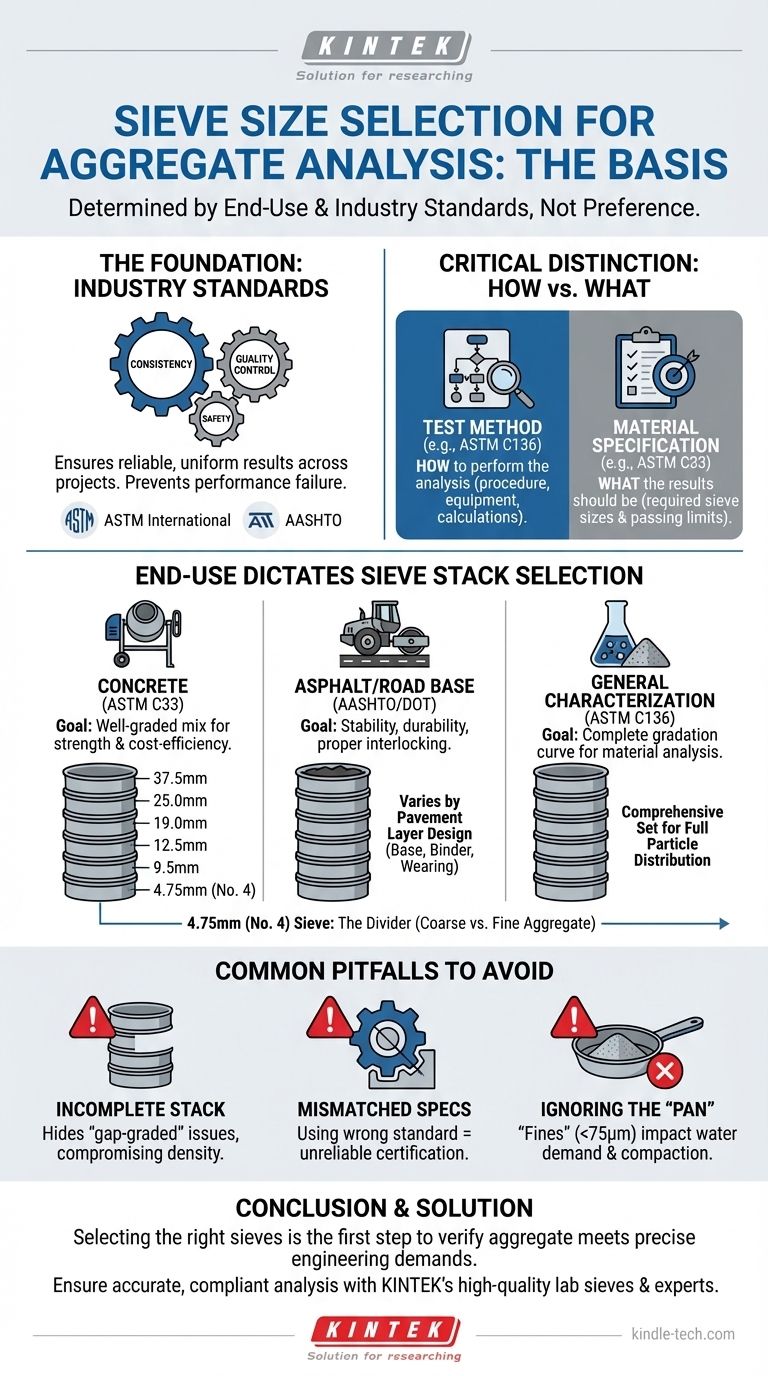
The fundamental basis for selecting sieve sizes for an aggregate analysis is the governing industry standard or project specification, which is determined by the aggregate's intended end-use. It is not an arbitrary choice but a requirement to ensure the material's particle size distribution is suitable for a specific engineering application, such as concrete, asphalt, or road base.
Sieve selection is a systematic process, not a matter of preference. The goal is to compare your aggregate's gradation against a predefined engineering standard (like ASTM C33 for concrete) to guarantee its performance, safety, and efficiency in the final product.

The Role of Industry Standards
The entire sieve analysis process is built on a foundation of standardization. Without it, results would be inconsistent and unreliable across different labs and projects.
Why Standards are Non-Negotiable
Standards exist to ensure consistency, quality control, and safety. An aggregate that is perfectly graded for one application, like drainage, could be disastrous for another, like high-strength concrete.
Following the correct standard ensures that everyone—from the quarry producer to the civil engineer—is evaluating the material against the same benchmark for performance.
Key Standardizing Bodies
In North America, the primary organizations that define these benchmarks are ASTM International (American Society for Testing and Materials) and AASHTO (American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials). Other regions follow their own standards, such as British Standards (BS) or Euro Norms (EN).
The Critical Link: Test Method vs. Specification
It is crucial to understand the difference between a test method and a material specification.
- The Test Method (e.g., ASTM C136): This standard tells you how to perform the sieve analysis—the procedure, the equipment, and the calculations.
- The Material Specification (e.g., ASTM C33): This standard tells you what the results should be. It provides the required set of sieve sizes and the acceptable percentage of material that can pass through each one for a specific application, like concrete aggregate.
How End-Use Dictates Sieve Selection
The required sieve stack is chosen to reveal key characteristics of the aggregate that are critical for its final purpose.
For Concrete Aggregates (ASTM C33)
The goal for concrete is a well-graded aggregate. This means the particles are distributed across a wide range of sizes, allowing smaller particles to fill the voids between larger ones. This minimizes the amount of cement paste needed, which reduces cost and shrinkage.
A typical sieve stack for coarse aggregate in concrete would include sizes like 37.5 mm (1½ in), 25.0 mm (1 in), 19.0 mm (¾ in), 12.5 mm (½ in), 9.5 mm (⅜ in), and 4.75 mm (No. 4).
For Asphalt and Pavement Bases
For asphalt, the gradation is critical for the stability and durability of the pavement. The aggregate structure must have sufficient voids to hold the liquid asphalt binder but also enough particle-to-particle contact for interlocking and strength.
Specifications, often from a state's Department of Transportation (DOT), will list the exact sieve sizes required to verify the aggregate meets the design criteria for a specific pavement layer (e.g., base course, binder course, or wearing course).
The Importance of the 4.75 mm (No. 4) Sieve
This specific sieve size is the internationally recognized dividing line between coarse aggregate (material retained on the sieve) and fine aggregate (material passing through the sieve).
The test procedure and required sieve sizes are often different for fine and coarse aggregates, so identifying this separation is a key first step.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes in sieve selection can lead to inaccurate data, causing a suitable aggregate to be rejected or an unsuitable one to be approved.
Using an Incomplete Sieve Stack
If you skip sieves required by the specification, you create blind spots in your gradation curve. This can hide "gap-graded" issues, where a particular particle size is missing, potentially compromising the final product's density and strength.
Mismatching Sieves to the Specification
You cannot use the sieve set for concrete aggregate to certify an aggregate for a specialized asphalt mix. Each application has its own set of performance requirements that are directly tied to the specific sieve sizes listed in its governing specification.
Ignoring the "Pan"
The material that passes through the very last sieve and collects in the pan is known as the "fines" or "minus 200" (75 µm). This smallest fraction has a massive impact on properties like water demand in concrete and compaction in soils. It must always be measured and accounted for.
Selecting the Correct Sieve Set for Your Project
Your choice must be deliberate and informed by the project's engineering requirements.
- If your primary focus is designing a concrete mix: You must use the sieve sizes and gradation limits specified in ASTM C33 (Standard Specification for Concrete Aggregates).
- If your primary focus is testing aggregates for a roadway: You must consult the project's governing specification, which is likely from a state DOT or based on AASHTO standards.
- If your primary focus is general material characterization without a specific use: Use a standard, comprehensive set of sieves as outlined in the test procedure ASTM C136 to get a complete picture of the particle size distribution.
Ultimately, selecting the right sieves is the first and most critical step in verifying that your aggregate meets the precise engineering demands of its intended use.
Summary Table:
| Aggregate Application | Governing Standard | Common Sieve Sizes | Key Goal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete Aggregates | ASTM C33 | 37.5 mm, 25.0 mm, 19.0 mm, 12.5 mm, 9.5 mm, 4.75 mm (No. 4) | Achieve a well-graded mix for strength and cost-efficiency |
| Asphalt & Pavement Bases | AASHTO / State DOT Specs | Varies by pavement layer design | Ensure stability, durability, and proper interlocking |
| General Characterization | ASTM C136 | Comprehensive set for full particle distribution | Obtain a complete gradation curve for material analysis |
Ensure your sieve analysis is accurate and compliant with the correct standards. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves and equipment for aggregate testing, helping laboratories and construction professionals achieve reliable, specification-compliant results. Contact our experts today to select the perfect sieve set for your concrete, asphalt, or material characterization needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis



















