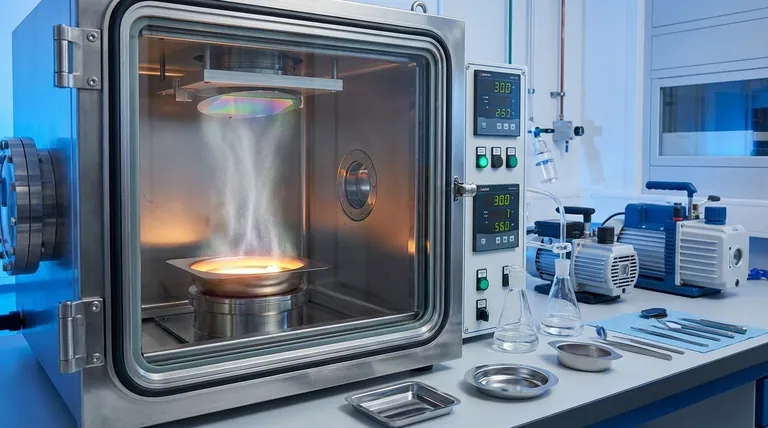
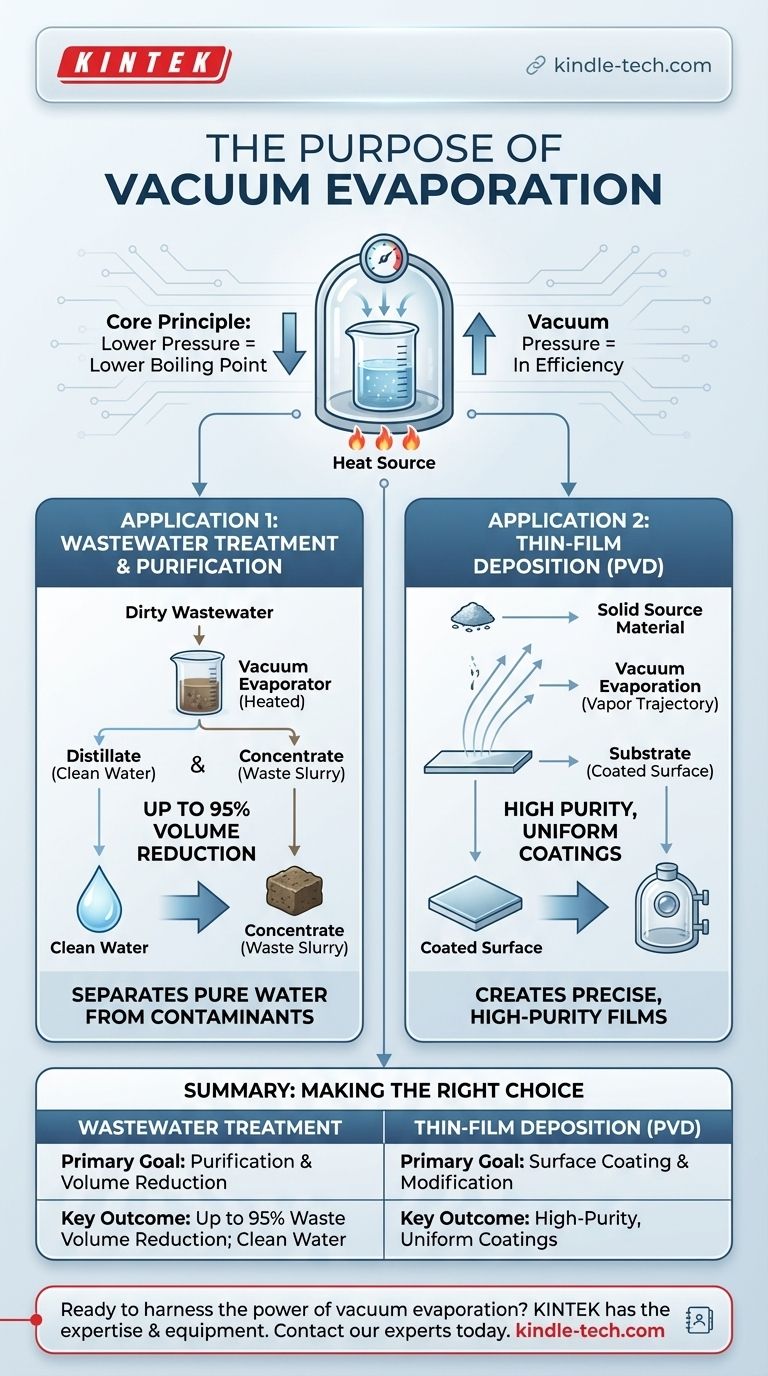
At its core, vacuum evaporation is a process that uses a vacuum to make substances boil at a much lower temperature. This single principle is leveraged for two distinct purposes: to purify and reduce the volume of wastewater by separating it from contaminants, and to create ultra-thin, high-purity coatings on surfaces in a process known as physical vapor deposition (PVD).
The fundamental purpose of vacuum evaporation is to exploit a physical principle: lowering pressure dramatically lowers a substance's boiling point. This allows for either the efficient separation of liquids from solids (like purifying water) or the controlled vaporization of solids for creating coatings (like depositing metal onto a surface).

The Core Principle: Lowering Pressure to Lower Boiling Point
The Physics of Boiling
Boiling occurs when a liquid's vapor pressure equals the pressure of the surrounding environment. At sea level, water boils at 100°C (212°F).
The Role of the Vacuum
By placing a substance in a vacuum, we drastically reduce the surrounding environmental pressure. This means the substance can reach its boiling point with far less heat.
This efficiency is the central advantage that makes vacuum evaporation a valuable industrial process for two very different applications.
Application 1: Wastewater Treatment and Purification
How It Separates Contaminants
In this context, vacuum evaporation is a highly effective method for separating pure water from contaminants that have a high boiling point, such as salts, heavy metals, and oils.
The wastewater is heated under vacuum, causing the water to boil off as a clean vapor at a low temperature, leaving the contaminants behind in a concentrated slurry.
The Key Outputs: Distillate and Concentrate
The process results in two distinct outputs. The water vapor is condensed and collected as distillate, which is clean water with very low conductivity.
The remaining waste material is called concentrate. This is a much smaller, highly concentrated volume of the original contaminants.
The Primary Benefit: Volume Reduction
A major goal of this application is waste management. Vacuum evaporation can achieve up to a 95% volume reduction of the initial wastewater, significantly lowering disposal costs and environmental impact.
Application 2: Thin-Film Deposition (PVD)
How It Creates a Coating
This process is a type of physical vapor deposition (PVD). A solid source material (like a metal or ceramic) is heated in a high vacuum until it evaporates into a vapor.
This vapor then travels in a straight, line-of-sight path through the vacuum chamber until it reaches a cooler target object, known as the substrate.
Upon contact, the vapor rapidly condenses back into a solid state, forming a very thin, uniform, and high-purity film on the substrate's surface. When used with metals, this is often called vacuum metallization.
Common Uses and Materials
This technique is critical for manufacturing a vast range of products where surface properties are essential.
Common applications include optical interference coatings, mirror coatings, decorative finishes, protective barriers on food packaging, and conductive films for electronics and integrated circuits.
A wide array of materials can be deposited, including metals, alloys, dielectric materials, and semiconductors.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
Advantage: High Purity and Precision
For thin-film deposition, vacuum evaporation is prized for its ability to create exceptionally high-purity films, as the process occurs in a clean vacuum, minimizing contamination.
The line-of-sight trajectory of the vapor allows for precise and controlled deposition, ideal for intricate electronic components.
Advantage: Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to other PVD methods like sputtering, vacuum evaporation is generally the least expensive and one of the simplest to implement, making it a popular choice for many industrial coating applications.
Limitation: Uniformity on Complex Shapes
Because the vapor travels in a straight line, it can be difficult to achieve a perfectly uniform coating on substrates with complex, non-flat geometries. The "line-of-sight" nature means surfaces not directly facing the source may receive little to no coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the purpose of using vacuum evaporation is dictated entirely by your end goal.
- If your primary focus is liquid purification or waste reduction: Use this process for its unmatched ability to separate pure water from dissolved contaminants, drastically reducing waste volume.
- If your primary focus is creating precise surface coatings: Use this process as a cost-effective PVD method for depositing high-purity thin films of various materials onto substrates.
Understanding this dual nature allows you to harness a simple physical principle for powerful and diverse industrial results.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Goal | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Wastewater Treatment | Purification & Volume Reduction | Up to 95% waste volume reduction; clean distillate water |
| Thin-Film Deposition (PVD) | Surface Coating & Modification | High-purity, uniform coatings for electronics, optics, and packaging |
Ready to harness the power of vacuum evaporation in your lab?
Whether your goal is advanced materials research requiring precise thin-film coatings or efficient sample preparation and purification, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your work. Our vacuum evaporation systems are designed for reliability and performance, helping you achieve superior results in thin-film deposition or sample concentration.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect vacuum solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What are the uses of evaporation in industry? From Food Concentration to High-Tech Thin Films
- What is evaporation material? The Key to Precision Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab
- How is deposition time calculated? Mastering the Clock for Strategic Legal Advantage



















