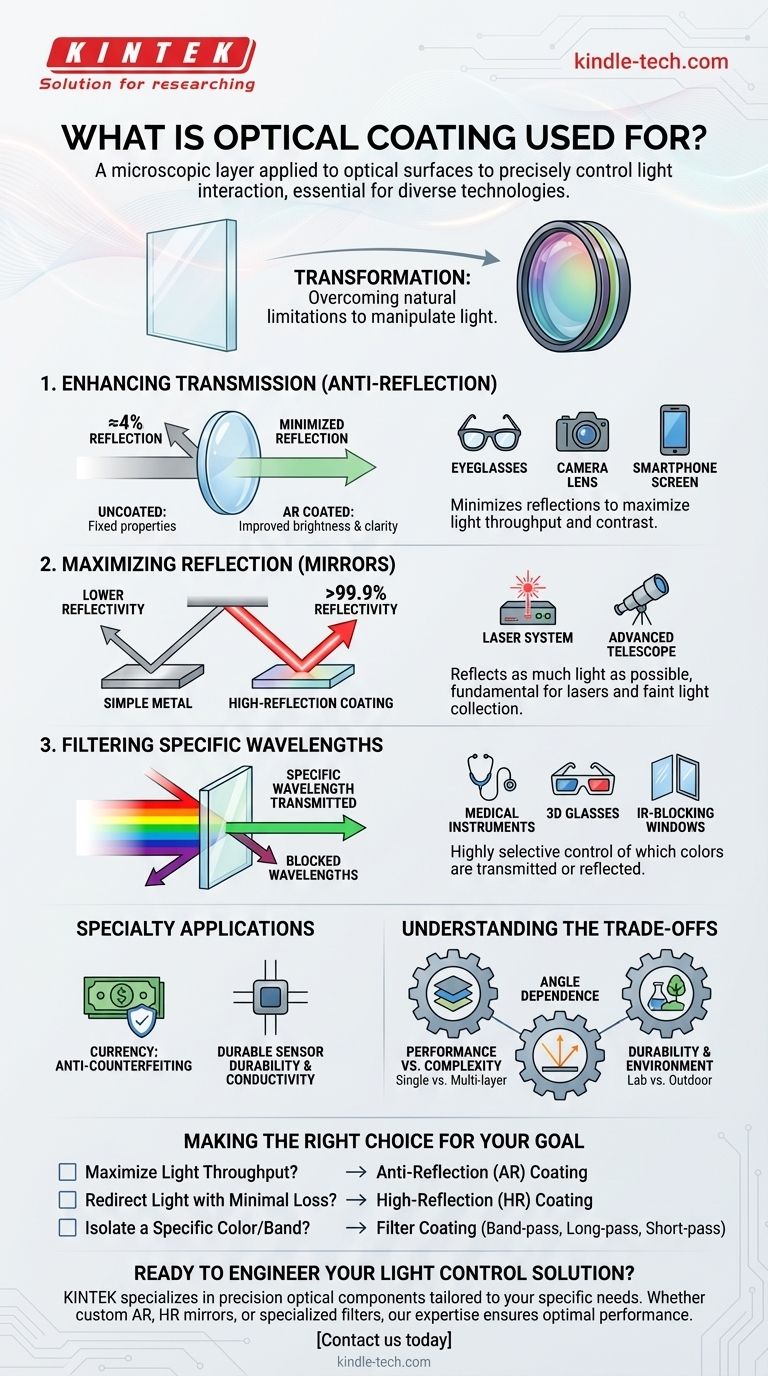
In short, an optical coating is a microscopic layer of specialized material applied to an optical surface, like a lens or mirror, to precisely control how it interacts with light. These coatings are essential for a vast range of technologies, from consumer eyeglasses to advanced scientific instruments, where they are used to reduce reflection, enhance reflectivity, or filter specific wavelengths of light.
The core purpose of an optical coating is to overcome the natural limitations of an optical material. It transforms a simple piece of glass into a high-performance component engineered to manipulate light for a specific, intended purpose.
The Core Functions of Optical Coatings
An uncoated optical surface has fixed properties; for example, a standard glass lens reflects about 4% of light at each of its surfaces. Optical coatings allow us to fundamentally change these properties to achieve a desired outcome.
Enhancing Transmission (Anti-Reflection)
The most common use of optical coatings is to reduce unwanted reflections, a process known as anti-reflection (AR).
By minimizing reflected light, AR coatings maximize the amount of light that passes through an optical system. This is critical for improving the brightness and contrast of images.
You encounter these coatings every day on eyeglasses, camera lenses, and smartphone screens, where they work to reduce glare and improve clarity.
Maximizing Reflection (Mirrors)
In other applications, the goal is the exact opposite: to reflect as much light as possible.
High-reflection (HR) coatings can create mirrors that reflect over 99.9% of specific wavelengths of light, far exceeding the performance of a simple polished metal surface.
These coatings are fundamental to devices like lasers, where light must be bounced between two highly reflective mirrors, and in advanced telescopes that need to collect faint light from distant objects.
Filtering Specific Wavelengths
Optical coatings can be engineered to be highly selective about which colors, or wavelengths, of light they transmit or reflect.
This allows for the creation of optical filters. A "cut-off" filter might block all light below a certain wavelength, while a "band-pass" filter allows only a very narrow range of colors to pass through.
These are used in scientific and medical instruments to isolate specific light signals, in 3D movie glasses to separate images for each eye, and even in architectural windows to block heat-carrying infrared light.
Specialty Applications
Beyond these primary functions, coatings serve other unique purposes.
For example, specialized coatings can be designed with features that are difficult to replicate, serving as an effective anti-counterfeiting measure on currency and high-value documents. They can also be used to make surfaces more durable or electrically conductive.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly powerful, optical coatings are not a universal solution. Their design and application involve critical trade-offs that determine their effectiveness and cost.
Performance vs. Complexity
A simple, single-layer anti-reflection coating is effective but may only work well for a single color of light.
Achieving high performance across a broad spectrum of colors (like for a camera lens) requires complex, multi-layer designs that are significantly more difficult and expensive to produce.
Angle Dependence
The performance of most optical coatings changes depending on the angle at which light strikes the surface.
A coating designed to work perfectly for light hitting it head-on may perform poorly if the light comes in at a steep angle. This must be accounted for in the design of the overall optical system.
Durability and Environment
A coating's durability must match its intended environment. A coating inside a sealed laboratory instrument does not need the same scratch resistance as one on a pair of eyeglasses or a military-grade sensor exposed to the elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right coating begins with defining the primary goal for manipulating light in your system.
- If your primary focus is maximum light throughput: You need an anti-reflection (AR) coating designed for your specific wavelength range to minimize loss from surface reflections.
- If your primary focus is redirecting light with minimal loss: You need a high-reflection (HR) or dielectric mirror coating to achieve the highest possible reflectivity.
- If your primary focus is isolating a specific color or band of light: You need a band-pass, long-pass, or short-pass filter coating to selectively transmit and block the correct wavelengths.
Ultimately, optical coatings transform standard components into precision instruments engineered to control light.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Primary Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Reflection (AR) | Maximize light transmission | Eyeglasses, camera lenses, screens |
| High-Reflection (HR) | Maximize light reflection | Lasers, telescopes, scientific mirrors |
| Filter Coatings | Transmit/block specific wavelengths | Medical instruments, 3D glasses, IR-blocking windows |
| Specialty Coatings | Durability, conductivity, anti-counterfeiting | Currency, sensors, durable optics |
Ready to Engineer Your Light Control Solution?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment and consumables, including optical components tailored to your specific needs. Whether you require custom anti-reflection coatings for maximum clarity, high-reflection mirrors for laser systems, or specialized filters for analytical instruments, our expertise ensures optimal performance for your laboratory.
Contact us today to discuss how our optical coatings can enhance your application's efficiency and accuracy!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
People Also Ask
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance












