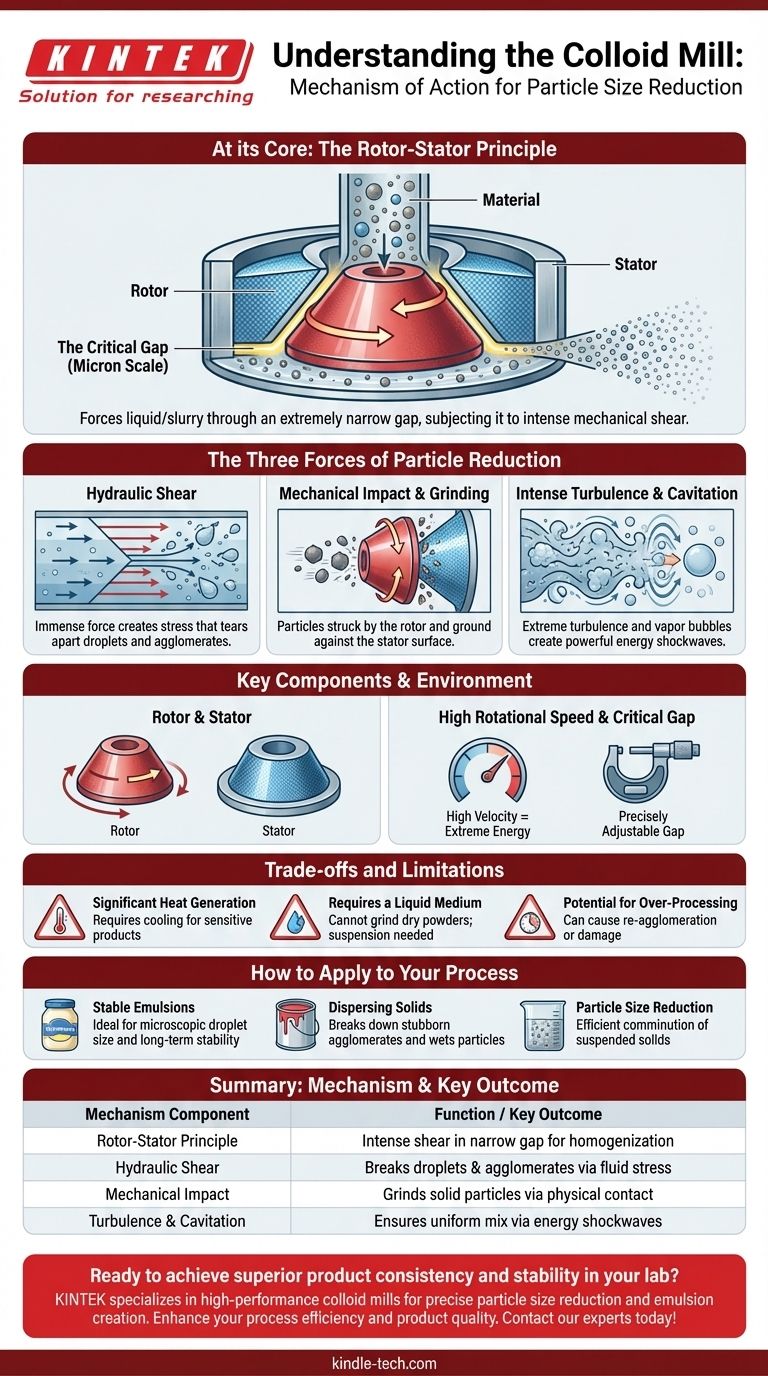
At its core, a colloid mill operates on the rotor-stator principle. It functions by forcing a liquid or slurry through an extremely narrow gap between a rapidly spinning rotor and a stationary stator, subjecting the material to intense mechanical shear that breaks down particles and creates a fine, uniform dispersion.
The fundamental purpose of a colloid mill is not merely to mix, but to apply immense localized energy. This energy, in the form of hydraulic shear, physically tears apart droplets and solid agglomerates to achieve a particle size and stability that simple agitation cannot.

The Rotor-Stator Principle: A Closer Look
To understand the mechanism, we must first look at the machine's two primary components and the environment they create. This simple design is the source of its powerful processing capability.
The Key Components: Rotor and Stator
The rotor is a cone- or disc-shaped component that rotates at very high speeds, often several thousand RPM. The stator is a stationary component that perfectly matches the rotor's shape, encasing it. Both surfaces are often grooved or textured to enhance turbulence.
The Critical Gap
The working action of the mill occurs in the minuscule, precisely adjustable gap between the rotor and stator. This gap can be as small as a fraction of a millimeter. The material to be processed is fed into the center of the rotor and is centrifugally forced outward through this gap.
The Role of High Rotational Speed
The high velocity of the rotor is what generates the extreme energy required for particle reduction. As the rotor spins, it accelerates the material within the gap to high speed, creating the conditions necessary for intense shearing action.
The Three Forces of Particle Reduction
As material passes through the narrow rotor-stator gap, it is subjected to a combination of powerful physical forces. It is this synergy of forces that allows the colloid mill to be so effective.
Hydraulic Shear
This is the primary mechanism. Because the rotor surface is moving at high velocity and the stator surface is stationary, the fluid in the gap is subjected to an immense shearing force. Layers of the liquid move at different speeds, creating a stress that rips apart droplets and breaks down clumps of solid particles.
Mechanical Impact and Grinding
For solid suspensions, there is also a degree of direct mechanical action. Particles are struck by the rapidly moving rotor and ground against the surface of the stator. This physical attrition contributes significantly to the reduction of solid particle size, a process known as comminution.
Intense Turbulence
The high speeds and textured surfaces of the rotor and stator create extreme turbulence and cavitation within the fluid. The rapid formation and collapse of microscopic vapor bubbles (cavitation) release powerful energy shockwaves that further assist in breaking down particles and ensuring a homogenous mix.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the colloid mill's mechanism comes with inherent trade-offs that are critical to consider for any application.
Significant Heat Generation
The intense energy and friction within the mill generate a substantial amount of heat. For temperature-sensitive products like certain emulsions or pharmaceuticals, this can be a major issue, often requiring the use of a cooling jacket on the mill housing.
Requires a Liquid Medium
A colloid mill is a wet-milling device. It cannot be used to grind dry powders. Its entire principle of operation is based on subjecting particles suspended within a fluid to hydraulic shear.
Potential for Over-Processing
There is a point of diminishing returns. Running a product through the mill for too long or at too high a shear can sometimes damage the material or, in some cases, cause particles to re-agglomerate due to excessive energy input.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Understanding the mechanism allows you to align the tool with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is creating stable emulsions (e.g., mayonnaise, lotions): The mill's high shear is ideal for reducing droplet size to a uniform and microscopic level, which is critical for long-term stability and preventing separation.
- If your primary focus is dispersing solids in a liquid (e.g., paints, inks): The combination of shear and impact excels at breaking down stubborn agglomerates and ensuring every solid particle is fully wetted by the liquid carrier.
- If your primary focus is reducing the particle size of a slurry: The mill offers an efficient method for particle comminution, provided the material is already suspended in a fluid that can be pumped through the system.
By mastering the principle of controlled, high-intensity shear, you can leverage the colloid mill to achieve superior consistency and quality in your final product.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism Component | Function | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Rotor-Stator Principle | Creates intense shear in a narrow gap | Particle size reduction and homogenization |
| Hydraulic Shear | Applies immense force between moving and stationary surfaces | Breaks apart droplets and agglomerates |
| Mechanical Impact | Grinds particles against surfaces | Comminution of solid particles in suspension |
| Turbulence & Cavitation | Generates energy shockwaves in the fluid | Ensures a uniform and stable final mix |
Ready to achieve superior product consistency and stability in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including colloid mills designed for precise particle size reduction and emulsion creation. Our solutions are tailored to meet the demanding needs of laboratories in pharmaceuticals, food science, and chemical processing.
Let us help you enhance your process efficiency and product quality. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect colloid mill for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Lab Sterile Slapping Type Homogenizer for Tissue Mashing and Dispersing
- Laboratory Micro Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
People Also Ask
- What is the function of high-shear dispersion equipment in corona-resistant nanocomposites? Elevate Your Insulation
- How does a high-efficiency homogenizing mixer contribute to the preparation of Tobermorite and Xonotlite precursors?
- Why is a rotary mechanical homogenizer used for extended periods for forsterite-spinel? Achieve Peak Ceramic Uniformity
- What is the difference between mixer and disperser? Choose the Right Tool for Your Process
- How does a constant temperature rotary shaker contribute to evaluating iron nanoparticles? Optimize Dye Degradation



















