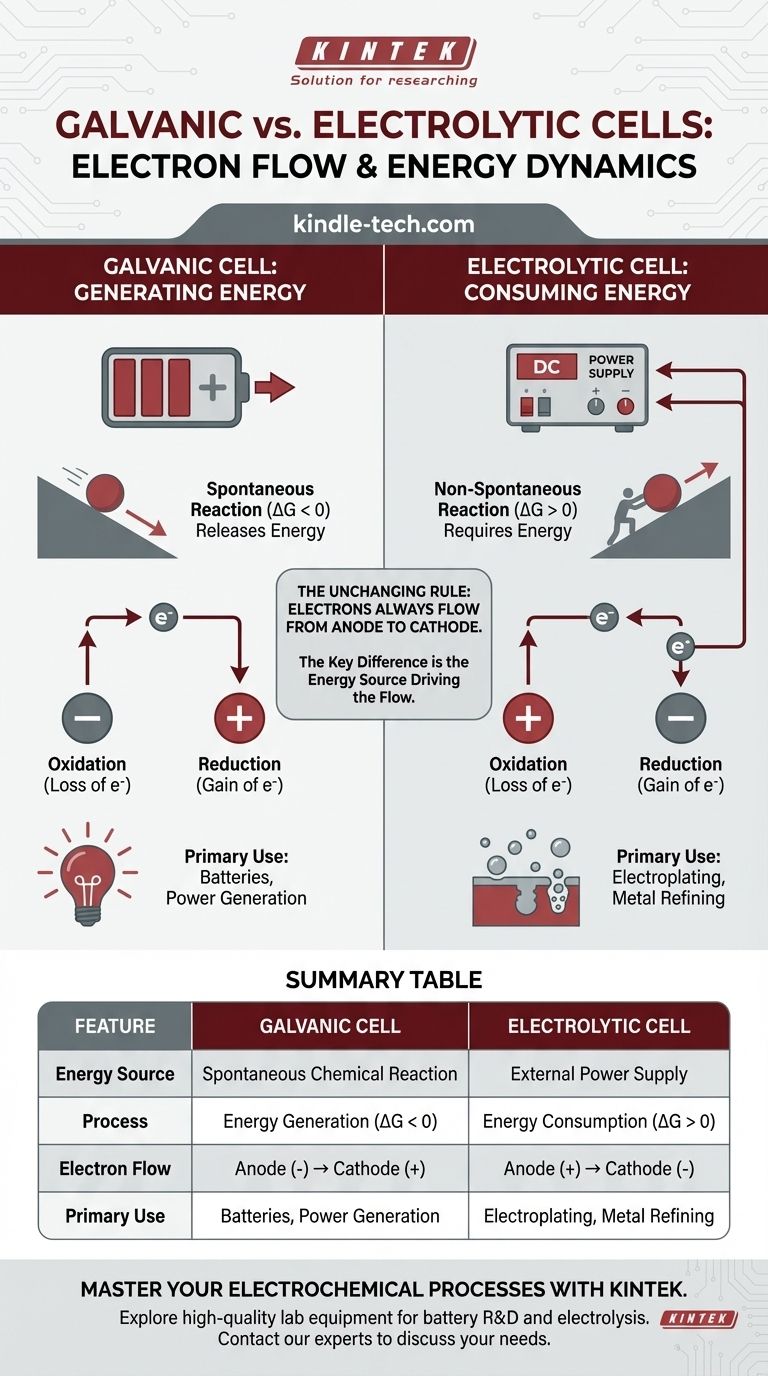
In any electrochemical cell, electron flow in the external circuit is always from the anode to the cathode. The critical distinction lies in why they flow. In a galvanic cell, a spontaneous chemical reaction generates energy and pushes the electrons. In an electrolytic cell, an external power source provides the energy to force electrons to flow and drive a non-spontaneous reaction.
The fundamental difference is not the direction of electron flow relative to oxidation and reduction, but the energy source driving the process. A galvanic cell converts stored chemical energy into electrical energy, while an electrolytic cell uses external electrical energy to force a chemical change.

The Core Principle: Spontaneous vs. Non-Spontaneous Reactions
To understand electron flow, you must first understand the energy dynamics of the cell. The entire system is governed by whether the chemical reaction happens on its own or must be forced.
Galvanic Cells: Generating Energy
A galvanic cell (also called a voltaic cell) harnesses a spontaneous chemical reaction. Think of it as a ball rolling downhill—the process releases energy naturally.
This spontaneous reaction has a negative Gibbs free energy (ΔG < 0). This release of chemical energy is converted directly into electrical energy, pushing electrons from the anode, through the external circuit, and to the cathode.
Galvanic cells are the basis for all conventional batteries.
Electrolytic Cells: Consuming Energy
An electrolytic cell is used to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. This is like pushing a ball uphill—it requires a constant input of external energy to happen.
This reaction has a positive Gibbs free energy (ΔG > 0). An external power source, like a battery or power supply, acts as an "electron pump." It forces electrons onto the cathode and pulls them away from the anode, driving a reaction that would not occur on its own.
Deconstructing Electron Flow and Electrode Polarity
The confusion around electron flow often stems from the changing polarity of the electrodes. While the roles of anode and cathode are fixed, their charges are not.
The Unchanging Rule: Anode to Cathode
By definition, the site of oxidation (loss of electrons) is always the anode, and the site of reduction (gain of electrons) is always the cathode.
Because electrons are lost at the anode and gained at the cathode, electrons in the external wire always flow from the anode to the cathode. This is a universal constant for both cell types.
The Critical Difference: Electrode Charge
The polarity (the positive or negative charge) of the electrodes flips between the two cell types, which is the source of most confusion.
In a galvanic cell, the anode is the site of spontaneous oxidation that releases electrons. This buildup of negative charge makes the anode the negative (-) terminal. The cathode, which consumes electrons, becomes the positive (+) terminal.
In an electrolytic cell, the external power source dictates the polarity. It connects its negative terminal to the cell's cathode to force electrons onto it and drive reduction. It connects its positive terminal to the cell's anode to pull electrons away and drive oxidation.
- Galvanic Cell: Anode (-) to Cathode (+)
- Electrolytic Cell: Anode (+) to Cathode (-)
Understanding the Practical Applications
The fundamental difference能量转换 (energy conversion) determines how these cells are used. One produces power, and the other consumes it to produce valuable materials.
Galvanic Cells: Power on Demand
The primary benefit of a galvanic cell is its ability to act as a portable source of electrical energy.
They are the foundation for batteries, from simple AA cells to a car battery. Their main limitation is that the chemical reactants are eventually consumed, causing the voltage to drop and the battery to die.
Electrolytic Cells: Forcing Chemical Change
The purpose of an electrolytic cell is to use electricity to create a chemical product.
This process, known as electrolysis, is essential for industrial applications like refining metals (e.g., producing pure aluminum), electroplating surfaces with a protective metal layer, and splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen. Their drawback is the need for a continuous and often costly supply of electrical energy.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your approach depends entirely on whether you need to generate electricity or drive a chemical reaction.
- If your primary focus is generating power or creating a battery: You are working with a galvanic cell, where a spontaneous reaction produces an electric current.
- If your primary focus is purifying a metal, electroplating a surface, or splitting a compound: You need an electrolytic cell, which uses external power to drive a non-spontaneous reaction.
- If your primary focus is understanding the core principle: Remember that oxidation is always at the anode and reduction is at the cathode; the key difference is whether the reaction is spontaneous (galvanic) or forced (electrolytic).
Understanding this distinction between spontaneous energy release and forced energy input is the key to mastering electrochemical cells.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Galvanic Cell | Electrolytic Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Spontaneous Chemical Reaction | External Power Supply |
| Process | Energy Generation (ΔG < 0) | Energy Consumption (ΔG > 0) |
| Electron Flow | Anode (-) → Cathode (+) | Anode (+) → Cathode (-) |
| Primary Use | Batteries, Power Generation | Electroplating, Metal Refining |
Master Your Electrochemical Processes with KINTEK
Whether you're developing new battery technologies or refining materials through electrolysis, having the right lab equipment is crucial for accurate and reliable results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables, providing the precise tools you need for all your electrochemical research and development.
Let us help you equip your lab for success. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your groundbreaking work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- PTFE Electrolytic Cell Electrochemical Cell Corrosion-Resistant Sealed and Non-Sealed
People Also Ask
- What is the structure of an H-type exchangeable membrane electrolytic cell? A Guide to Precise Electrochemical Separation
- What is a H type cell? A Guide to Divided Electrochemical Cells for Accurate Experiments
- How should the H-type electrolytic cell be stored when not in use? Expert Storage & Maintenance Guide
- What optical features does the H-type electrolytic cell have? Precision Quartz Windows for Photoelectrochemistry
- What are the typical volumes and aperture configurations for a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Optimize Your Electrochemical Setup



















