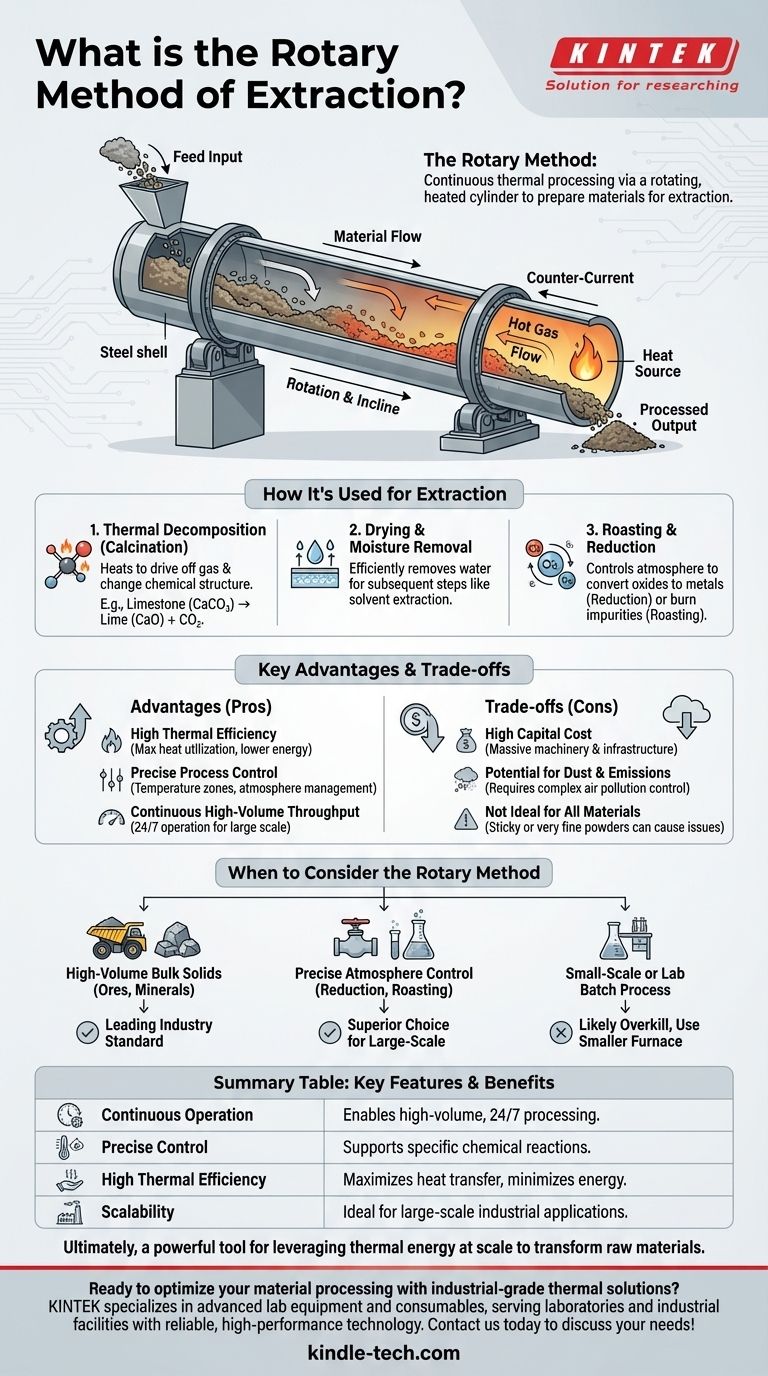
While the "rotary method of extraction" is not a standard industry term, it almost invariably refers to the use of a rotary kiln for the thermal processing of materials. This method involves continuously feeding materials through a rotating, heated cylinder to induce physical or chemical changes. This is often a crucial preparatory step in a larger process designed to extract a valuable component from a raw solid.
The rotary method uses the high efficiency and controlled environment of a rotary kiln to heat materials, driving off impurities or preparing them for subsequent extraction steps. Its core value lies in its ability to process large volumes of material continuously with precise control over temperature and atmospheric conditions.

What is a Rotary Kiln?
A rotary kiln is a piece of industrial equipment at the heart of this method. Understanding its simple but powerful design is key to understanding its function.
The Core Principle: A Rotating Cylinder
The kiln itself is a long, cylindrical steel shell lined with heat-resistant brick, known as refractory.
It is mounted at a slight angle to the horizontal and rotates slowly on its axis. Raw material is fed into the upper end, and it gradually moves down to the lower end due to the rotation and incline.
The Heating Mechanism
Heat is typically introduced at the lower end, creating a counter-current flow where the material moves in the opposite direction of the hot gases.
This design is extremely efficient. The material is heated directly by the flame and hot gases, as well as by radiation and conduction from the hot kiln shell, ensuring thorough and uniform heating.
Material Flow and Residence Time
The combination of the kiln's rotational speed, its angle of incline, and its length determines the residence time—how long the material spends inside.
This is a critical parameter that is carefully controlled to ensure the desired chemical reaction or physical change is completed.
How This Method is Used for Extraction
A rotary kiln rarely performs the entire extraction itself. Instead, it prepares the material in a way that makes subsequent extraction possible or far more efficient.
Thermal Decomposition (Calcination)
This is one of the most common uses. The kiln heats a material to drive off a component as a gas, fundamentally changing its chemical structure.
For example, limestone (calcium carbonate) is heated to produce lime (calcium oxide) by "extracting" carbon dioxide. Similarly, ores are often calcined to break them down before a chemical leaching step.
Drying and Moisture Removal
Efficiently removing water from a material is often the first step in a process. Rotary kilns act as industrial-scale dryers, preparing materials for subsequent steps like solvent extraction where the presence of water would be problematic.
Roasting and Reduction
The ability to control the atmosphere inside the kiln is a significant advantage. By introducing specific gases, a kiln can perform a reducing roast.
This process uses a reducing atmosphere (like one rich in carbon monoxide) to convert metal oxides in an ore directly into their base metal form, a direct act of extraction. It can also be used for oxidizing roasts to burn off impurities like sulfur.
Understanding the Key Advantages
The references you found highlight the core strengths that make this method a cornerstone of heavy industry.
High Thermal Efficiency
Modern rotary kilns are designed for maximum heat utilization. The tumbling action constantly exposes new material surfaces, maximizing heat transfer.
Combined with counter-current flow and advanced insulation (like lightweight fiber materials), this design minimizes heat loss and reduces energy consumption.
Precise Process Control
Kilns offer exceptional control over the processing environment. Operators can manage multiple temperature zones along the kiln's length.
Furthermore, the sealed design allows for precise management of the internal atmosphere, enabling oxidizing, neutral, or reducing conditions as required by the specific chemical process.
Continuous, High-Volume Throughput
Unlike a batch furnace where you load, heat, and unload one batch at a time, a rotary kiln operates continuously.
Material is constantly fed in one end and discharged at the other, making it ideal for the large-scale, 24/7 operations found in mining, cement production, and chemical processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is a universal solution. The power of a rotary kiln comes with significant considerations.
High Capital Cost
Rotary kilns are massive, complex pieces of machinery. The initial investment for the kiln and its supporting infrastructure (feed systems, fuel delivery, emissions control) is substantial.
Potential for Dust and Emissions
The tumbling action that makes heat transfer so efficient can also create significant dust from fine or friable materials. This necessitates complex and costly air pollution control systems to capture dust and treat off-gases.
Not Ideal for All Materials
Materials that are very sticky can build up on the inside of the kiln, disrupting flow and heat transfer. Extremely fine powders can become entrained in the gas flow and exit the kiln too quickly.
When to Consider the Rotary Method
The decision to use a rotary kiln depends entirely on the material you are processing and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-volume thermal processing of bulk solids like ores, minerals, or limestone: The rotary kiln is a leading industry standard due to its efficiency and continuous operation.
- If your primary focus is precise atmosphere control for chemical reactions like reduction or roasting: The excellent sealing and gas management of a modern rotary kiln make it a superior choice for large-scale production.
- If your primary focus is a small-scale or laboratory batch process: A rotary kiln is likely overkill; a smaller stationary furnace or other heating method would be more appropriate and cost-effective.
Ultimately, the "rotary method" is a powerful industrial tool for leveraging thermal energy at scale, transforming raw materials into valuable intermediate or finished products.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Continuous Operation | Enables high-volume, 24/7 processing of bulk solids |
| Precise Temperature & Atmosphere Control | Supports specific chemical reactions like reduction or calcination |
| High Thermal Efficiency | Maximizes heat transfer and minimizes energy consumption |
| Scalability | Ideal for large-scale industrial applications in mining and chemical processing |
Ready to optimize your material processing with industrial-grade thermal solutions? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories and industrial facilities with reliable, high-performance technology. Whether you're scaling up from lab research or need robust equipment for continuous production, our expertise ensures precise control, efficiency, and durability. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific extraction and processing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products



















