At its core, the process you are asking about is more accurately known as reactive sputtering. It is an advanced form of a fundamental vacuum deposition technique called physical sputtering. Physical sputtering uses high-energy ions from an inert gas, like argon, to physically knock atoms off a source material (the "target"), which then deposit as a thin film onto a substrate. Reactive sputtering adds a chemical step to this process by introducing a second, reactive gas to form a new compound material on the substrate.
Sputtering is a physical process where atoms are ejected from a target by ion bombardment. When a reactive gas is intentionally added to the chamber, this physical process is combined with a chemical reaction to create compound thin films, a technique known as reactive sputtering.

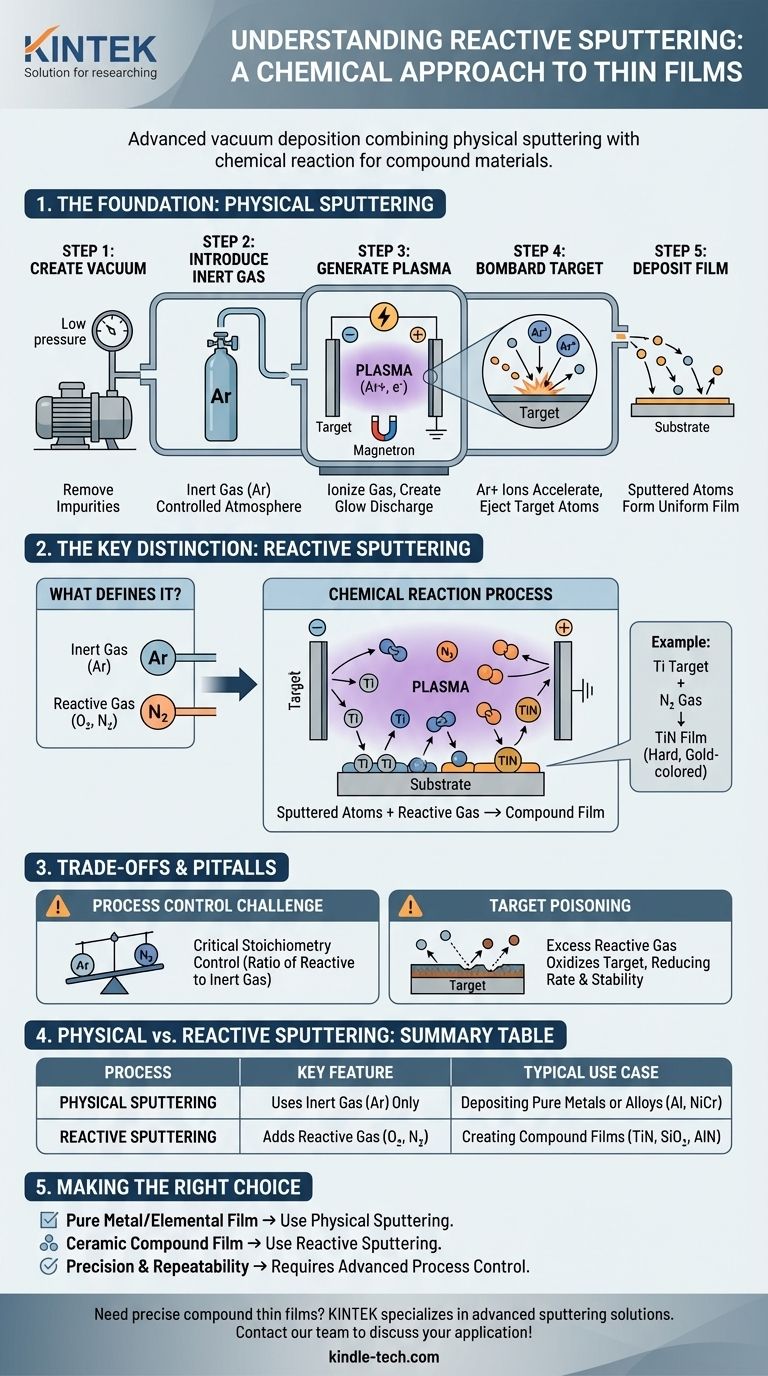
The Foundation: How Physical Sputtering Works
To understand reactive sputtering, you must first grasp the fundamental mechanics of physical sputtering. This process occurs in a vacuum and involves several distinct steps to transfer material atom-by-atom from a source to a substrate.
Step 1: Creating the Vacuum
The entire process takes place inside a sealed vacuum chamber. The internal pressure is reduced dramatically, typically to a high vacuum range, to remove residual gases like oxygen, water vapor, and other impurities.
This initial step is critical to ensure the purity of the final film and to prevent unwanted chemical reactions.
Step 2: Introducing the Sputtering Gas
Once a stable vacuum is achieved, an inert gas—most commonly argon (Ar)—is pumped into the chamber. The chamber pressure is carefully controlled at a low level, creating a specific atmosphere for the process.
Argon is chosen because it is chemically non-reactive and has a sufficient atomic mass to effectively dislodge atoms from the target without forming chemical bonds with them.
Step 3: Generating the Plasma
A high voltage is applied within the chamber, creating a strong electric field. This energy strips electrons from the argon gas atoms, creating a mixture of positively charged argon ions (Ar+) and free electrons.
This ionized gas is known as a plasma or a glow discharge. To increase efficiency, magnets are often placed behind the target (a technique called magnetron sputtering) to trap electrons near the target, intensifying the plasma where it's needed most.
Step 4: The Bombardment Phase
The source material, known as the target, is given a strong negative electrical charge. The positively charged argon ions (Ar+) in the plasma are forcefully accelerated toward this negatively charged target.
These ions collide with the target surface with immense energy. This collision is a pure momentum transfer event, much like a cue ball striking a rack of billiard balls.
Step 5: Deposition on the Substrate
If the energy transferred from the argon ion is greater than the energy binding the target atoms together, one or more target atoms are ejected or "sputtered" from the surface.
These sputtered, neutral atoms travel through the vacuum chamber and land on the substrate (e.g., a silicon wafer, glass, or plastic part), gradually building up a thin, uniform film.
The Key Distinction: From Physical to Reactive Sputtering
Reactive sputtering leverages the entire physical sputtering framework and adds a crucial chemical component. This is where the term "chemical sputtering" finds its true meaning.
What Defines Reactive Sputtering?
Reactive sputtering involves introducing a second, reactive gas into the chamber along with the inert argon gas. Common reactive gases include oxygen (O₂) for forming oxides and nitrogen (N₂) for forming nitrides.
How the Chemical Reaction Occurs
As the target atoms are sputtered, they travel through a plasma that now contains both argon ions and reactive gas molecules. The sputtered atoms react with this gas to form a new chemical compound.
This reaction can happen on the surface of the target, in transit through the plasma, or, most commonly, on the surface of the substrate as the film is being formed.
A Practical Example: Titanium Nitride
Imagine you want to create a hard, gold-colored coating of titanium nitride (TiN). You would start with a pure titanium (Ti) target.
You would run the physical sputtering process with argon gas but also bleed a controlled amount of nitrogen gas into the chamber. The sputtered titanium atoms would react with the nitrogen to form a TiN film on the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While powerful, reactive sputtering introduces complexities that must be carefully managed to achieve the desired film properties.
The Challenge of Process Control
The most significant challenge is balancing the gas flows and sputtering rate. The ratio of reactive gas to inert gas determines the stoichiometry (the chemical composition) of the final film.
For example, when making an oxide, too little oxygen results in a metal-rich, sub-oxidized film. Too much oxygen can lead to a phenomenon known as target poisoning, where the surface of the target itself becomes oxidized, drastically reducing the sputtering rate and altering the process stability.
When to Use Physical vs. Reactive Sputtering
The choice is dictated entirely by the desired final material.
Physical sputtering is used when you need a film of a pure element or an alloy. For instance, depositing a layer of pure aluminum for a reflective coating or a nickel-chromium alloy for a resistor.
Reactive sputtering is used exclusively when the goal is to create a compound film that is different from the target material, such as silicon dioxide (SiO₂), aluminum nitride (AlN), or the aforementioned titanium nitride (TiN).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application dictates the correct sputtering technique. The decision hinges on the chemical nature of the thin film you intend to create.
- If your primary focus is depositing a pure metal or elemental film: You will use standard physical sputtering with only an inert gas like argon.
- If your primary focus is creating a ceramic compound film (like an oxide, nitride, or carbide): You will use reactive sputtering by adding a controlled flow of a reactive gas (e.g., oxygen, nitrogen) to the argon plasma.
- If your primary focus is precision and repeatability: You must implement advanced process controls for gas flow and power, as reactive sputtering is highly sensitive to these parameters.
Ultimately, mastering sputtering requires understanding that you are controlling not just a physical process of atomic transfer, but also a delicate chemical environment to build materials one atom at a time.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Feature | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Sputtering | Uses inert gas (Argon) only | Depositing pure metals or alloys (e.g., Aluminum, NiCr) |
| Reactive Sputtering | Adds a reactive gas (e.g., O₂, N₂) | Creating compound films (e.g., TiN, SiO₂, AlN) |
| Key Challenge | Maintaining stoichiometry & avoiding target poisoning | Requires precise control of gas flows and power |
Need to deposit precise compound thin films for your research or production? KINTEK specializes in advanced sputtering equipment and consumables for laboratories. Our experts can help you select the right system and optimize your process for reliable, high-quality results. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















