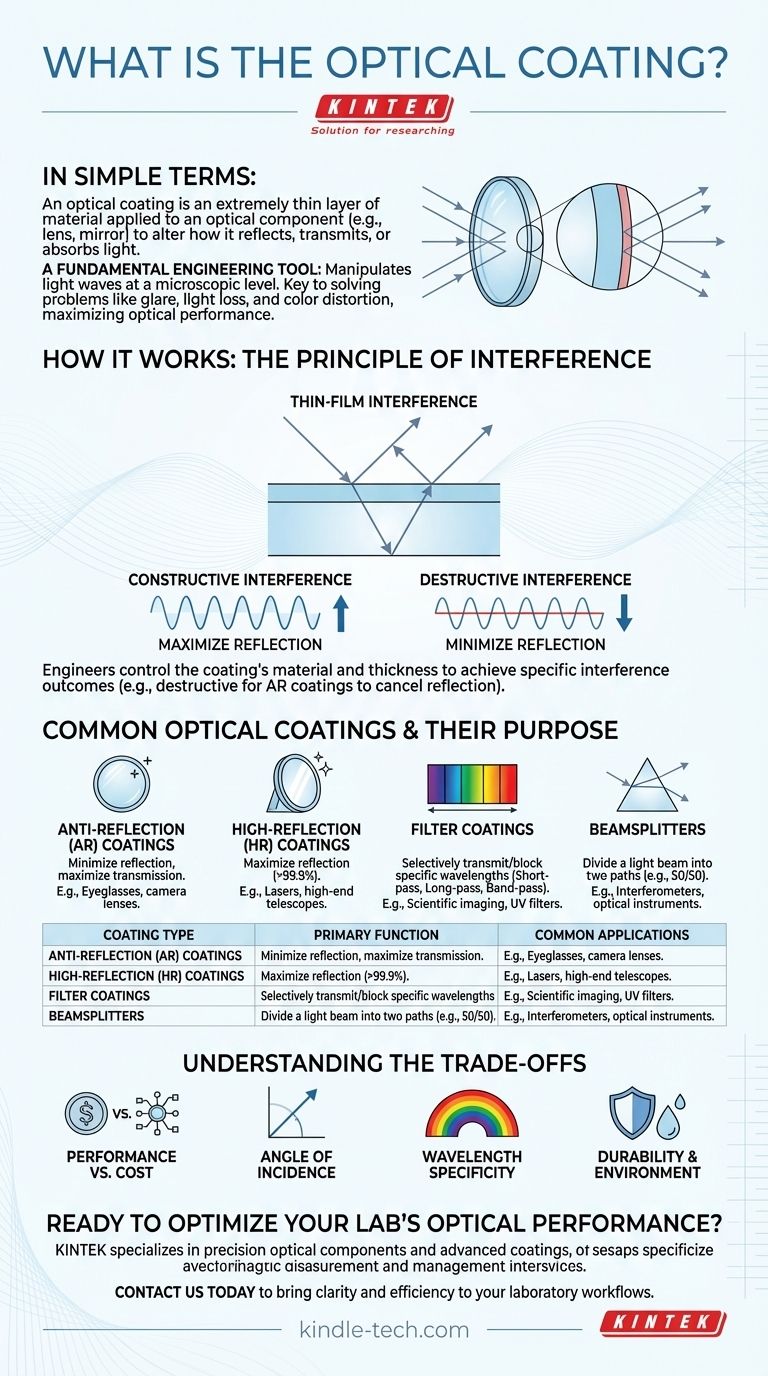
In simple terms, an optical coating is an extremely thin layer of material meticulously applied to an optical component, like a lens or mirror. Its purpose is to alter the way that component reflects, transmits, or absorbs light. The most common example is the anti-reflection coating on eyeglasses and camera lenses that reduces glare and improves clarity.
Optical coatings are not merely a surface treatment; they are a fundamental engineering tool that manipulates light waves at a microscopic level. Understanding their function is key to solving common optical problems like glare, light loss, and color distortion, thereby maximizing the performance of any optical system.

How Optical Coatings Work: The Principle of Interference
At its core, an optical coating's function relies on a wave phenomenon called thin-film interference. The coating's thickness is precisely controlled to be a fraction of the wavelength of light it is designed to affect.
Light Waves in a Layer
When a light wave strikes a coated surface, some of it reflects off the top surface of the coating. The rest of the wave enters the coating and reflects off the bottom surface (at the lens or mirror).
These two reflected waves then travel back out and combine.
Constructive vs. Destructive Interference
Think of two ripples in a pond. If their crests align, they create a larger wave (constructive interference). If a crest from one aligns with a trough from the other, they cancel each other out (destructive interference).
Optical coatings engineer this exact effect for light waves.
Engineering a Specific Outcome
By carefully choosing the coating's material (its refractive index) and its exact thickness, engineers can control whether the two reflected light waves interfere constructively or destructively.
For an anti-reflection coating, the thickness is designed to cause destructive interference, effectively canceling out the reflection and allowing more light to pass through the lens.
Common Types of Optical Coatings and Their Purpose
Different coatings are engineered to achieve specific goals, and many complex optics use multiple types in a single system.
Anti-Reflection (AR) Coatings
This is the most prevalent type of coating. Its goal is to minimize reflection and maximize transmission of light through a surface. A typical uncoated glass surface reflects about 4% of light; a good multi-layer AR coating can reduce this to less than 0.5%.
High-Reflection (HR) Coatings
Also known as dielectric mirrors, these are the opposite of AR coatings. They are designed to cause massive constructive interference to maximize reflection, often achieving over 99.9% reflectivity for a specific range of light. These are critical for lasers and high-end telescopes.
Filter Coatings
These coatings are designed to selectively transmit some wavelengths (colors) of light while blocking others.
- Short-pass filters transmit shorter wavelengths and block longer ones.
- Long-pass filters transmit longer wavelengths and block shorter ones (e.g., UV filters).
- Band-pass filters transmit only a very narrow band of wavelengths, essential for scientific analysis.
Beamsplitters
A beamsplitter coating is designed to divide a single beam of light into two. For example, a 50/50 beamsplitter will reflect exactly 50% of the light and transmit the other 50%, which is vital for instruments like interferometers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single coating is perfect for all situations. Choosing or designing an optical system involves balancing competing priorities.
Performance vs. Cost
A simple, single-layer magnesium fluoride AR coating is inexpensive but only moderately effective. A high-performance, multi-layer AR coating that works across the entire visible spectrum requires a complex manufacturing process and is significantly more expensive.
Angle of Incidence
Most coatings are optimized for light hitting the surface straight-on (at a 0° angle of incidence). Their performance can degrade significantly as the angle of the incoming light changes. This is a critical consideration for wide-angle lenses or scanning systems.
Wavelength Specificity
A coating's performance is intrinsically tied to the wavelength of light it was designed for. An AR coating designed for visible light will likely perform poorly for infrared (IR) or ultraviolet (UV) light, and may even act as a reflector at those wavelengths.
Durability and Environment
Coatings for laboratory instruments may not be robust enough for field equipment exposed to humidity, salt spray, abrasion, and large temperature fluctuations. Specialized "hard" or hydrophobic (water-repelling) coatings are often applied to protect the delicate optical layers beneath.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal coating depends entirely on your specific application and priorities. When evaluating a coated optic, focus on what problem you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is visual clarity and reducing glare (e.g., eyeglasses, photography): Prioritize multi-layer anti-reflection (AR) coatings, as they maximize light transmission and improve contrast.
- If your primary focus is directing light with minimal loss (e.g., lasers, advanced instruments): You need high-reflection (HR) or dielectric mirror coatings precisely designed for your specific wavelength.
- If your primary focus is isolating or blocking specific types of light (e.g., scientific imaging, UV protection): Look for filter coatings like longpass, shortpass, or bandpass that match your required spectral range.
- If your primary focus is use in harsh environments: Seek out durable, hydrophobic, or oleophobic top-coats in addition to the primary optical coating to ensure longevity.
By understanding that coatings are not an optional feature but a targeted solution, you can more effectively select the right optical tools for your work.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Primary Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Reflection (AR) | Minimize reflection, maximize transmission | Eyeglasses, camera lenses, displays |
| High-Reflection (HR) | Maximize reflection (often >99.9%) | Lasers, telescopes, resonators |
| Filter Coatings | Selectively transmit/block wavelengths | Scientific imaging, UV/IR filtering, spectroscopy |
| Beamsplitters | Divide a light beam into two paths | Interferometers, optical instruments |
Ready to optimize your lab's optical performance? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including precision optical components with advanced coatings tailored to your specific needs—whether for research, analysis, or industrial applications. Let our experts help you select the right coating to reduce glare, enhance light transmission, or isolate specific wavelengths. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can bring clarity and efficiency to your laboratory workflows.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
People Also Ask
- What is electron beam coating? A Guide to High-Performance PVD Thin Films
- What are sputtering systems used for? A Guide to Advanced Thin-Film Deposition
- What is gold sputtered? A Guide to High-Purity Vacuum Coating for Electronics & SEM
- What is the container that holds the metal source material called in e-beam evaporation? Ensure Purity and Quality in Your Thin-Film Deposition
- What is sputter coating used for? Achieve Superior Thin Films for Electronics, Optics, and Tools









