At its core, an industrial mixer's internal structure consists of a mixing chamber where two rotors rotate to shear and blend materials. This core is supported by systems for loading, sealing, temperature control, lubrication, and power transmission, all working together to achieve a homogenous mix.
The essential design of an internal mixer involves two counter-rotating rotors within a sealed, temperature-controlled chamber. The interaction between the rotors and the chamber wall creates the intense shearing and mixing action required for materials like rubber and plastic.
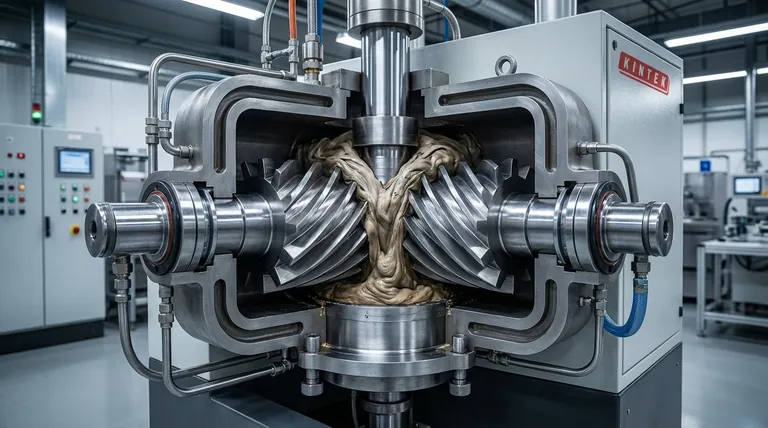
The Core Components: Chamber and Rotors
The primary work of the mixer happens within the mixing chamber, driven by the action of the rotors. These two components define the machine's fundamental capability.
The Mixing Chamber
The mixing chamber is the main body that contains the material during processing. It is typically constructed from two C-shaped halves joined together.
A key feature is the double circulating water jacket built into the chamber walls. This allows for either cooling or heating, providing the critical temperature control necessary for different mixing processes.
The Rotors
The rotors are the primary working elements inside the chamber. There are two of them, and they are designed to rotate relative to each other.
Often, the rotors turn at different speeds. This differential speed, combined with the geometry of the rotors and the chamber wall, generates the high-shear forces needed to plasticize and thoroughly mix the material.
Support and Containment Systems
To function effectively, the core components require systems that load, pressurize, and contain the material.
Upper and Lower Bolts
The term "bolts" in this context refers to the mechanisms for loading and discharging. The upper bolt, often called a ram or plunger, pushes down on the material in the chamber, ensuring it makes contact with the rotors.
The lower bolt functions as the discharge door, which opens to allow the mixed batch to be removed from the chamber.
The Sealing Device
A sealing device is critical for any internal mixer. These seals are located where the rotor shafts exit the mixing chamber.
Their purpose is to prevent material from leaking out and to stop contaminants from entering the mix. Proper sealing is essential for both safety and product quality.
Understanding Operational Trade-offs
While the design is robust, its effectiveness depends on managing key operational variables and anticipating wear.
The Challenge of Temperature Control
The intense shearing action of the rotors generates a significant amount of frictional heat. The cooling system must be powerful enough to counteract this heat to prevent scorching the material.
Conversely, some materials require heat to be added at the start of the cycle to soften them. The system must be responsive enough to manage this balance precisely.
Wear on Rotors and Seals
The rotors and the chamber walls are subject to extreme abrasive and corrosive wear, especially when processing filled compounds. Over time, this wear can reduce the mixer's efficiency.
Likewise, the rotor seals are high-wear components. A failing seal can lead to costly material leakage and downtime for repairs. Regular inspection and maintenance are non-negotiable.
Key Considerations for Mixer Operation
To apply this understanding, focus on how these components influence your specific goals.
- If your primary focus is process consistency: Pay close attention to the cooling/heating system to maintain precise temperature control throughout the mixing cycle.
- If your primary focus is machine longevity: Implement a strict maintenance schedule for the lubrication system and regularly inspect the sealing devices for wear.
- If your primary focus is mixing efficiency: Understand how the rotors and the force from the upper bolt (ram) work together to create the necessary shearing action for your specific material.
Ultimately, every component inside the mixer is engineered to work in concert to transform raw materials into a uniform, high-quality product.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Mixing Chamber | Contains material; temperature-controlled via water jacket. | Critical for precise thermal management. |
| Rotors | Two counter-rotating elements that shear and blend materials. | Different speeds and geometry define mixing efficiency. |
| Upper Bolt (Ram) | Pressurizes material, ensuring contact with rotors. | Affects shear force and mixing intensity. |
| Sealing Device | Prevents material leakage and contamination at rotor shafts. | A high-wear component requiring regular maintenance. |
| Lower Bolt (Door) | Discharges the finished mixed batch from the chamber. | Ensures complete and clean batch removal. |
Optimize Your Mixing Process with KINTEK
Understanding your mixer's internal structure is the first step to maximizing efficiency and product quality. Whether your focus is on process consistency, machine longevity, or mixing efficiency, having the right equipment and support is crucial.
KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and R&D facilities. We can help you select the ideal mixer for your application or provide the consumables and expert advice needed to maintain peak performance.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's mixing requirements and help you achieve a uniform, high-quality product every time.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
- Laboratory Oscillating Orbital Shaker
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
People Also Ask
- What role does high-speed stirring equipment play in fungal pre-cultures? Optimize Your Solid-State Fermentation
- What is the function of a laboratory shaker during batch adsorption experiments? Optimize Fly Ash Kinetic Research
- What role does a laboratory shaker play in the extraction of plant compounds for green synthesis? Maximize Your Yield
- What is the difference between a shaker and a vortex? Choose the Right Mixer for Your Lab Workflow
- How does a laboratory stirrer influence MOF product quality? Master Precision in Non-Solvothermal Synthesis

















