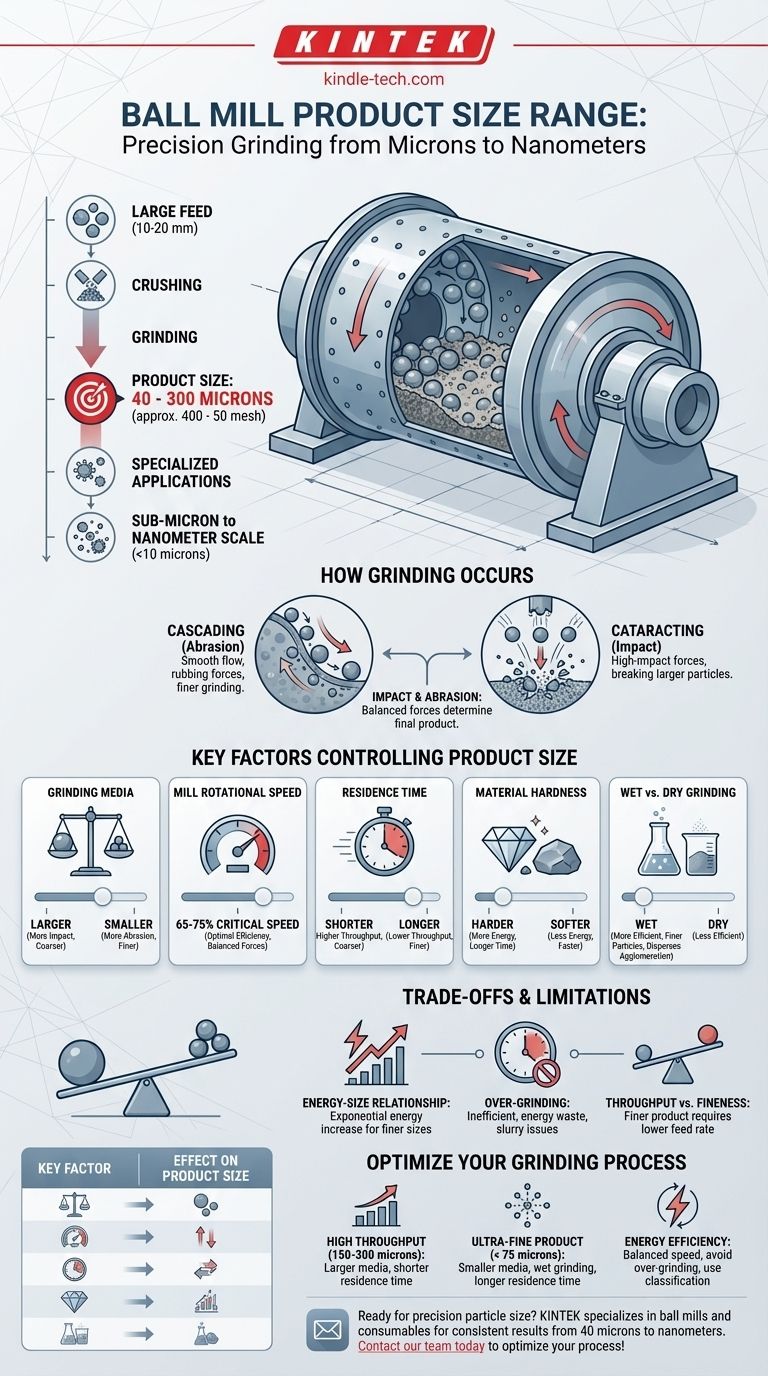
In material processing, a ball mill is a fine grinding machine that typically reduces material down to a product size range of 40 to 300 microns (approximately 400 to 50 mesh). For specialized applications, particularly with wet grinding and optimized media, ball mills can achieve sizes well below 10 microns, entering the sub-micron or even nanometer scale.
The final product size from a ball mill is not a fixed number but a highly controllable output. It is determined by the interplay between the grinding media, the properties of the material being ground, and the mill's operational parameters.

The Mechanics of Particle Reduction
A ball mill is a hollow cylinder that rotates on its axis, partially filled with grinding media like steel or ceramic balls. As the mill turns, the media is lifted up the side of the shell and then tumbles back down, crushing and grinding the material trapped between the balls.
How Grinding Occurs
The tumbling motion of the media creates two primary grinding forces. Cascading is when the balls tumble over each other in a smooth flow, creating abrasive forces that grind particles. Cataracting is when the balls are thrown from near the top of the shell, creating high-impact forces that shatter particles.
The Two Grinding Forces
Impact is the dominant force for breaking down larger feed particles. Abrasion (or attrition) is the rubbing action that grinds particles down to a very fine size. The balance between these two forces is key to controlling the final product.
The Importance of Proper Feed Size
A ball mill is a fine grinder, not a primary crusher. It operates most efficiently with a pre-crushed feed, typically with a top size of less than 10-20 millimeters. Feeding oversized material to a ball mill leads to inefficiency and excessive wear.
Key Factors Controlling Final Product Size
You can adjust several variables to precisely control the fineness of the output product. Understanding these levers is critical for process optimization.
Grinding Media Characteristics
The size, density, and material of the grinding balls are crucial. Smaller media provides more surface area and contact points, resulting in a finer product size through increased abrasion. Larger, denser media increases the impact force, which is better for coarser feed.
Mill Rotational Speed
Mill speed is expressed as a percentage of "critical speed"—the speed at which the media would centrifuge and stick to the mill's inner wall. Most mills operate at 65-75% of critical speed to achieve the optimal balance of cascading and cataracting for efficient grinding.
Residence Time
This is the amount of time the material spends inside the mill. A longer residence time naturally results in a finer grind, as the particles are subjected to more impact and abrasion events. This is a direct trade-off with the mill's throughput (tons per hour).
Material Hardness and Friability
The intrinsic properties of the material being ground have a significant effect. Harder, less friable materials (like quartz) require more energy and time to break down compared to softer materials (like limestone).
Wet vs. Dry Grinding
Grinding can be done dry or in a slurry (wet). Wet grinding is generally more efficient, consumes less energy per ton, and can produce finer particles. The liquid helps disperse the particles, preventing cushioning and agglomeration.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a ball mill is not a universal solution. Its operation involves fundamental trade-offs that impact efficiency and cost.
The Energy-Size Relationship
Reducing particle size is an energy-intensive process. The energy required to achieve a certain fineness increases exponentially as the target particle size decreases. Grinding from 100 microns down to 20 microns requires far more energy than grinding from 500 to 100.
The Problem of Over-Grinding
Leaving material in the mill for too long is inefficient. It wastes energy creating ultra-fine particles that may not be necessary for the process and can even cause issues like slurry thickening or particle agglomeration.
Throughput vs. Fineness
This is the most common operational trade-off. Achieving a finer product size almost always requires reducing the feed rate, which lowers the overall plant throughput.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your optimal ball mill setup depends entirely on your final objective. Consider these guiding principles to match the machine's parameters to your process needs.
- If your primary focus is high throughput for a moderate product (150-300 microns): Use larger grinding media to maximize impact forces and operate with a shorter residence time to increase the feed rate.
- If your primary focus is an ultra-fine product (< 75 microns): Prioritize smaller grinding media, consider wet grinding to improve efficiency, and accept that a longer residence time and lower throughput will be necessary.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Carefully balance mill speed and media charge to ensure you are not over-grinding, and use a classification system (like a hydrocyclone) to remove correctly sized particles from the circuit promptly.
By mastering these variables, you can transform the ball mill from a simple grinder into a precision tool for meeting your specific particle size requirements.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Effect on Product Size |
|---|---|
| Grinding Media Size | Smaller media = finer product |
| Residence Time | Longer time = finer product |
| Mill Speed | Optimized speed (65-75% critical) for efficiency |
| Wet vs. Dry Grinding | Wet grinding enables finer particles |
| Material Hardness | Harder materials require more energy |
Ready to optimize your grinding process for the perfect particle size? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including ball mills and consumables, to help you achieve consistent results from 40 microns down to the nanometer scale. Our experts can help you select the right mill and media for your specific material and throughput goals. Contact our team today to discuss your application and request a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do stainless steel grinding jars and balls contribute to mechanical alloying? Optimize HEA Powder Synthesis
- Why are zirconia (ZrO2) milling jars recommended for sulfide electrolytes? Ensure Purity in Li6PS5Cl Synthesis
- Why is a ball mill jar lined with Y-ZrO2 required for Na3PS4 synthesis? Ensuring Purity in Sulfide Electrolytes
- Why are tungsten carbide grinding jars and balls preferred for high-purity lithium ceramic powders? Ensure Peak Purity.
- What are the advantages of polyurethane ball mill jars for silicon nitride? Ensure Purity & Prevent Metal Contamination



















