The production of "zirconium" involves two distinct industrial paths depending on the final material desired: pure zirconium metal or the ceramic zirconium dioxide (zirconia). For the metal, the Kroll process is used, which involves chemically converting ore into a chloride and then reducing it with magnesium. For the ceramic, raw zirconium compounds are chemically processed and then subjected to high-temperature calcination and sintering to form a dense, hard solid.
The core challenge in all zirconium production is managing its high reactivity, especially with oxygen. This necessitates complex, energy-intensive purification and processing steps—like the Kroll process for the metal and controlled sintering for the ceramic—which ultimately define the material's final cost and performance.
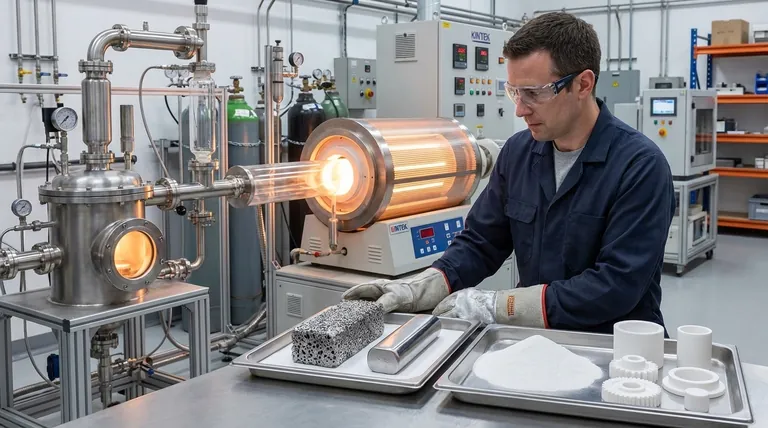

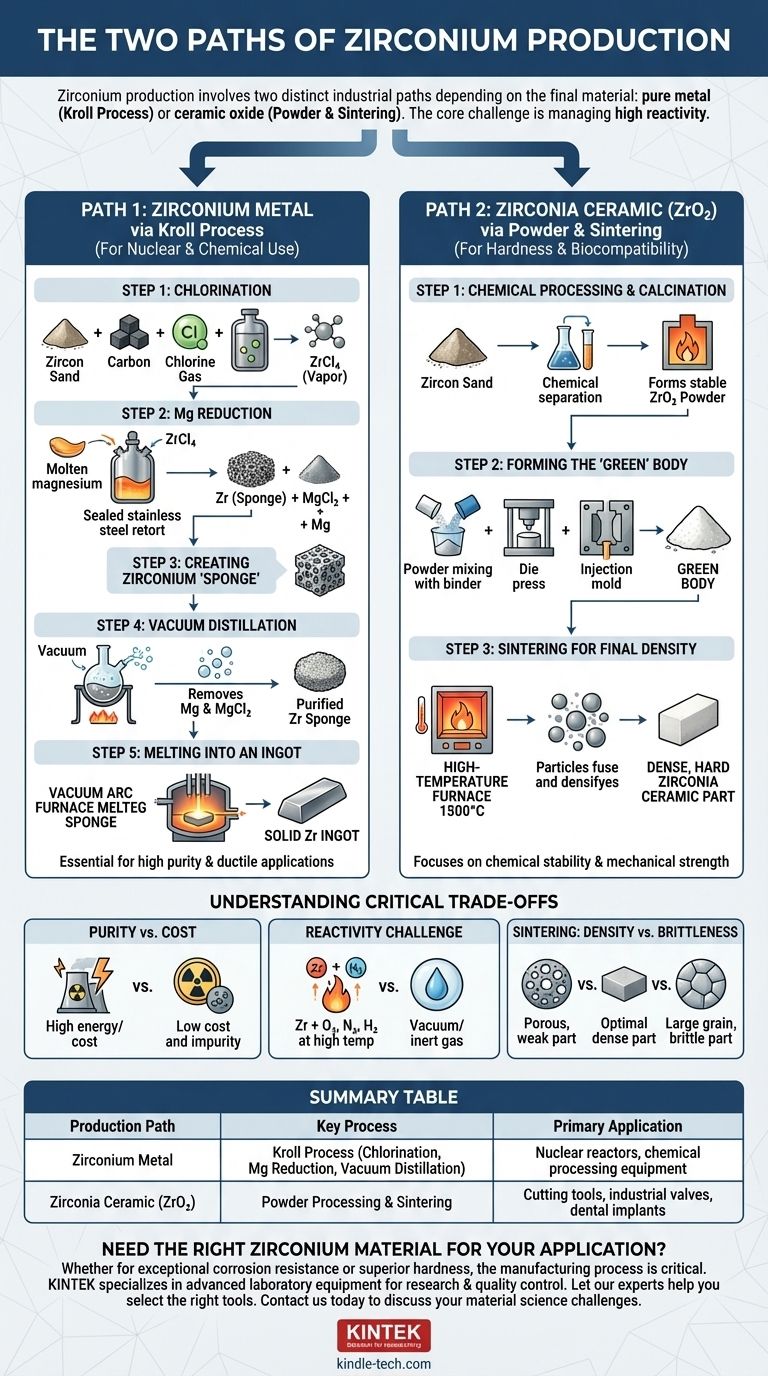
The Two Paths of Zirconium Production
The term "zirconium" can be a source of confusion. It is crucial to distinguish between the silvery, ductile metal (Zr) and its brilliant white ceramic oxide, zirconia (ZrO₂). Their manufacturing processes are entirely different, tailored to their unique applications.
Path 1: Zirconium Metal via the Kroll Process
This multi-stage batch process is the dominant method for producing high-purity, ductile zirconium metal, which is essential for nuclear and chemical processing applications. The starting point is typically zircon sand (zirconium silicate, ZrSiO₄).
Step 1: Chlorination
The zircon sand is first heated with carbon in a stream of chlorine gas. This reaction converts the zirconium silicate into crude zirconium tetrachloride (ZrCl₄), a volatile compound that can be separated from other impurities.
Step 2: Reduction with Magnesium
This is the heart of the Kroll process. The purified zirconium tetrachloride vapor is fed into a sealed stainless steel retort containing molten magnesium under an inert argon atmosphere. The magnesium, being more reactive, strips the chlorine from the zirconium, leaving behind pure zirconium metal.
Step 3: Creating Zirconium 'Sponge'
The result of the reduction is not a solid ingot but a porous, metallic mass called a zirconium sponge. This sponge is interspersed with magnesium chloride (a byproduct) and unreacted magnesium.
Step 4: Purification via Vacuum Distillation
The retort is heated under a vacuum. This process boils off the residual magnesium and magnesium chloride, which are removed, leaving behind a purified zirconium sponge. This step is critical for achieving the high purity needed for demanding applications.
Step 5: Melting into an Ingot
Finally, the purified sponge is crushed, pressed into blocks, and melted in a vacuum arc furnace to form a solid, usable metal ingot. This melting process consolidates the metal and removes any final volatile impurities.
Path 2: Zirconia Ceramic (ZrO₂)
Producing a finished zirconia ceramic part is a process of powder metallurgy and thermal treatment. It focuses on creating a chemically stable and mechanically robust material from refined powders.
Step 1: Chemical Processing and Calcination
Like the metal, zirconia production often starts with zircon sand. The sand undergoes complex chemical processing to separate the zirconium from silicon and other impurities, yielding various zirconium chemical compounds. These compounds are then heated to extreme temperatures in a process called calcination. This step burns off any remaining volatile components and converts the material into a stable, high-purity zirconium dioxide (ZrO₂) powder.
Step 2: Forming the 'Green' Body
The fine zirconia powder is mixed with a binder and then shaped into the desired form. This can be done through methods like die pressing, isostatic pressing, or injection molding. The resulting object is known as a "green" body—it is chalky, fragile, and holds its shape but has no significant strength.
Step 3: Sintering for Final Density
The green body is placed in a high-temperature furnace for sintering. During this step, the part is heated to a temperature below its melting point (typically around 1500°C). The heat causes the individual powder particles to fuse together, eliminating the pores between them and densifying the part into a hard, strong, solid mass. The precise control of the sintering temperature and duration is critical, as it dictates the final grain structure and mechanical properties like strength and fracture toughness.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
The complexity and cost of zirconium production are dictated by fundamental chemical and physical challenges.
Purity vs. Cost
The Kroll process is incredibly energy-intensive and expensive, but it is necessary to produce metal pure enough for nuclear reactors, where impurities like hafnium must be almost completely removed. Cheaper methods simply cannot achieve this level of purity.
The Challenge of Reactivity
Zirconium metal is highly reactive with oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen at elevated temperatures. This is why the entire Kroll process and subsequent melting must be performed in a vacuum or inert gas. Any atmospheric contamination during processing would make the final metal brittle and useless.
Sintering: Density vs. Brittleness
For zirconia ceramics, sintering is a balancing act. Insufficient temperature or time results in a porous, weak part. However, excessive temperature or time can cause abnormal grain growth, which can make the final ceramic part more brittle and prone to fracture.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The manufacturing process directly determines the material's properties and ideal use case.
- If your primary focus is extreme corrosion resistance and nuclear transparency: You require high-purity zirconium metal produced via the Kroll process for applications like nuclear fuel cladding or chemical reactors.
- If your primary focus is exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and biocompatibility: You need a fully dense zirconia ceramic component made via the powder-and-sintering route for applications like cutting tools, industrial valves, or dental implants.
Ultimately, understanding the production journey is key to selecting and specifying the correct form of zirconium for your technical challenge.
Summary Table:
| Production Path | Key Process | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Zirconium Metal | Kroll Process (Chlorination, Mg Reduction, Vacuum Distillation) | Nuclear reactors, chemical processing equipment |
| Zirconia Ceramic (ZrO₂) | Powder Processing & Sintering | Cutting tools, industrial valves, dental implants |
Need the Right Zirconium Material for Your Application?
Whether your project requires the exceptional corrosion resistance of high-purity zirconium metal or the superior hardness and biocompatibility of zirconia ceramic, the manufacturing process is critical to performance. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced laboratory equipment and consumables necessary for research and quality control in material production.
Let our experts help you select the right tools for your needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's material science challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- At what temperature does wood pyrolysis begin? Control the Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, or Syngas



















