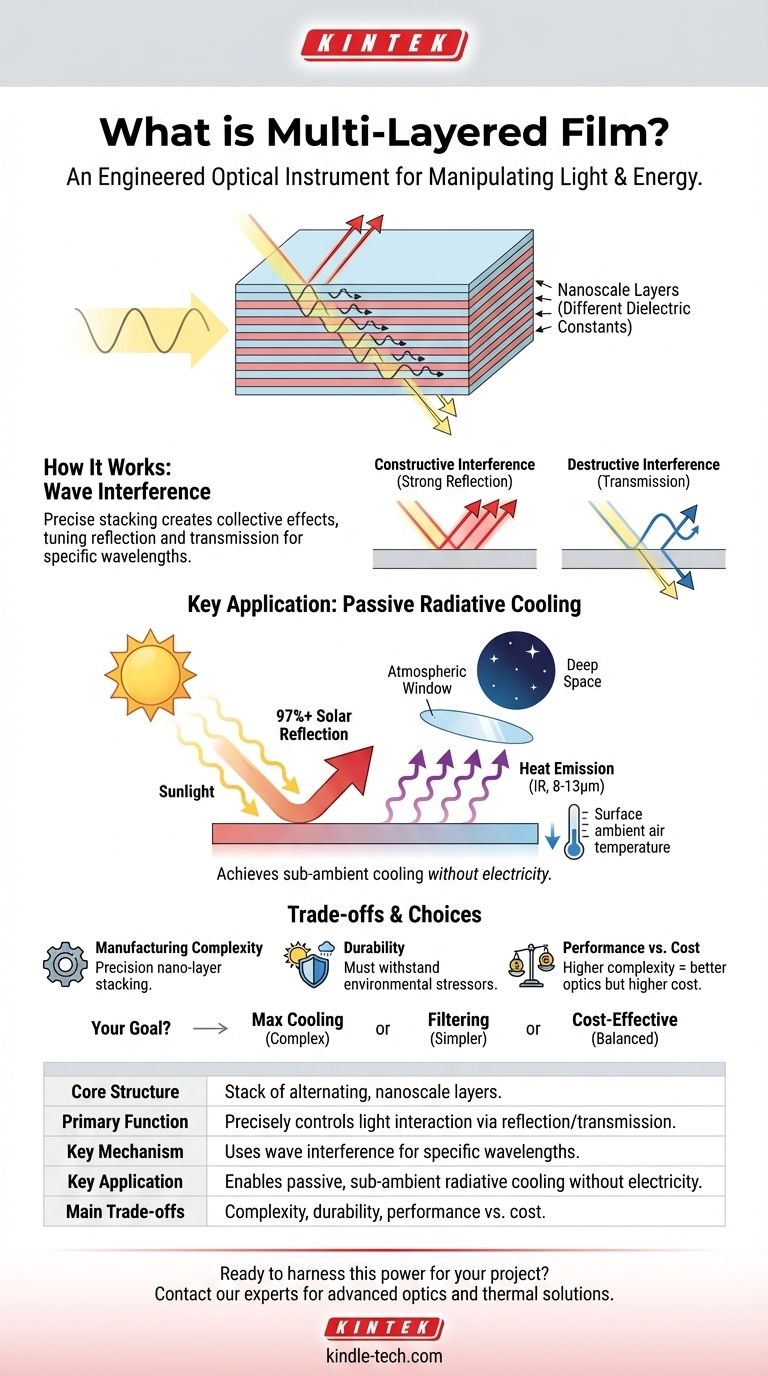
At its core, a multi-layered film is an engineered material constructed from a stack of incredibly thin, alternating layers of different substances. Its purpose is not just to be a physical barrier, but to precisely control how it interacts with light. By carefully selecting the materials—specifically their dielectric constants, which describe how they respond to an electric field—and the thickness of each layer, the film can be designed to reflect certain wavelengths of light while allowing others to pass through.
The true power of a multi-layered film lies in its structure. It is not merely a stack of materials, but a precisely tuned optical instrument designed to manipulate light and energy, enabling technologies like passive, power-free cooling.

How Multi-Layered Films Manipulate Light
A multi-layered film functions by exploiting the physics of light waves at the boundaries between different materials. The precise stacking of layers creates a collective effect that is far more powerful than any single material could achieve.
The Principle of Alternating Layers
Each time light passes from one layer to the next, a small portion of it is reflected. This is due to the difference in the dielectric constant (or refractive index) between the two adjacent materials.
By stacking dozens or even hundreds of these layers, these small reflections can be made to interact with each other in very specific ways.
Creating Interference
The magic happens through a phenomenon called wave interference. As light waves reflect off the many different interfaces within the film, they can either reinforce each other (constructive interference) or cancel each other out (destructive interference).
This is the key mechanism. By engineering the layer thicknesses, you can ensure that specific colors (wavelengths) of light experience constructive interference and are strongly reflected, while other wavelengths experience destructive interference and are transmitted through the film.
Tuning for Specific Wavelengths
This principle allows for incredible precision. A film can be designed to reflect ultraviolet light, transmit visible light, and reflect infrared light—all at the same time.
This ability to select which parts of the electromagnetic spectrum are reflected or transmitted is what makes these films so valuable.
A Key Application: Radiative Cooling
The reference to "sub-ambient diurnal radiative cooling" highlights one of the most powerful applications of this technology. Multi-layered films can be used to create surfaces that cool themselves down, even under direct sunlight, without using any electricity.
The Goal: Passive Cooling
The challenge of daytime cooling is twofold: you must get rid of the object's internal heat while simultaneously preventing the sun from heating it up.
Step 1: Reflect Sunlight
First, the film is designed to act as an almost perfect mirror for the wavelengths of sunlight (primarily visible and near-infrared light).
This high reflectivity, often over 97%, prevents the sun's energy from being absorbed by the object in the first place.
Step 2: Emit Heat as Infrared
Second, the film is designed to be a highly efficient emitter of thermal radiation in a very specific band of the infrared spectrum (roughly 8 to 13 micrometers).
This range is known as the "atmospheric window" because the atmosphere is transparent to these wavelengths, allowing the heat to radiate directly into the cold of deep space.
Achieving Sub-Ambient Temperatures
By combining extreme solar reflection with high thermal emittance, the surface gets rid of its own heat much faster than it absorbs heat from the sun.
This allows the object to cool to a temperature below that of the surrounding air, achieving power-free, sub-ambient cooling.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, multi-layered films come with practical limitations that are critical to consider in any real-world application.
Manufacturing Complexity
Creating hundreds of uniform layers, each with a thickness measured in nanometers, is a complex and precise manufacturing process. This can make high-performance films expensive to produce at a large scale.
Durability and Lifespan
The materials used in the film must be able to withstand environmental stressors like UV radiation, moisture, and temperature swings without degrading. Ensuring long-term durability is a significant engineering challenge.
Performance vs. Cost
A film with more layers and more exotic materials will generally offer better optical performance. However, this comes at a higher cost. For many applications, a simpler design with fewer layers may provide a "good enough" solution that is far more commercially viable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal design of a multi-layered film depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum cooling performance: You need a highly complex film with many layers, optimized for near-perfect solar reflectance and maximum emittance in the atmospheric window.
- If your primary focus is simple optical filtering: For applications like selective mirrors or anti-reflection coatings, a simpler design with fewer layers tailored to specific visible or IR wavelengths is sufficient.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, large-scale deployment: The key is to balance performance with manufacturability, potentially using fewer layers or more common materials to achieve a practical price point.
Ultimately, multi-layered film technology provides a powerful toolkit for commanding the flow of light and heat.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Structure | Stack of alternating, nanoscale layers of different materials. |
| Primary Function | Precisely controls light interaction via reflection and transmission. |
| Key Mechanism | Uses wave interference to reflect or transmit specific wavelengths. |
| Key Application | Enables passive, sub-ambient radiative cooling without electricity. |
| Main Trade-offs | Manufacturing complexity, durability, and performance vs. cost. |
Ready to harness the power of multi-layered films for your project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced materials and expert consultation for cutting-edge applications in optics and thermal management. Whether you're developing next-generation cooling systems or specialized optical filters, our team can help you select the right solutions to meet your performance and budget requirements.
Let's discuss how we can support your laboratory's innovation. Contact our experts today to explore the possibilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Aluminum-Plastic Flexible Packaging Film for Lithium Battery Packaging
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Laboratory ITO FTO Conductive Glass Cleaning Flower Basket
People Also Ask
- What is the process of pyrolysis of rubber? A Step-by-Step Guide to Converting Waste into Fuel
- What size are injection molding machines? Match Tonnage to Your Part for Quality & Efficiency
- What is a moulding machine used for? Automate Sand Casting for High-Quality Metal Parts
- What finishes are done using calendering technique? Achieve High Gloss, Embossing, and More
- What is the principle of mixing on open two roll mill? Master Shear, Compression & Heat for Uniform Blending
- What is the difference between monolayer and multilayer film? Choose the Right Packaging for Your Product
- What is pyrolysis of rubber? Transform Waste Tires into Oil, Carbon & Gas
- How does a vulcanizing machine work? Mastering the Art of Rubber Transformation










