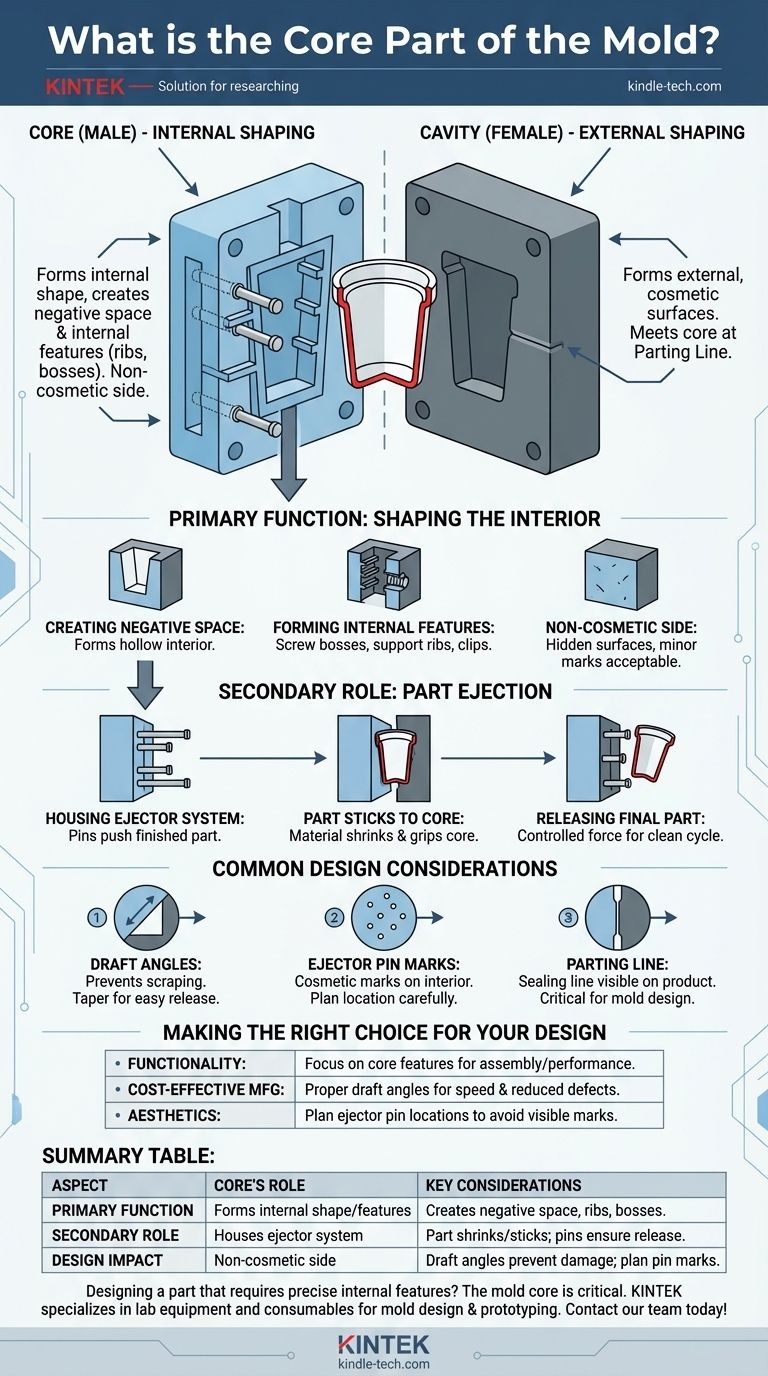
In simple terms, the core is the part of the mold that forms the internal shape of a component. It is one of the two primary halves of a mold, working in tandem with its counterpart, the cavity. For a hollow part like a cup, the core is the male component that creates the inside surface where you would pour a liquid.
The core and cavity are the two essential halves of any mold. The core shapes the internal, often non-cosmetic, features of a part, while the cavity shapes the external, cosmetic surfaces. The final product is formed in the space between them.

The Core's Primary Function: Shaping the Interior
The most fundamental purpose of the core is to define the internal geometry of the molded part. It creates the features that are typically not visible from the outside.
Creating Negative Space
Think of the core as the "positive" shape that creates the "negative" space inside your final part. If you are molding a plastic box, the core is the block that forms the hollow interior.
Forming Internal Features
The core isn't just for creating empty space. It's also responsible for forming any internal functional features, such as screw bosses, support ribs, or clips that will be used for assembly.
The Non-Cosmetic Side
Because the core forms the interior of the part, it is often referred to as the non-cosmetic side. Minor imperfections from the molding process are more acceptable on these surfaces as they are typically hidden from the end-user.
The Core's Secondary Role: Part Ejection
Beyond just shaping the part, the core plays a critical mechanical role in the manufacturing process itself.
Housing the Ejector System
In most standard molds, the core half contains the ejector system. This system consists of pins that push the finished, cooled part out of the mold once it opens.
Why the Part Sticks to the Core
As molten material cools and solidifies, it naturally shrinks. This shrinking action causes the finished part to grip tightly onto the core half of the mold, almost like a suction cup.
Releasing the Final Part
Without the ejector pins pushing against the part, it would be extremely difficult to remove it from the core without causing damage. The ejector system provides a controlled, even force to ensure a clean release cycle after cycle.
Common Design Considerations
Understanding the core's function directly impacts how a part should be designed for manufacturing. Ignoring these principles leads to defects and production failures.
The Necessity of Draft Angles
All surfaces on the core must have a slight angle, known as a draft angle. This taper prevents the part from scraping against the core during ejection, which would cause drag marks and damage.
Ejector Pin Marks
The force from the ejector pins will often leave small, circular marks on the interior surface of the part. Designers must be aware of where these marks will appear and ensure they don't interfere with the part's function or aesthetics if the interior is visible.
The Parting Line
The core and cavity must meet perfectly to form a seal. The line where these two halves meet is called the parting line, and it will be visible as a faint line on the final product. The location of this line is a critical decision in mold design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Design
Understanding the core's role helps you design parts that are not only functional but also manufacturable.
- If your primary focus is part functionality: Pay close attention to the features you place on the core, as it defines the internal geometry critical for assembly and performance.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective manufacturing: Incorporate proper draft angles on all core surfaces to ensure the part can be ejected easily and reliably, increasing production speed and reducing defects.
- If your primary focus is part aesthetics: Be aware that ejector pins housed in the core can leave cosmetic marks, and you must plan their location carefully if the inside of your part will be visible.
Ultimately, viewing a mold as an interplay between the internal-shaping core and the external-shaping cavity is the foundation of successful part design.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Core's Role | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Forms the internal shape and features of the part | Creates negative space, internal ribs, bosses |
| Secondary Role | Houses the ejector system for part release | Part shrinks and sticks to the core; ejector pins ensure clean release |
| Design Impact | Non-cosmetic side; affects draft angles and parting line | Draft angles prevent damage; ejector pin marks must be planned |
Designing a part that requires precise internal features? The mold core is critical to your component's functionality and manufacturability. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed to support your mold design and prototyping processes. Whether you're focused on functionality, cost-effective manufacturing, or aesthetics, our expertise can help you optimize your design for success. Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory and manufacturing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE or high-quality steel molds recommended for geopolymer specimens? Ensure Data Integrity and Easy Release
- How long does a steel mold last? Maximize Your Mold's Lifespan and ROI
- What size are XRF pellets? A Guide to Standard Dimensions and Preparation
- What are the key functions of graphite molds in hot pressing sintering? Enhance High Entropy Alloy Coating Density
- What are the stages of the molding process? A Guide to Plastic, Metal, and Ceramic Molding
- How to work with ceramic molds? Master the Art of Slip Casting for Consistent Results
- What are the advantages of using a heating die for Li6PS5Cl pellets? Optimize Electrolyte Molding and Densification
- What are the steps involved in making a mould? A Strategic Guide from Design to Production
















