At its core, sputter coating is a sophisticated method for applying an exceptionally thin and durable film of one material onto another. This is a Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) process that works by ejecting atoms from a source material (the "target") and depositing them, atom by atom, onto the surface of an object (the "substrate"). The entire process occurs within a vacuum to ensure the atoms can travel unimpeded.
Sputter coating is not a simple spray or plating; it is a momentum-transfer process that embeds atoms into a substrate's surface. This creates an incredibly strong, atomic-level bond, making the new film a permanent part of the original object.

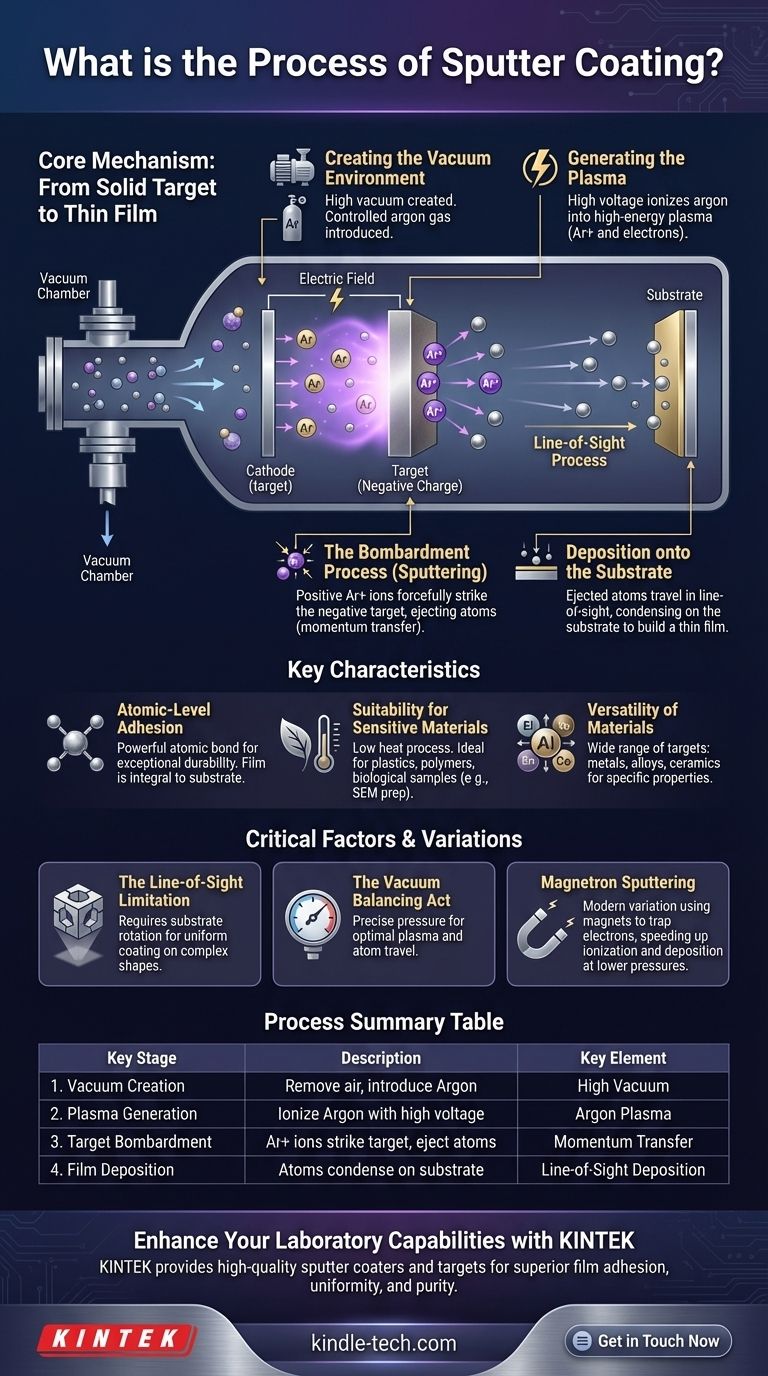
The Core Mechanism: From Solid Target to Thin Film
Understanding the sputter coating process involves a few key steps that transform a solid block of material into a high-performance thin film. The precision of this process is what gives the final coating its unique properties.
Step 1: Creating the Vacuum Environment
Before anything can happen, the chamber containing the target material and the substrate is evacuated to create a high vacuum.
A small, precisely controlled amount of an inert gas, most commonly argon, is then introduced into the chamber. This vacuum is critical because it ensures the sputtered atoms can travel directly to the substrate without colliding with air or other particles.
Step 2: Generating the Plasma
A high voltage is applied within the chamber, creating a powerful electric field. The target material is given a negative charge.
This energy strips electrons from the argon gas atoms, turning the gas into an ionized plasma—a high-energy mixture of positive argon ions and free electrons.
Step 3: The Bombardment Process (Sputtering)
The positively charged argon ions are forcefully accelerated by the electric field and slam into the negatively charged target material.
This bombardment is a purely physical process. The impact's momentum is transferred to the atoms on the target's surface, knocking them loose and ejecting them into the vacuum chamber. This is the "sputtering" effect.
Step 4: Deposition onto the Substrate
The ejected atoms from the target travel through the vacuum and strike the substrate, which is strategically placed to intercept them.
Because the atoms travel in straight lines, this is known as a "line-of-sight" process. The atoms condense on the substrate's surface, gradually building a thin, uniform, and highly dense film.
Key Characteristics of a Sputtered Coating
The way a sputtered film is created gives it distinct advantages over other coating methods.
Atomic-Level Adhesion
The sputtered atoms arrive at the substrate with high kinetic energy. This energy drives them into the substrate's surface, creating a powerful bond at the atomic level.
The coating doesn't just sit on top; it becomes an integral part of the substrate, resulting in exceptional adhesion and durability.
Suitability for Sensitive Materials
The sputtering process imparts very little heat to the substrate itself. The sputtered atoms have low temperatures, and the process doesn't rely on melting or evaporation.
This makes it an ideal method for coating heat-sensitive materials like plastics, polymers, and biological samples, which are often coated with gold for analysis in a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM).
Versatility of Materials
A wide range of materials can be used as the sputtering target. This includes pure metals, complex alloys, and even ceramic compounds. This versatility allows for the creation of coatings with specific electrical, optical, or wear-resistant properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
While powerful, sputter coating requires careful control over several variables to be successful.
The 'Line-of-Sight' Limitation
The straight-line path of sputtered atoms means that surfaces not directly facing the target will not be coated.
To coat complex, three-dimensional objects uniformly, the substrate must be rotated or manipulated on multiple axes during the deposition process to ensure all surfaces are exposed to the atomic flux.
The Vacuum Balancing Act
The vacuum level is a delicate balance. The pressure must be low enough to allow atoms to travel freely but high enough to sustain the argon plasma needed for sputtering.
If the pressure is too high, sputtered atoms will collide with gas atoms, losing energy and failing to bond properly with the substrate.
An Important Variation: Magnetron Sputtering
Many modern systems use magnetron sputtering. This technique uses powerful magnets behind the target to trap free electrons in the plasma.
Trapping electrons near the target dramatically increases the rate of argon ionization. This creates a denser plasma, which speeds up the sputtering process, improves deposition rates, and allows the system to operate at even lower pressures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding the principles of sputter coating allows you to determine if it is the right solution for your specific engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials: Sputtering is an excellent choice due to its low-temperature deposition process, which prevents damage to plastics or biological samples.
- If your primary focus is creating an extremely durable, wear-resistant film: The atomic-level adhesion provided by sputtering creates a superior bond that significantly outperforms simple plating or painting.
- If your primary focus is achieving a highly pure, dense, and uniform coating: The controlled vacuum environment and atomic-level deposition of sputtering offer unparalleled control over film quality and structure.
By grasping that sputtering builds a film atom by atom, you can leverage its unique strengths for the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Stage | Description | Key Element |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Vacuum Creation | Chamber is evacuated to remove air particles. | High Vacuum |
| 2. Plasma Generation | Inert gas (Argon) is ionized by a high-voltage electric field. | Argon Plasma |
| 3. Target Bombardment | Positive argon ions strike the negatively charged target, ejecting atoms. | Momentum Transfer |
| 4. Film Deposition | Ejected atoms travel and condense on the substrate surface. | Line-of-Sight Deposition |
Ready to Enhance Your Laboratory Capabilities?
Sputter coating is essential for creating high-performance, durable thin films for applications ranging from SEM sample preparation to advanced electronics and optical coatings.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reliable sputter coaters and targets, to meet your specific laboratory needs. Our expertise ensures you achieve superior film adhesion, uniformity, and purity for your most demanding projects.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your thin film deposition process and drive your research forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition


















