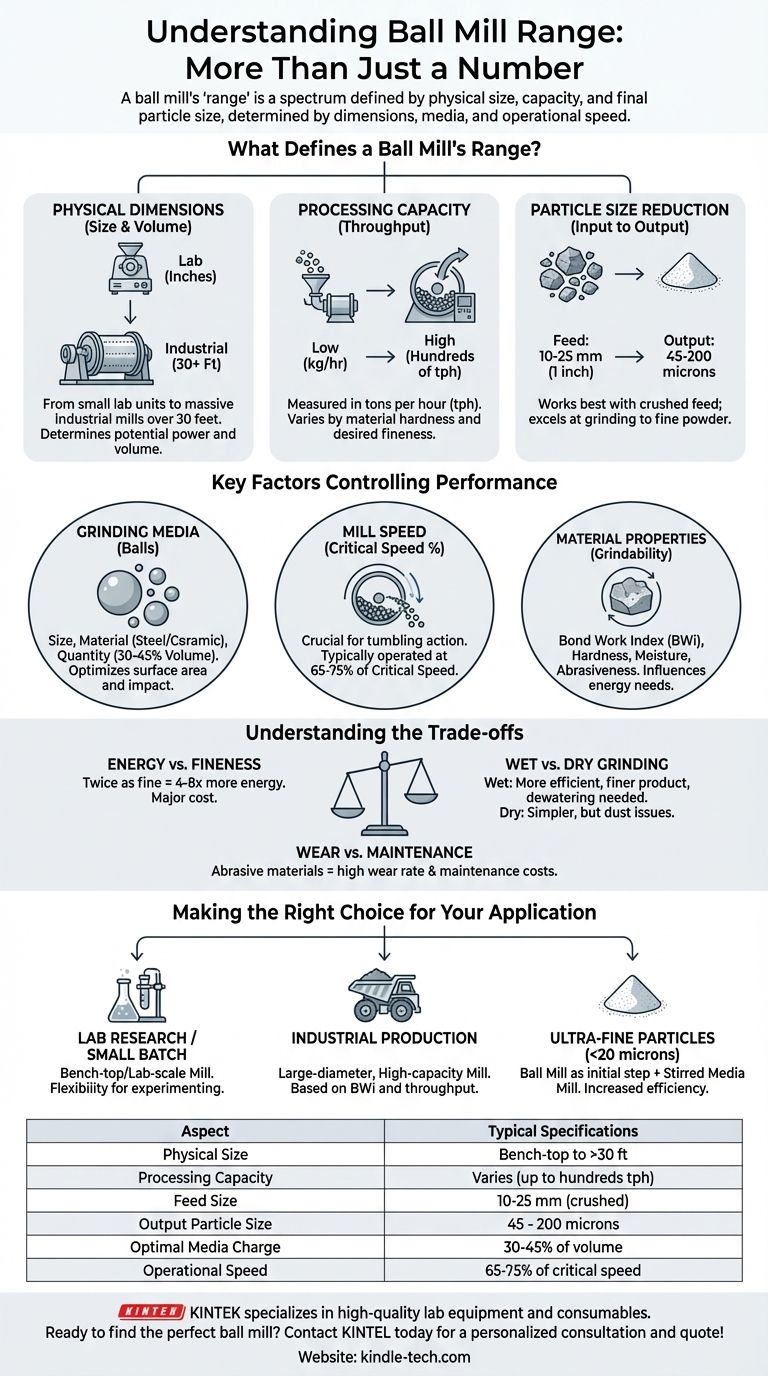
The "range" of a ball mill is not a single number, but rather a spectrum of capabilities defined by its physical size, processing capacity, and the final particle size it can achieve. Ball mills can be as small as laboratory units a few inches in diameter or as large as massive industrial mills over 30 feet in diameter capable of processing hundreds of tons of material per hour.
A ball mill's effective range is determined by a balance of its dimensions, grinding media, and operational speed. The goal is not simply to find the largest or smallest mill, but to select a system where these variables are correctly matched to your material's properties and desired final particle size.

What Defines a Ball Mill's Range?
To understand the full scope of a ball mill, we must break down the term "range" into three distinct, yet interconnected, categories.
Physical Dimensions
The most direct interpretation of range is physical size. This spans from small, bench-top mills used in laboratories for sample preparation and analysis to enormous, industrial-scale mills that are foundational to industries like mining and cement production.
The dimensions, primarily the internal diameter and length, are the first factor in determining the mill's potential power draw and processing volume.
Processing Capacity (Throughput)
Capacity refers to how much material a mill can process in a given time, often measured in tons per hour (tph). This is directly influenced by the mill's physical size.
However, capacity is not fixed. It is a variable range that depends heavily on the hardness of the material being ground and the desired fineness of the final product. Grinding a softer material to a coarse size will yield a much higher throughput than grinding a very hard material to an ultra-fine powder in the same mill.
Particle Size Reduction
This is the functional range of the mill. A ball mill is typically a secondary or tertiary grinding device. It works best when fed crushed material with a top size of around 10-25 mm (about 1 inch).
Its output range is where it truly excels, efficiently grinding materials down to a fineness of 45 to 200 microns (comparable to the size of fine table salt or flour).
Key Factors Controlling Performance
The effective range and efficiency of any ball mill are not inherent to its size alone. They are controlled by a precise set of operational parameters.
The Grinding Media
The "balls" inside the mill are the heart of the grinding action. Their characteristics are critical. This includes their size, material (steel or ceramic), and quantity (charge volume).
Larger, heavier balls are used for breaking down coarser feed particles, while smaller balls provide the greater surface area needed for fine grinding. The charge volume is typically maintained between 30-45% of the mill's internal volume for optimal performance.
Mill Speed (The Critical Speed)
A ball mill does its work by lifting the media and allowing it to tumble and cascade onto the material. The speed of this rotation is crucial and is expressed as a percentage of the "critical speed."
Critical speed is the theoretical velocity at which the grinding media would simply be held against the mill's shell by centrifugal force, ceasing all grinding action. Mills are typically operated between 65% and 75% of critical speed to achieve the perfect balance of impact and abrasion.
Material Properties
The material itself dictates the mill's performance. The Bond Work Index (BWi) is a standard measure of a material's resistance to grinding. A higher BWi means more energy is required to reduce its size.
Factors like moisture content, abrasiveness, and density also fundamentally influence the throughput and efficiency of the grinding process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting and operating a ball mill involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for an efficient and cost-effective operation.
Energy Consumption vs. Fineness
Grinding is an energy-intensive process. The relationship between energy input and particle size is not linear; grinding particles to be twice as fine can require four to eight times the energy. This is the single largest operational cost and a primary consideration.
Wet vs. Dry Grinding
Ball mills can be operated with or without water. Wet grinding is generally more energy-efficient, produces a finer product, and eliminates dust issues. However, it requires a downstream process for dewatering the material, adding complexity and cost.
Dry grinding is simpler but can be less efficient and may require extensive dust collection systems, especially for fine products.
Wear and Maintenance
The constant tumbling and impact of hard media and abrasive material result in wear on the grinding balls and the mill's internal steel or rubber liners. This is a significant and unavoidable operational cost. The harder the material being ground, the higher the wear rate and the more frequent the need for maintenance and replacement of components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the appropriate ball mill, you must first define your objective. The "correct" range is the one that aligns with your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is laboratory research or small-batch testing: A bench-top or lab-scale ball mill provides the necessary flexibility for experimenting with different materials and parameters.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial production (e.g., mineral processing): You need a large-diameter, high-capacity overflow or grate discharge mill, with its specifications calculated based on the material's Bond Work Index and required throughput.
- If your primary focus is achieving ultra-fine particles (sub-20 microns): Consider a ball mill as an initial grinding step, followed by a more efficient fine-grinding technology like a stirred media mill, as a ball mill's efficiency decreases significantly at these sizes.
Ultimately, defining the right range for a ball mill begins with a clear understanding of your material and your processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Ball Mill Range Aspect | Typical Specifications |
|---|---|
| Physical Size | Bench-top lab units to mills over 30 ft diameter |
| Processing Capacity | Varies by material; up to hundreds of tons per hour (tph) |
| Feed Size | 10-25 mm (crushed material) |
| Output Particle Size | 45 - 200 microns (fine grinding) |
| Optimal Media Charge | 30-45% of mill volume |
| Operational Speed | 65-75% of critical speed |
Ready to find the perfect ball mill for your specific material and throughput needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing robust ball mills for every application—from R&D sample preparation to full-scale industrial production. Our experts will help you select a mill that delivers optimal particle size, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for your laboratory or processing plant.
Contact KINTEL today for a personalized consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory ball mill used in Co-Ni catalyst research? Optimize CO2 Conversion with Precise Milling
- How does a high-energy planetary ball mill facilitate the synthesis of sulfide glassy electrolytes? Achieve Amorphization
- What is the purpose of ball milling? A Versatile Tool for Material Synthesis and Modification
- What is the product size of a ball mill? Achieve Micron-Level Precision for Your Materials
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a sag mill? A Guide to Primary vs. Secondary Grinding



















