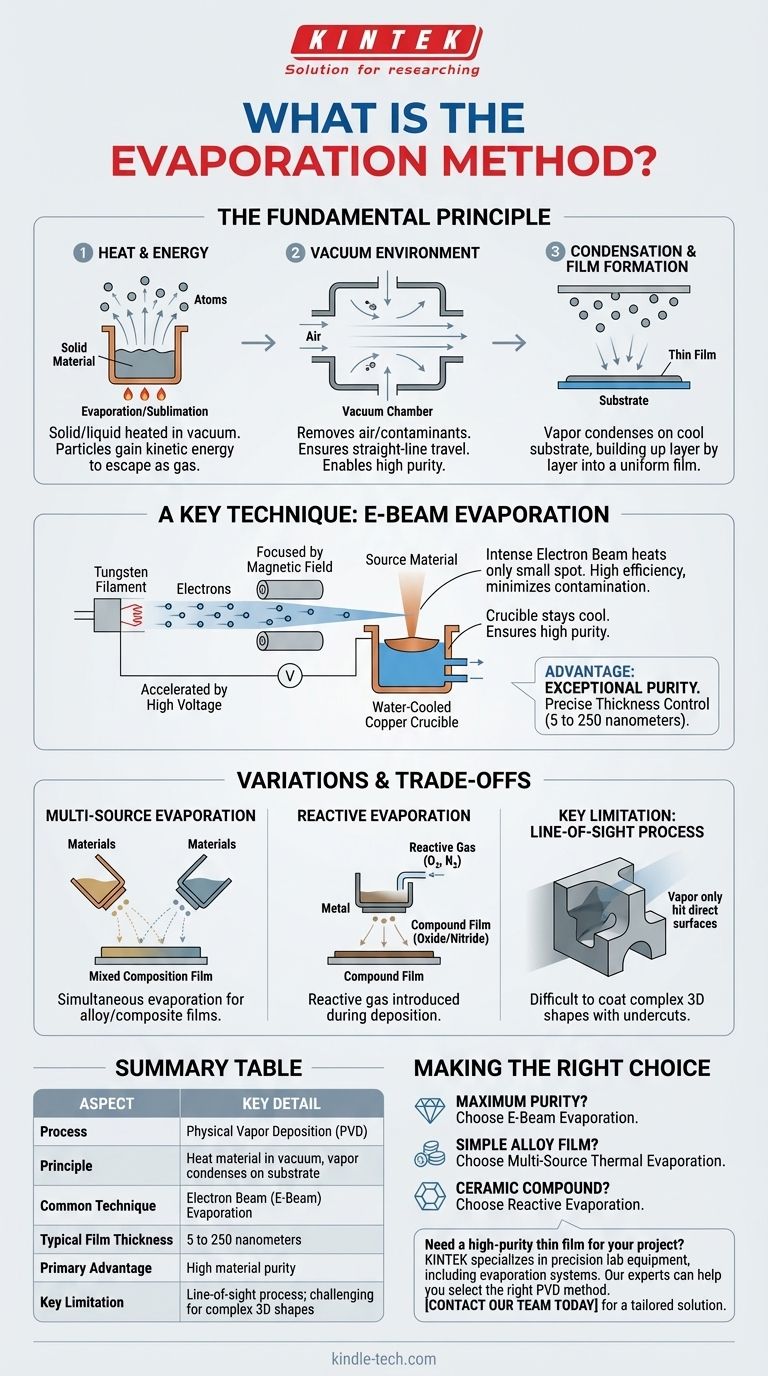
The evaporation method is a process where a source material is heated in a vacuum until it transforms into a vapor. This vapor then travels and condenses onto a cooler surface, known as a substrate, to form a very thin and highly pure film. This technique is a fundamental type of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
At its core, the evaporation method is a refined way to build materials one layer of atoms at a time. It uses heat to "boil" a solid into a gas within a vacuum, allowing that gas to re-solidify as an ultra-thin, high-purity coating on a target object.

The Fundamental Principle: From Solid to Vapor to Film
The entire process relies on a controlled phase transition of matter. By understanding each step, the purpose of the method becomes clear.
The Role of Heat and Energy
Atoms and molecules in a solid or liquid are held together by binding forces. Applying sufficient heat gives these particles enough kinetic energy to overcome those forces, allowing them to escape into the gas phase. This is the act of evaporation or, if from a solid, sublimation.
The Necessity of a Vacuum
This process is conducted in a high-vacuum chamber for two critical reasons. First, it removes air and other gas molecules that the vaporized material could collide with. This ensures the vapor travels in a relatively straight line to the substrate, a key principle of PVD.
Second, the vacuum eliminates unwanted atoms and molecules that could contaminate the final film, which is essential for achieving high purity.
Condensation and Film Formation
When the hot vapor particles reach the cooler substrate, they rapidly lose their energy. This causes them to condense back into a solid state, adhering to the surface and building up layer by layer to form a thin, uniform film.
A Key Technique: Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
While simple heating elements can be used, e-beam evaporation is a more advanced and widely used technique that offers superior control and purity.
How E-Beam Evaporation Works
An intense, focused beam of electrons is used as the heat source. A current passes through a tungsten filament, which emits electrons. These electrons are then accelerated by a high voltage and focused by a magnetic field into a narrow beam.
This high-energy beam is directed onto the source material, which is held in a water-cooled copper crucible. The immense energy transfer from the electrons causes the material to melt and evaporate with high efficiency.
Advantages of the E-Beam Method
The primary advantage of e-beam evaporation is purity. Because the electron beam heats only a small spot on the source material, the crucible itself remains cool. This prevents the crucible material from contaminating the vapor stream.
The result is an exceptionally pure thin film, with a thickness that can be precisely controlled, typically between 5 to 250 nanometers.
Understanding the Variations and Trade-offs
The basic evaporation principle can be adapted for more complex applications, but it's important to recognize its inherent limitations.
Multi-Source Evaporation
For creating alloy or composite films, multiple evaporation sources can be used simultaneously. By independently controlling the heating and evaporation rate of two or more different materials, a film with a specific, mixed composition can be deposited onto a single substrate.
Reactive Evaporation
To create non-metallic films like oxides or nitrides, a reactive gas (such as oxygen or nitrogen) is intentionally introduced into the vacuum chamber during deposition. The evaporated metal atoms react with the gas as they deposit on the substrate, forming the desired compound.
Inherent Limitations
The most significant trade-off of evaporation methods is that they are "line-of-sight" processes. The vapor travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This makes it very difficult to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with undercuts or hidden surfaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct evaporation strategy depends entirely on the desired properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity: E-beam evaporation is the superior choice, as its localized heating minimizes contamination from the container.
- If your primary focus is creating a simple alloy film: Multi-source thermal evaporation provides direct control over the film's final composition.
- If your primary focus is depositing a ceramic compound like an oxide: Reactive evaporation is the necessary approach to form the correct chemical structure during deposition.
Ultimately, the evaporation method provides a powerful and precise tool for engineering surfaces with specific optical, electronic, or mechanical properties.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
| Principle | Heating a material in a vacuum to form a vapor that condenses on a substrate |
| Common Technique | Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation |
| Typical Film Thickness | 5 to 250 nanometers |
| Primary Advantage | High material purity |
| Key Limitation | Line-of-sight process; challenging for complex 3D shapes |
Need a high-purity thin film for your project? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including evaporation systems for advanced materials research. Our experts can help you select the right PVD method to achieve the specific optical, electronic, or mechanical properties you require. Contact our team today to discuss your application and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What are the disadvantages of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Managing the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What are the uses of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications



















