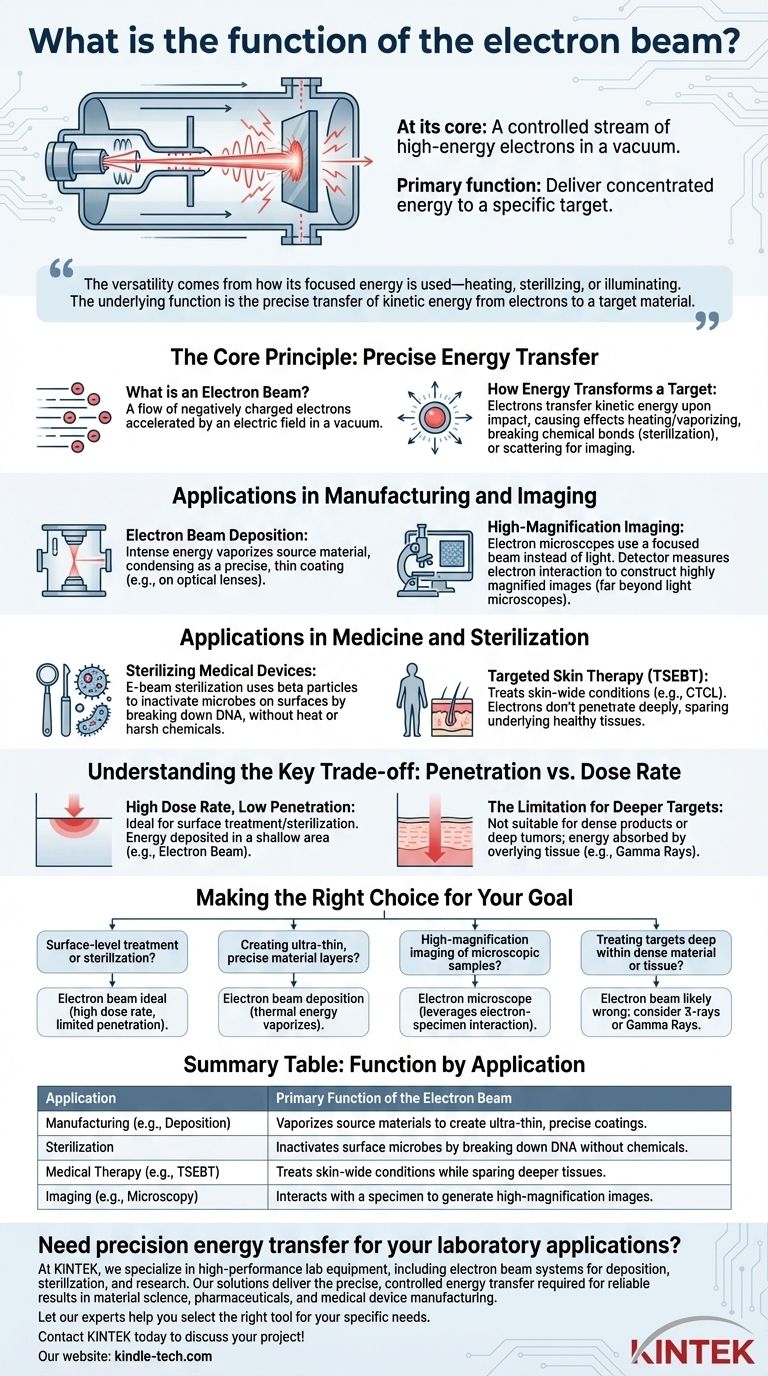
At its core, an electron beam is a controlled stream of electrons accelerated to high energy within a vacuum. Its primary function is to deliver this concentrated energy to a specific target, with applications ranging from creating images on screens and in microscopes to performing medical therapies and manufacturing high-precision coatings. The specific effect of the beam depends entirely on how its energy interacts with the target material.
The versatility of an electron beam comes not from the beam itself, but from how its focused energy is used. Whether it heats, sterilizes, or illuminates, the underlying function is the precise transfer of kinetic energy from electrons to a target material.
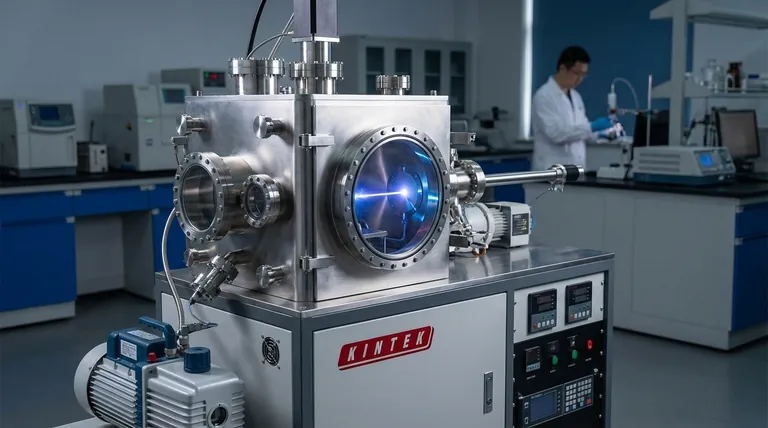

The Core Principle: Precise Energy Transfer
An electron beam's power lies in its ability to act as a highly controllable energy delivery system. The effects it produces are a direct result of this fundamental principle.
What is an Electron Beam?
An electron beam is a flow of electrons, which are negatively charged subatomic particles. These electrons are generated and then accelerated by a strong electric field, typically inside a vacuum chamber, to prevent them from scattering off air molecules.
How Energy Transforms a Target
When these high-energy electrons strike a target material, they transfer their kinetic energy. This energy transfer can cause several effects: heating and vaporizing the material, breaking chemical bonds to sterilize a surface, or scattering in a way that can be detected to form an image.
Applications in Manufacturing and Imaging
In industrial and scientific settings, the electron beam is a tool for manipulation and observation at a microscopic level.
Electron Beam Deposition
In this manufacturing process, the beam's intense energy is focused on a source material, such as a powder or granule. The energy heats the material until it vaporizes. This vapor then condenses as a precise, uniform, and extremely thin coating onto a target surface, such as an optical lens.
High-Magnification Imaging
Electron microscopes use a focused beam of electrons instead of light to "see" a specimen. As the electrons pass through or bounce off the sample, detectors measure their pattern to construct a highly magnified image, revealing details far beyond the capability of traditional light microscopes. This same principle was historically used to create images on cathode-ray tube (CRT) television screens and oscilloscopes.
Applications in Medicine and Sterilization
The ability of an electron beam to affect biological material in a controlled way makes it invaluable in the medical field.
Sterilizing Medical Devices
Known as e-beam sterilization, this process uses electrons (beta particles) to inactivate microbes on the surface of medical devices. The beam's energy effectively breaks down the DNA and other vital components of bacteria and viruses, rendering the device sterile without the use of high heat or harsh chemicals.
Targeted Skin Therapy (TSEBT)
Total skin electron beam therapy is a specialized radiation treatment. Because electrons do not penetrate deeply into tissue, they can be used to treat skin-wide conditions like cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) while minimizing damage to underlying healthy organs and tissues.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Penetration vs. Dose Rate
The primary characteristic that defines an electron beam's suitability for a task is its penetration depth. This creates a critical trade-off that is essential to understand.
High Dose Rate, Low Penetration
Compared to other radiation sources like gamma rays, electron beams deliver a very high dose of energy very quickly. However, this energy is deposited in a very shallow area. This makes them ideal for treating skin or sterilizing the surface of an object.
The Limitation for Deeper Targets
This low penetration depth is also the beam's main limitation. An electron beam is not suitable for sterilizing dense products or treating tumors located deep within the body, as the energy would be absorbed by the overlying tissue before it could reach the intended target.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The function of an electron beam is determined entirely by the problem you need to solve. Your application dictates whether its unique properties are an advantage or a limitation.
- If your primary focus is surface-level treatment or sterilization: An electron beam is ideal due to its high dose rate and limited, predictable penetration depth.
- If your primary focus is creating ultra-thin, precise material layers: Electron beam deposition is the correct application, using the beam's thermal energy to vaporize source materials.
- If your primary focus is high-magnification imaging of microscopic samples: An electron microscope leverages the interaction between electrons and a specimen to generate detailed images.
- If your primary focus is treating targets deep within dense material or tissue: An electron beam is likely the wrong tool, and a more penetrative radiation source like X-rays or gamma rays should be considered.
Ultimately, the function of an electron beam is defined by the precise and controlled way its energy transforms the material it touches.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Function of the Electron Beam |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing (e.g., Deposition) | Vaporizes source materials to create ultra-thin, precise coatings. |
| Sterilization | Inactivates surface microbes by breaking down DNA without chemicals. |
| Medical Therapy (e.g., TSEBT) | Treats skin-wide conditions while sparing deeper tissues. |
| Imaging (e.g., Microscopy) | Interacts with a specimen to generate high-magnification images. |
Need precision energy transfer for your laboratory applications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including electron beam systems for deposition, sterilization, and research. Our solutions deliver the precise, controlled energy transfer required for reliable results in material science, pharmaceuticals, and medical device manufacturing.
Let our experts help you select the right tool for your specific needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What is the most common machine used to sterilize medical supplies? The Definitive Guide to Autoclaves
- Do you need to autoclave glassware? A Guide to Sterilization vs. Cleaning
- What are the advantages of autoclaving in hospitals? Achieve Unmatched Sterilization for Patient Safety
- What is a lab autoclave? Your Guide to Sterilization with Pressurized Steam
- How does the lab autoclave work? Achieve Complete Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam



















