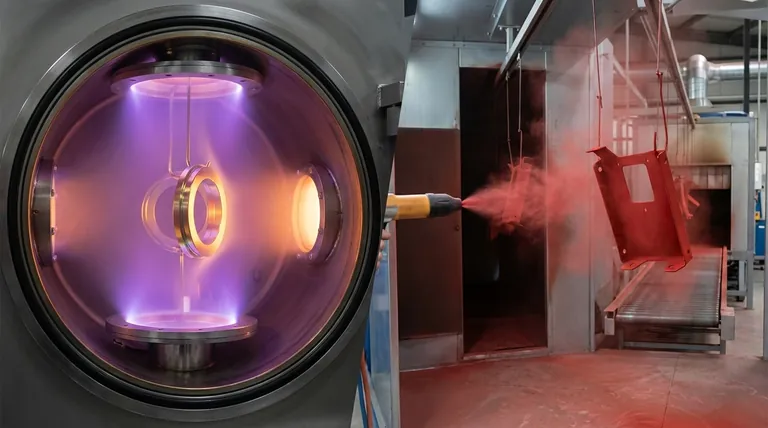
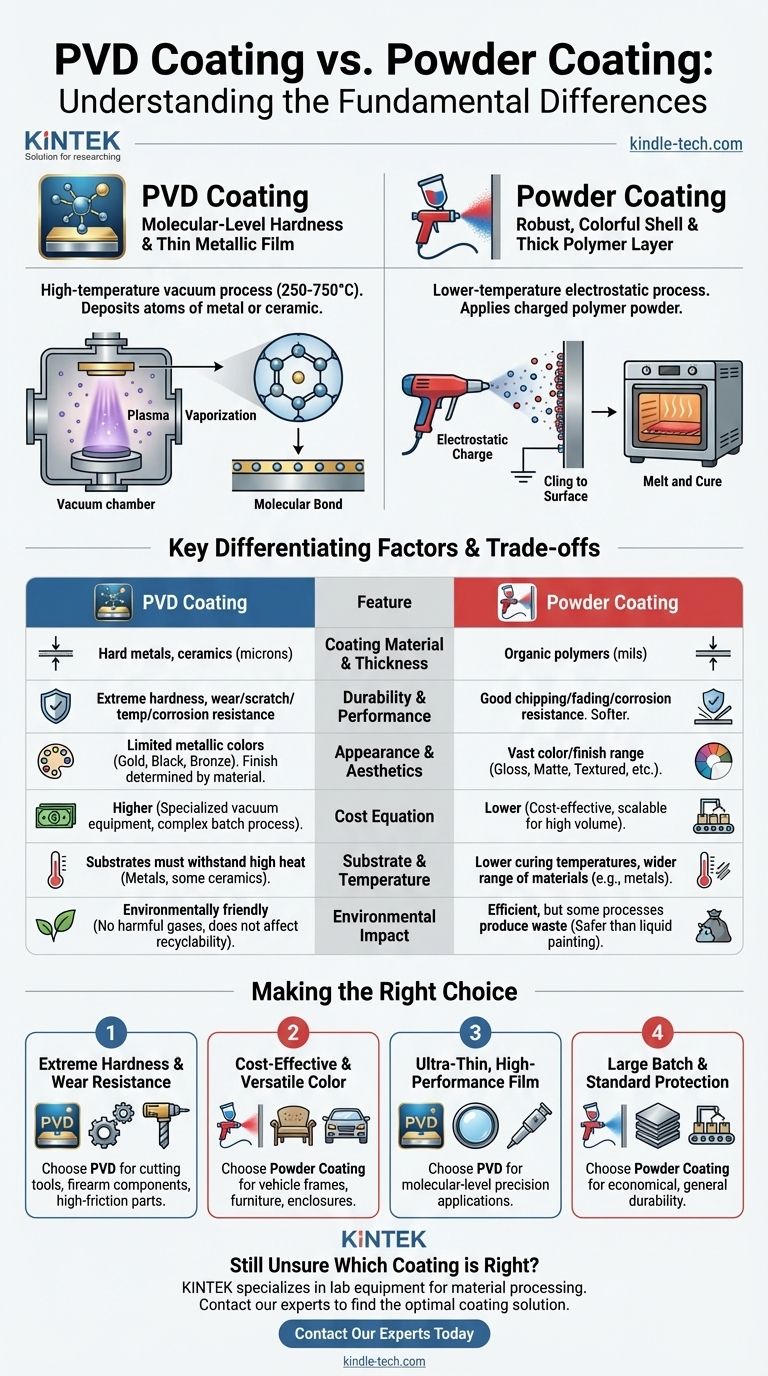
The fundamental difference between PVD and powder coating lies in the material and the process. PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) is a high-temperature vacuum process that deposits a very thin, hard film of metal or ceramic onto a surface, atom by atom. In contrast, powder coating is a lower-temperature process that uses an electrostatic charge to apply a thick, protective layer of polymer (plastic) powder, which is then melted into a solid shell.
Choosing between PVD and powder coating isn't a question of which is "better," but which serves your product's specific need. The decision hinges on whether you require the molecular-level hardness of a thin metallic film or the robust, colorful shell of a thick polymer layer.
How Each Process Fundamentally Works
To understand the differences in performance, you must first understand the vast difference in application methods. Each process creates a fundamentally different type of bond with the substrate.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): A Molecular Bond
PVD takes place inside a high-vacuum chamber. A solid source material, such as titanium or chromium, is vaporized into a plasma.
These vaporized atoms then travel and embed themselves onto the surface of the part, forming an extremely strong bond at the molecular level. This process is performed at high temperatures, often between 250°C and 750°C.
Think of it as spray painting with individual atoms in a vacuum, creating a new, integrated surface layer rather than just a coating on top.
Powder Coating: An Electrostatic 'Cling'
Powder coating uses a fine polymer powder and an electrostatic spray gun. The gun gives the powder particles a positive electric charge.
The part to be coated is electrically grounded, causing the charged powder to be drawn to and cling to the surface. The entire part is then placed in an oven, where the powder melts and cures into a smooth, solid, and continuous coating.
This is more like statically charged dust clinging to a surface before being melted into a durable plastic shell.
Key Differentiating Factors
The differences in process lead to vastly different outcomes in performance, appearance, and cost.
Coating Material and Thickness
PVD coatings are exceptionally thin, measured in microns. They are made from hard materials like metals, alloys, and ceramics (e.g., Titanium Nitride).
Powder coatings are significantly thicker, measured in mils (thousandths of an inch). They are exclusively made from organic polymers like polyester, epoxy, or polyurethane.
Durability and Performance
PVD creates an extremely hard, dense surface with superior resistance to abrasion, scratches, high temperatures, and corrosion. It's the standard for high-wear applications like cutting tools, engine components, and premium hardware.
Powder coating is also very durable, providing excellent protection against chipping, fading, and general corrosion. However, it is a much softer material than a PVD ceramic and is not intended for high-wear or sharp-edge applications.
Appearance and Aesthetics
Powder coating is the clear winner for aesthetic versatility. It offers a nearly limitless range of colors, along with various finishes like gloss, matte, satin, and textured surfaces.
PVD is more limited in its color palette, typically offering metallic finishes in shades of black, gray, gold, and bronze. The finish is determined by the specific metal or ceramic being deposited.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is universally superior; they are engineered for different purposes and come with distinct limitations.
The Cost Equation
Powder coating is a relatively straightforward and cost-effective process, making it ideal for high-volume production of consumer and industrial goods.
PVD requires highly specialized and expensive vacuum chamber equipment and is a more complex batch process. This makes it significantly more expensive than powder coating.
Substrate and Temperature Limitations
The high temperatures required for PVD mean it can only be applied to substrates that can withstand the heat, primarily metals and some ceramics.
Powder coating's lower curing temperatures allow it to be used on a wider range of materials, although it is still most common on metals.
Environmental Impact
PVD is considered a very environmentally friendly process. It occurs in a vacuum and produces no harmful gases or waste byproducts, and it does not affect the recyclability of the base metal.
While modern powder coating is efficient, some processes can produce waste, though it is generally considered much safer than traditional liquid painting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice depends entirely on the primary functional and aesthetic requirements of your component.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: PVD is the only choice for applications like cutting tools, firearm components, or high-performance parts that see intense friction.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective protection and versatile color: Powder coating offers excellent value and a vast aesthetic range for parts like vehicle frames, outdoor furniture, and electronic enclosures.
- If your primary focus is creating an ultra-thin, high-performance metallic film: PVD is the specific technology designed to achieve this result with molecular-level precision.
- If your primary focus is coating a large batch of parts in a standard protective color: Powder coating is the far more economical and scalable solution for general durability.
Ultimately, understanding these core differences empowers you to select a coating that acts as a functional asset, not just a surface finish.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Coating | Powder Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Process | High-temperature vacuum deposition | Electrostatic application & oven curing |
| Material | Thin metal/ceramic film (microns) | Thick polymer layer (mils) |
| Durability | Extreme hardness, wear & corrosion resistance | Good chipping & corrosion resistance |
| Appearance | Limited metallic colors (gold, black, bronze) | Vast color & finish options (gloss, matte, etc.) |
| Cost | Higher (specialized equipment) | Lower (cost-effective for high volume) |
| Best For | Cutting tools, high-wear components | Consumer goods, furniture, enclosures |
Still Unsure Which Coating is Right for Your Project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for advanced material processing, including surface coating analysis and preparation. Our expertise can help you determine the optimal coating solution for your specific needs, ensuring performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Let us help you make an informed decision. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance



















