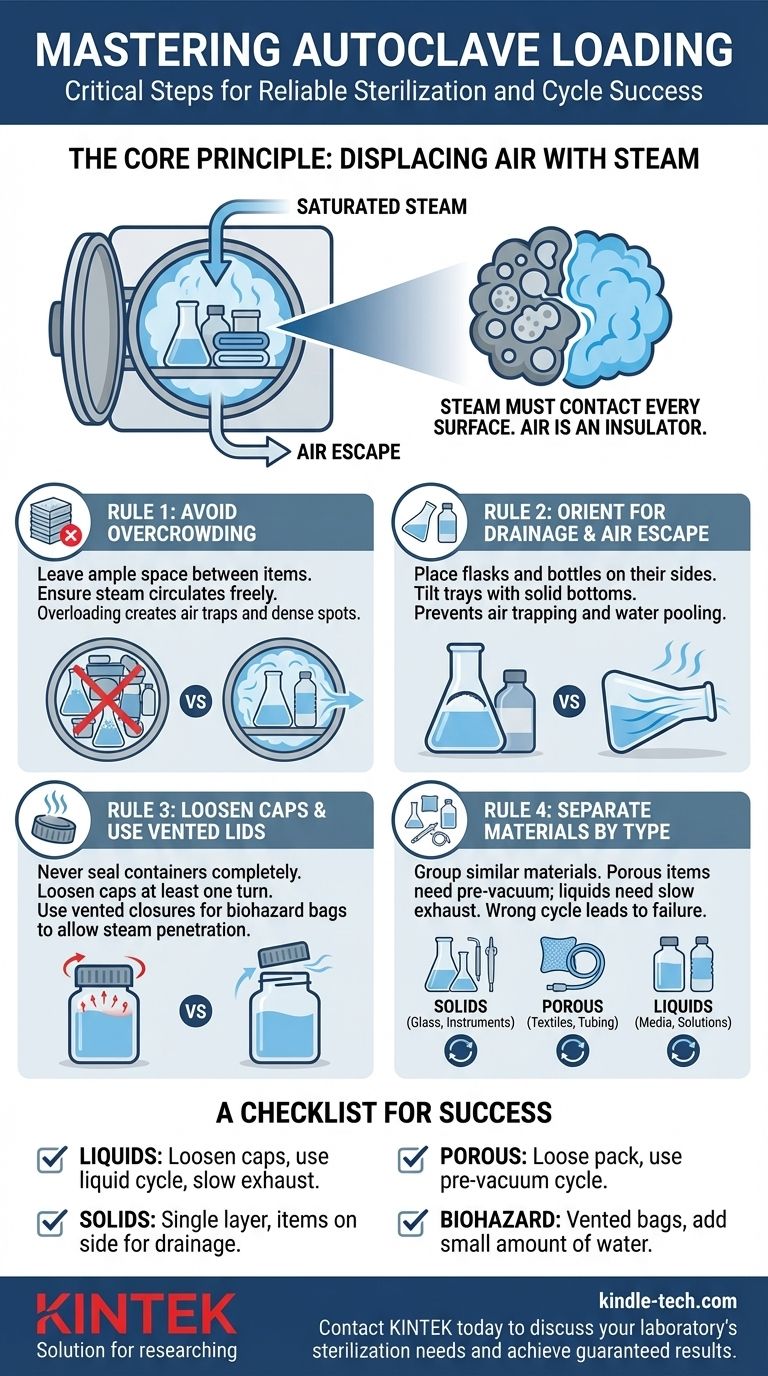
Properly loading an autoclave is as critical as the cycle you select. The most important consideration is arranging all items to allow for the complete removal of air and the uninhibited penetration of steam. This means avoiding overcrowding, ensuring containers are not sealed airtight, and orienting items to prevent air from becoming trapped or water from pooling.
Effective sterilization is not about heat alone; it's about saturated steam making direct contact with every single surface. Your loading strategy's primary goal is to eliminate air pockets and create clear pathways for steam to flow in and condensate to drain out.
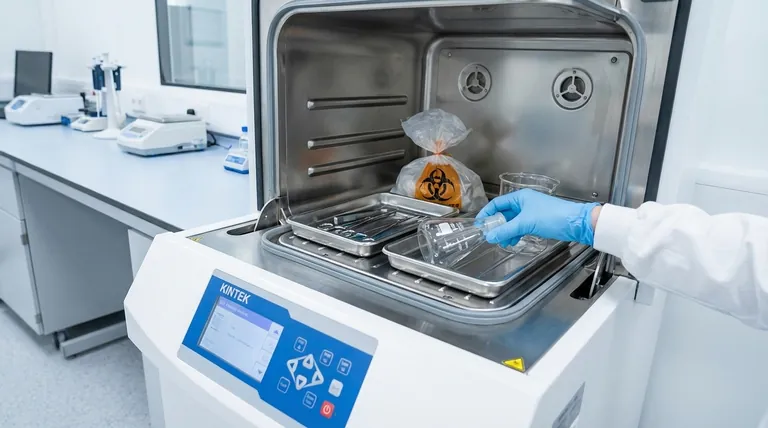

The Core Principle: Displacing Air with Steam
An autoclave works by replacing the air in its chamber with saturated steam under pressure. Understanding this principle is the key to understanding why loading methodology is so crucial.
Why Air is the Enemy of Sterilization
Air is a poor conductor of heat and acts as an insulating barrier. If an air pocket gets trapped inside a flask or within a dense pack of instruments, it prevents the superheated steam from making contact with the surfaces inside that pocket. The temperature in that air pocket will not reach the required level for sterilization, leading to a cycle failure.
The Role of Steam Penetration
Saturated steam is the actual sterilizing agent. It efficiently transfers thermal energy to all the items in the load, denaturing the proteins in any microorganisms present. For this to happen, the steam must flow freely around and into every item.
How Loading Directly Impacts Air Removal
Even autoclaves with advanced vacuum systems, which are designed to actively pull air out of the chamber, can be defeated by improper loading. If a beaker is placed upright, it creates a perfect bucket for trapping air that the vacuum cannot easily remove. The loading configuration must work with the autoclave's systems, not against them.
Practical Rules for Effective Loading
Following a few simple rules will dramatically increase the reliability and effectiveness of your sterilization cycles.
Rule 1: Do Not Overcrowd the Chamber
Leave ample space between all items—whether they are instrument trays, media bottles, or waste bags. Overloading prevents steam from circulating freely and can create dense spots where air becomes trapped. A good rule of thumb is to ensure you can see the back wall of the chamber from the front.
Rule 2: Orient Containers for Drainage and Air Escape
This is arguably the most common mistake. All containers like flasks, beakers, and bottles should be placed on their sides. Trays with solid bottoms should be tilted. This orientation allows air to flow out as steam flows in, and it allows condensate (water) to drain away during the drying phase.
Rule 3: Loosen Caps and Use Vented Lids
Never seal a container completely. The pressure changes inside an autoclave can cause sealed containers to break or even explode. Loosen the caps on bottles and jars to at least one full turn. For biohazard bags, ensure they are not twisted and sealed shut; they should be left slightly open or use a vented closure to allow steam to penetrate.
Rule 4: Separate Materials by Type
Whenever possible, run loads containing similar materials together. Porous items like gowns or tubing require more aggressive air removal (a pre-vacuum cycle) than hard, non-porous goods like glassware. Liquid loads require a completely different cycle with slow exhaust to prevent boiling over.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Attempting to "optimize" by cutting corners on loading practices almost always leads to failure and rework, costing more time in the long run.
The Myth of the "Efficient" Overloaded Cycle
The single biggest pitfall is trying to sterilize too much at once. While it may feel efficient to pack the chamber tightly, an overcrowded load frequently results in a failed cycle. This means everything must be repackaged and re-run, doubling the time and resource consumption.
The Risk of Wet Packs
If items are oriented incorrectly, water (condensate) will pool inside them. This moisture can compromise the sterility of the packaging after the cycle is complete, creating a pathway for microorganisms to enter. A pack that is wet at the end of a cycle is considered unsterile.
Ignoring Load Density
A tightly wrapped surgical kit or a dense bag of waste is much harder to sterilize than a single instrument on a tray. Dense loads require longer cycle times and, critically, a pre-vacuum function to ensure all trapped air is removed from the interior of the pack. Simply placing a dense load in an autoclave without considering this will likely result in an unsterile core.
A Checklist for the Right Load
Use this guide to ensure your loading strategy matches your materials and sterilization goal.
- If your load contains liquids (e.g., media bottles): Loosen all caps and use a dedicated liquid cycle with a slow exhaust to prevent the liquid from boiling over.
- If your load contains solid, non-porous items (e.g., glassware, instruments): Arrange items in a single layer where possible, and place all containers on their side to facilitate drainage.
- If your load contains porous items (e.g., textiles, filters, plastic tubing): Pack these items loosely and always use a cycle with a pre-vacuum phase to guarantee air is removed from deep within the material.
- If your load contains biohazard waste: Ensure bags are permeable to steam and not sealed airtight. Adding a small amount of water (approx. 100-200ml) to each bag helps generate steam from within, aiding sterilization.
By mastering the principles of loading, you transform the autoclave from a simple machine into a reliable and precise sterilization tool.
Summary Table:
| Key Loading Principle | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Avoid Overcrowding | Ensures free steam circulation and prevents air traps. |
| Orient Containers on Side | Allows air to escape and condensate to drain. |
| Loosen Caps & Lids | Prevents pressure buildup and allows steam penetration. |
| Separate Loads by Material | Matches the cycle type (e.g., liquid, porous) to the load for optimal results. |
Ensure your laboratory's sterilization is never compromised by improper loading. KINTEK specializes in high-performance autoclaves and lab equipment designed for reliability and ease of use. Our experts can help you select the right autoclave and provide guidance on best practices for your specific applications, from processing liquids and glassware to porous materials and biohazard waste.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's sterilization needs and achieve guaranteed results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What conditions does a dynamic autoclave provide for PWR corrosion testing? Simulate Extreme Reactor Environments
- How often should autoclave maintenance be performed? A Guide to Reliable Sterilization
- What is the primary role of high-pressure high-temperature autoclaves in SCWR research? Key Roles in Material Validation
- Which is better dry-heat or steam autoclave? Choose the Right Sterilization Method
- How does a slow strain rate testing system integrated with an autoclave facilitate material research? | KINTEK
- What is the temperature of a low autoclave? The Critical Minimum for Sterilization
- What is the role of high-pressure high-level autoclaves in simulating 9Cr–1Mo steel reactions? Expert Insights
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy



















