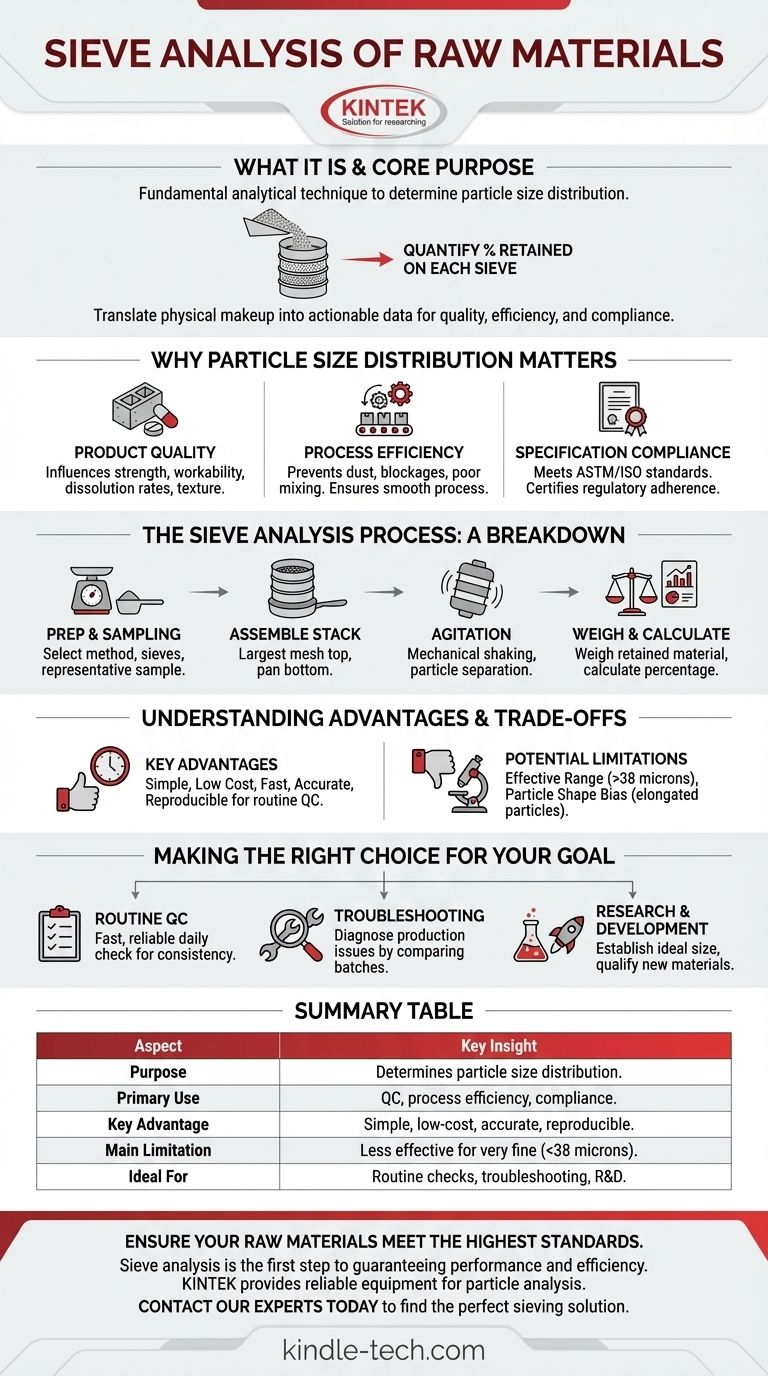
Sieve analysis is a fundamental analytical technique used to determine the particle size distribution of a granular raw material. The method works by passing a precisely weighed sample through a series of stacked sieves with progressively smaller mesh openings. This mechanical sorting process allows you to quantify the percentage of material that is retained on each sieve, revealing the full spectrum of particle sizes within the sample.
The core purpose of sieve analysis is to translate a raw material's physical makeup into actionable data. Understanding this particle size distribution is not just an academic exercise; it is a critical factor for controlling product quality, ensuring process efficiency, and meeting industry specifications.

Why Particle Size Distribution Matters
The size and distribution of particles in a raw material have a direct and profound impact on both the final product and the manufacturing process. It is a key indicator of material quality.
The Impact on Final Product Quality
The properties of the final product often depend on the granulometry of its components. For example, the strength and workability of concrete are directly influenced by the size distribution of the sand and crushed rock used.
In pharmaceuticals or food production, the particle size of powders can affect everything from dissolution rates and bioavailability to texture and mouthfeel.
The Influence on Process Efficiency
Inconsistent particle sizes can wreak havoc on production lines. Materials that are too fine may cause dust issues or blockages, while materials that are too coarse can lead to incomplete reactions, poor mixing, or increased wear on equipment.
By monitoring the input material with sieve analysis, you can ensure a smooth, predictable, and efficient process.
Ensuring Specification Compliance
Many industries operate under strict standards (like ASTM or ISO) that define acceptable particle size ranges for raw materials.
Sieve analysis provides the accurate, reproducible data required to certify that your materials meet these contractual and regulatory obligations.
The Sieve Analysis Process: A Breakdown
While specific methods vary by material and industry standard, the fundamental process follows four distinct steps.
Step 1: Preparation and Sampling
The process begins with careful preparation. This includes selecting the appropriate standard method, choosing a set of sieves with the correct mesh sizes, and determining the necessary sample quantity.
The sample itself must be representative of the entire batch. It may also require pre-drying or conditioning to ensure moisture doesn't affect the results.
Step 2: Assembling the Sieve Stack
The selected sieves are stacked in order, with the sieve having the largest mesh openings at the top and the one with the smallest openings at the bottom. A solid pan is placed at the very bottom to collect the finest particles.
Step 3: Agitation and Separation
The pre-weighed raw material sample is placed in the top sieve. The entire stack is then agitated, typically by a mechanical shaker, for a set amount of time.
This motion causes the particles to move through the stack, with each sieve retaining particles larger than its mesh size while allowing smaller particles to pass through to the sieve below.
Step 4: Weighing and Calculation
After agitation is complete, the material retained on each individual sieve (and in the bottom pan) is carefully weighed.
These weights are then used to calculate the percentage of the total sample that was retained at each size level, creating a clear picture of the particle size distribution.
Understanding the Advantages and Trade-offs
Sieve analysis is widely used because it offers a superb balance of simplicity and utility, but it's important to recognize its limitations.
The Key Advantages
The primary benefits of sieve analysis are its simplicity and low cost. The equipment is relatively inexpensive, and the procedure does not require highly specialized operators.
Furthermore, when performed correctly, the method provides accurate and reproducible results in a short amount of time, making it ideal for routine quality control. It also physically separates the material into different size fractions, which can be useful for further analysis.
Potential Limitations
The main limitation of sieve analysis is its effective size range. It is not well-suited for extremely fine materials (typically below 38 microns), where particles may agglomerate or clog the mesh. For these sub-sieve materials, other methods like laser diffraction are more appropriate.
Additionally, the results can be influenced by particle shape. Elongated or flat particles may pass through mesh openings end-on, potentially skewing the results compared to more spherical particles of the same mass.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sieve analysis is a versatile tool. How you apply it depends on your ultimate objective.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Use sieve analysis as a fast and reliable daily check to ensure incoming raw materials are consistent with your established specifications.
- If your primary focus is process troubleshooting: Use it to diagnose production issues by comparing the particle size of a "good" batch of material against a "bad" one.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Employ sieve analysis to establish the ideal particle size distribution for a new product or to qualify materials from a new supplier.
Ultimately, mastering sieve analysis provides you with direct control over a fundamental property of your raw materials, ensuring quality and consistency from the very start.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Determines the particle size distribution of a granular material. |
| Primary Use | Quality control, process efficiency, and specification compliance. |
| Key Advantage | Simple, low-cost, and provides accurate, reproducible results. |
| Main Limitation | Less effective for very fine materials (typically below 38 microns). |
| Ideal For | Routine quality checks, process troubleshooting, and R&D. |
Ensure your raw materials meet the highest standards of quality and consistency.
Sieve analysis is the first step to guaranteeing your product's performance and your process's efficiency. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory equipment and consumables for all your particle analysis needs.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your laboratory and unlock the full potential of your raw materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
People Also Ask
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution



















