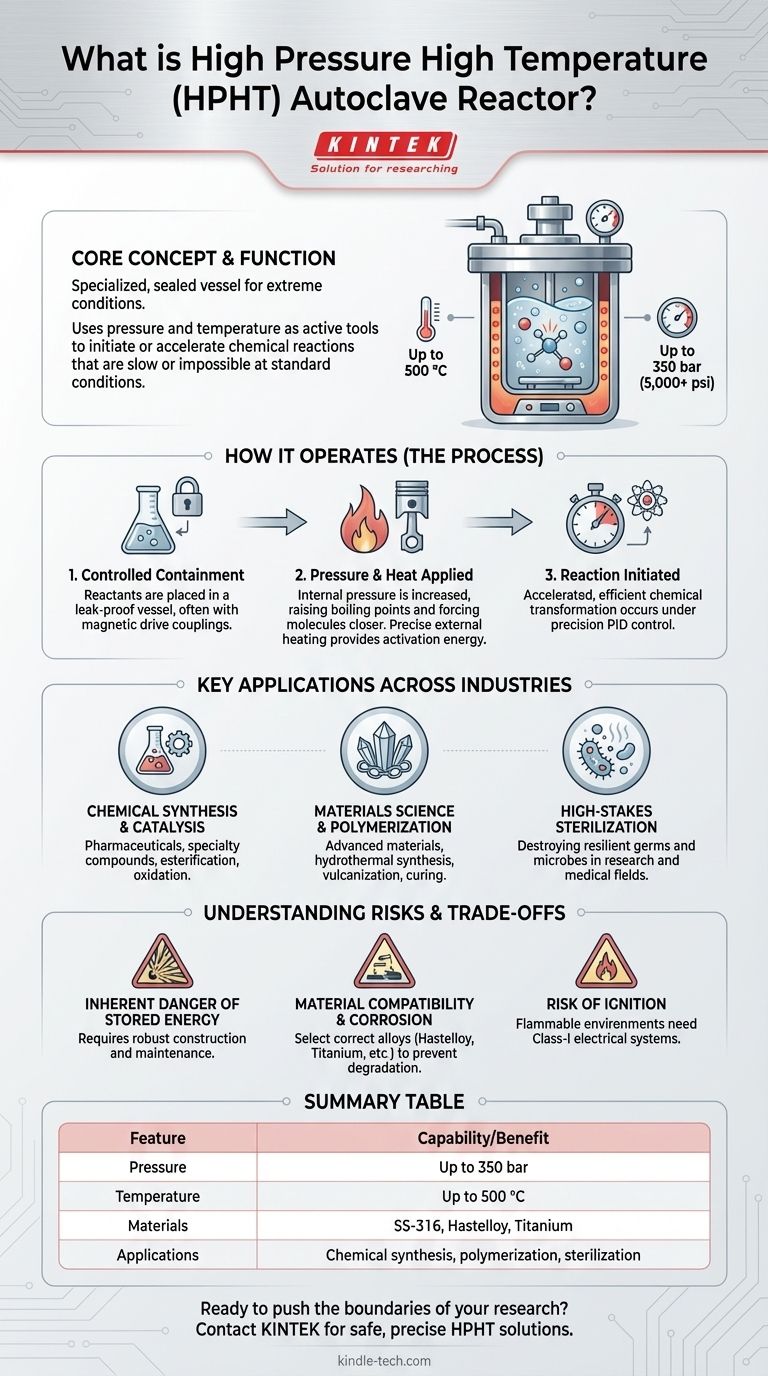
At its core, a high-pressure high-temperature (HPHT) autoclave reactor is a specialized, sealed vessel engineered to contain and control chemical processes under extreme conditions. These reactors are typically built from robust materials like SS-316, Hastelloy, or Titanium to safely manage pressures up to 350 bar (over 5,000 psi) and temperatures as high as 500 °C. Their purpose is to create an environment where these intense conditions can initiate or accelerate specific chemical reactions.
The true function of an HPHT autoclave is to use pressure and temperature as active tools. By manipulating this controlled environment, scientists and engineers can force chemical reactions that would otherwise be too slow, inefficient, or entirely impossible at standard atmospheric conditions.

How an HPHT Reactor Fundamentally Works
An HPHT autoclave operates on the principle of using a contained, high-energy environment to manipulate matter at a molecular level. It is far more than a simple heating vessel; it's a precision instrument for chemical transformation.
The Principle of Controlled Containment
The process begins by placing reactants or materials inside the sealed reactor chamber. A key feature is a leak-proof seal, often achieved with advanced magnetic drive couplings, which prevents any material from escaping even under immense pressure.
Using Pressure to Drive Reactions
Once sealed, the internal pressure is increased. This pressure serves two primary functions: it raises the boiling point of liquids (allowing for higher reaction temperatures) and it forces molecules into closer proximity, significantly increasing the rate of reaction. This is essential for processes like hydrogenation, polymerization, and alkylation.
Precision Temperature Management
Simultaneously, an external heating system, precisely managed by a PID controller, raises the internal temperature to the desired setpoint. This high temperature provides the necessary activation energy to start the reaction and ensures the complete destruction of any microbes in sterilization applications.
Key Applications Across Industries
The ability to control these extreme conditions makes HPHT autoclaves indispensable in several advanced scientific and industrial fields.
Chemical Synthesis and Catalysis
HPHT reactors are workhorses in the chemical industry for a wide range of organic and inorganic reactions. They are routinely used for esterification, oxidation, nitration, and ethoxylation to produce novel chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and specialty compounds.
Materials Science and Polymerization
The creation of advanced materials often relies on processes that only occur under high pressure. This includes the vulcanization of rubber, the curing of industrial coatings, and hydrothermal synthesis for creating single-crystal materials and high-performance composites.
High-Stakes Sterilization
In research and medical applications, the combination of high pressure and steam temperature provides a powerful sterilization method. This process can effectively destroy even the most resilient germs and microbes on equipment where other methods might fail.
Understanding the Critical Risks and Trade-offs
While incredibly powerful, the operation of HPHT reactors involves significant risks that demand expert knowledge and strict safety protocols.
The Inherent Danger of Stored Energy
Operating at pressures of 50 to 350 bar means the vessel contains a massive amount of stored energy. Any structural failure could result in a catastrophic release. This necessitates robust construction, regular maintenance, and comprehensive operator training.
Material Compatibility and Corrosion
The combination of aggressive chemicals and extreme temperatures can quickly corrode even strong metals. Selecting the correct reactor material—whether stainless steel, Hastelloy, Monel, or Zirconium—is critical to prevent vessel degradation and process contamination.
The Risk of Ignition
Many chemical reactions are flammable, and a sealed, high-pressure environment can amplify the danger. It is crucial to prevent any potential sources of ignition. This includes using properly grounded equipment and ensuring the facility has a Class-I electrical system to prevent sparks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if an HPHT autoclave is the correct tool, you must align its capabilities with the specific requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is advanced chemical synthesis: The reactor's ability to overcome high activation energy barriers and control reaction pathways is its most valuable asset.
- If your primary focus is new material development: The autoclave is essential for processes like polymerization and hydrothermal synthesis, where pressure directly influences the final material's structure and properties.
- If your primary focus is absolute sterilization: The combination of intense pressure and heat offers a definitive method for destroying highly resistant biological contaminants.
Ultimately, the HPHT autoclave is an indispensable instrument for pushing the boundaries of what is chemically and materially possible in a controlled environment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Capability | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Max Pressure | Up to 350 bar (5,000+ psi) | Forces molecular proximity, accelerates reactions |
| Max Temperature | Up to 500 °C | Provides activation energy for difficult reactions |
| Common Materials | SS-316, Hastelloy, Titanium | Resists corrosion from aggressive chemicals |
| Primary Applications | Chemical synthesis, polymerization, sterilization | Enables reactions impossible at standard conditions |
Ready to push the boundaries of your research or production?
An HPHT autoclave reactor from KINTEK can be the key to unlocking new chemical pathways, developing advanced materials, or achieving definitive sterilization. Our reactors are engineered for safety and precision, tailored to your specific process requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a high-pressure, high-temperature solution can accelerate your projects. Get in touch via our contact form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why are batch reactors used in pharmaceutical industry? Unmatched Flexibility & Control for Drug Manufacturing
- What is the role of a high-pressure reactor in steam explosion? Unlock Biomass Potential with Precision
- What conditions does a high-pressure hydrothermal reactor provide for PE microplastic degradation? Master AOPs Today
- What are the advantages of nickel-based alloy reactors for HI decomposition? Ensure Durability in Acidic Environments
- What are the primary functions of a precision reactor? Optimize Halogenated Unsaturated Polyester Resin Synthesis
- Why does the design of supercritical fluid electrochemical autoclaves use a nickel-base shell and a titanium liner?
- What are the primary advantages of using Hastelloy C-22 for reactors? Ensure Corrosion Resistance in Hydrate Research
- How does a magnetic drive high-pressure reactor simulate oil and gas field environments? Safe H2S/CO2 Testing



















