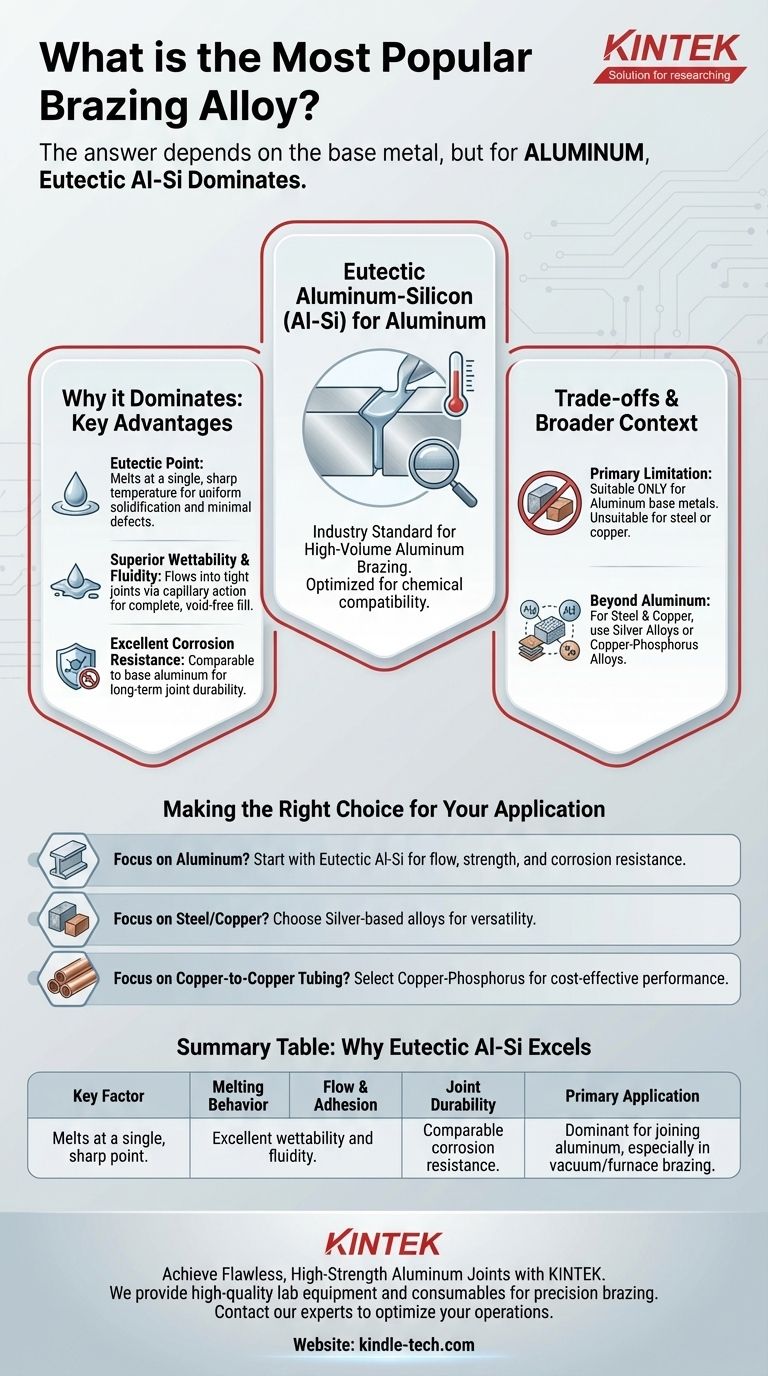
While the single most popular alloy depends on the specific base metals being joined, for the vast and critical application of aluminum brazing, the clear industry standard is eutectic aluminum-silicon (Al-Si). This material is overwhelmingly chosen for its unique combination of properties that make it ideally suited for creating strong, reliable joints between aluminum components, particularly in high-volume manufacturing settings.
The popularity of a brazing alloy is not arbitrary; it is a direct function of its chemical compatibility with the base metal. Eutectic Al-Si dominates for aluminum because its properties are perfectly tuned for it, underscoring the fundamental rule of brazing: the filler metal must be engineered for the specific material it is intended to join.

Why Eutectic Aluminum-Silicon Dominates for Aluminum
The widespread use of eutectic Al-Si in aluminum brazing, especially in methods like vacuum and furnace brazing, is a result of several key performance characteristics. These properties work in concert to produce consistent, high-quality joints.
The Advantage of a Eutectic Point
A eutectic alloy is a specific mixture of elements that melts and solidifies at a single, sharp temperature, rather than over a range. For Al-Si, this means it transitions from solid to liquid quickly and cleanly.
This behavior is highly desirable in brazing as it ensures the entire joint solidifies uniformly, minimizing the risk of defects, cracks, or weak spots that can occur with alloys that have a mushy, semi-solid phase.
Superior Wettability and Fluidity
Wettability is the ability of a liquid filler metal to flow over and adhere to the surface of the base metal. Eutectic Al-Si exhibits excellent wetting on aluminum.
This is coupled with high fluidity, which allows the molten alloy to be drawn into tight-fitting joints via capillary action. The result is a complete, void-free fill that is essential for a strong and leak-proof bond.
Excellent Corrosion Resistance
When brazing, it is critical that the finished joint does not become a point of galvanic corrosion. The joint should be as resistant to environmental factors as the parent aluminum itself.
Eutectic Al-Si alloys are formulated to create brazed joints with corrosion resistance that is comparable to the base aluminum, ensuring the long-term durability of the assembled product.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Broader Context
While Al-Si is the leader for aluminum, it is crucial to recognize its specific application. Choosing the wrong alloy for a given base metal will result in a failed joint.
The Primary Limitation: For Aluminum Only
The properties that make Al-Si alloys perfect for joining aluminum make them entirely unsuitable for other metals like steel, copper, or stainless steel.
Their melting point and chemical composition are tailored specifically for aluminum base metals. Using them on other materials would not create a proper metallurgical bond.
The Brazing Method Matters
The references mention various brazing methods, from torch and furnace to induction and vacuum brazing. Each method controls heat application and atmosphere differently.
The choice of filler metal must be compatible with the process. For example, vacuum brazing is a clean, flux-less process where Al-Si alloys excel. The specific form of the alloy (e.g., paste, wire, preform) will also be dictated by the brazing method.
Beyond Aluminum: Other Popular Alloy Families
For other materials, different alloy families are dominant.
- Silver Alloys (Silver Solders): These are extremely versatile and used for joining most ferrous and non-ferrous metals, including steel, copper, and brass. They are popular for their strength and lower brazing temperatures.
- Copper and Copper-Phosphorus Alloys: These are a cost-effective choice primarily used for joining copper to copper (where they are self-fluxing) or to copper alloys like brass and bronze.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection of a brazing alloy must always be driven by the materials you are joining and the performance required of the final assembly.
- If your primary focus is brazing aluminum alloys: Eutectic aluminum-silicon (Al-Si) is your default starting point due to its unmatched combination of flow, strength, and corrosion resistance.
- If your primary focus is joining steel, stainless steel, or copper: You must look to other alloy families, most commonly silver-based brazing alloys, for their versatility and strength.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective joining of copper-to-copper tubing: Copper-phosphorus alloys are the industry standard and offer an excellent balance of performance and cost.
Ultimately, successful brazing is achieved by precisely matching the filler alloy not just to the material, but to the specific demands of the final product.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Why Eutectic Al-Si Excels |
|---|---|
| Melting Behavior | Melts at a single, sharp eutectic point for uniform solidification and minimal defects. |
| Flow & Adhesion | Excellent wettability and fluidity for complete, void-free joint filling via capillary action. |
| Joint Durability | Provides corrosion resistance comparable to the base aluminum for long-term reliability. |
| Primary Application | The dominant choice for joining aluminum components, especially in vacuum and furnace brazing. |
Achieve Flawless, High-Strength Aluminum Joints with KINTEK
Choosing the right brazing alloy is critical to the performance and longevity of your assembled products. The unique properties of eutectic aluminum-silicon alloys make them the undisputed leader for aluminum brazing applications, ensuring strong, leak-proof, and corrosion-resistant bonds.
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need for precision brazing processes. Whether you are in high-volume manufacturing or developing specialized components, our expertise supports your success.
Let us help you optimize your brazing operations. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your productivity and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Precision Machined Yttrium Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Rod for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Rod for High Temperature Applications
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
People Also Ask
- What are the high temperature properties of alumina? Discover Its Stability, Strength, and Limits
- What is the advantage of ceramic over metal? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is the maximum operating temperature of alumina? The Critical Role of Purity and Form
- Is ceramic chemically inert? Unlock the Power of Ultimate Chemical Resistance
- What is the maximum temperature for alumina tube? Unlock Its Full Potential with High Purity















