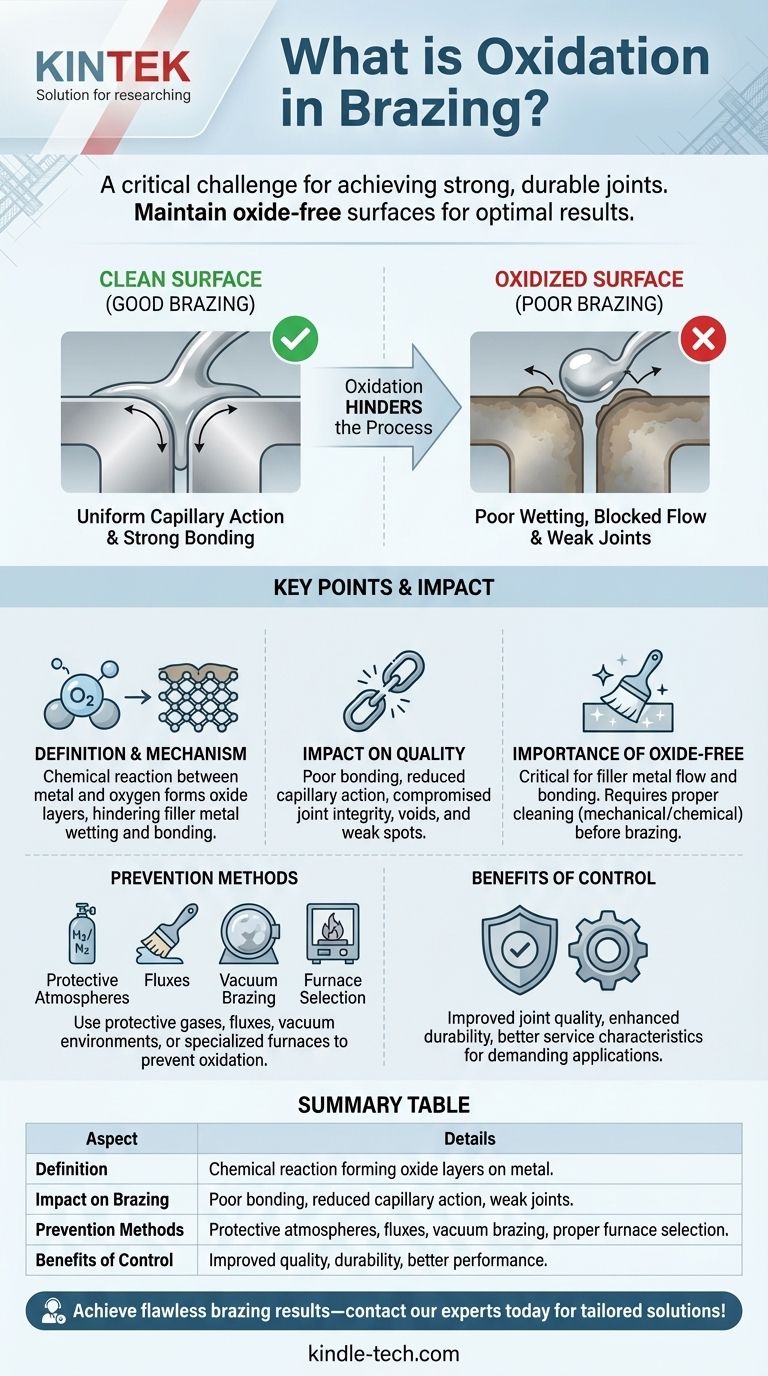
Brazing is a metal-joining process that involves melting a filler metal and distributing it between two or more close-fitting parts through capillary action. One of the critical challenges in brazing is oxidation, which occurs when the metal surfaces react with oxygen, forming oxide layers. These oxide layers can significantly hinder the brazing process by preventing the filler metal from properly bonding or flowing over the surfaces. To achieve a strong and durable brazed joint, it is essential to maintain oxide-free surfaces. This can be accomplished through proper cleaning, the use of protective atmospheres (such as hydrogen), and selecting appropriate furnace types. Understanding and controlling oxidation is vital for ensuring the integrity and performance of brazed components.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition of Oxidation in Brazing
- Oxidation refers to the chemical reaction between metal surfaces and oxygen, resulting in the formation of oxide layers.
- During brazing, these oxide layers can prevent the filler metal from effectively wetting and bonding to the base metal, leading to weak or incomplete joints.
- Oxidation is particularly problematic because it disrupts the capillary action required for the filler metal to flow evenly between the parts.
-
Impact of Oxidation on Brazing Quality
- Poor Bonding: Oxide layers act as barriers, preventing the filler metal from adhering properly to the base metal.
- Reduced Capillary Action: Uniform capillary action, which is essential for distributing the filler metal evenly, can only occur on clean, oxide-free surfaces.
- Compromised Joint Integrity: Oxidation can lead to voids, weak spots, or incomplete joints, reducing the durability and performance of the finished part.
-
Importance of Oxide-Free Surfaces
- Oxide-free surfaces are critical for ensuring that the filler metal can flow and bond effectively.
- Clean surfaces free of grease, oil, dirt, and oxides are necessary to achieve uniform capillary action and strong brazed joints.
- Proper surface preparation, such as mechanical cleaning or chemical treatments, is often required before brazing to remove contaminants and oxides.
-
Methods to Prevent Oxidation During Brazing
- Protective Atmospheres: Using gases like hydrogen or inert gases (e.g., argon or nitrogen) in the brazing furnace can prevent oxidation by displacing oxygen.
- Fluxes: Chemical fluxes can be applied to dissolve or prevent the formation of oxides during the brazing process.
- Vacuum Brazing: This method eliminates oxygen entirely by conducting the brazing process in a vacuum environment, ensuring oxide-free surfaces.
- Furnace Selection: The type of furnace used can influence the ability to maintain an oxide-free environment. For example, hydrogen brazing furnaces are effective at reducing surface oxides.
-
Benefits of Controlling Oxidation
- Improved Joint Quality: Reducing or eliminating oxides results in cleaner, stronger, and more reliable brazed joints.
- Enhanced Durability: Oxide-free joints are less prone to failure, improving the longevity and performance of the finished part.
- Better Service Characteristics: Parts brazed in controlled environments exhibit superior mechanical and thermal properties, making them suitable for demanding applications.
By understanding the role of oxidation in brazing and implementing strategies to prevent it, manufacturers can achieve high-quality, durable brazed joints that meet the performance requirements of various industries.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Chemical reaction between metal and oxygen, forming oxide layers. |
| Impact on Brazing | Poor bonding, reduced capillary action, compromised joint integrity. |
| Prevention Methods | Protective atmospheres, fluxes, vacuum brazing, proper furnace selection. |
| Benefits of Control | Improved joint quality, enhanced durability, better service characteristics. |
Achieve flawless brazing results—contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques
- What is the process of vacuum brazing? Achieve High-Purity, Strong Metal Joining
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.



















