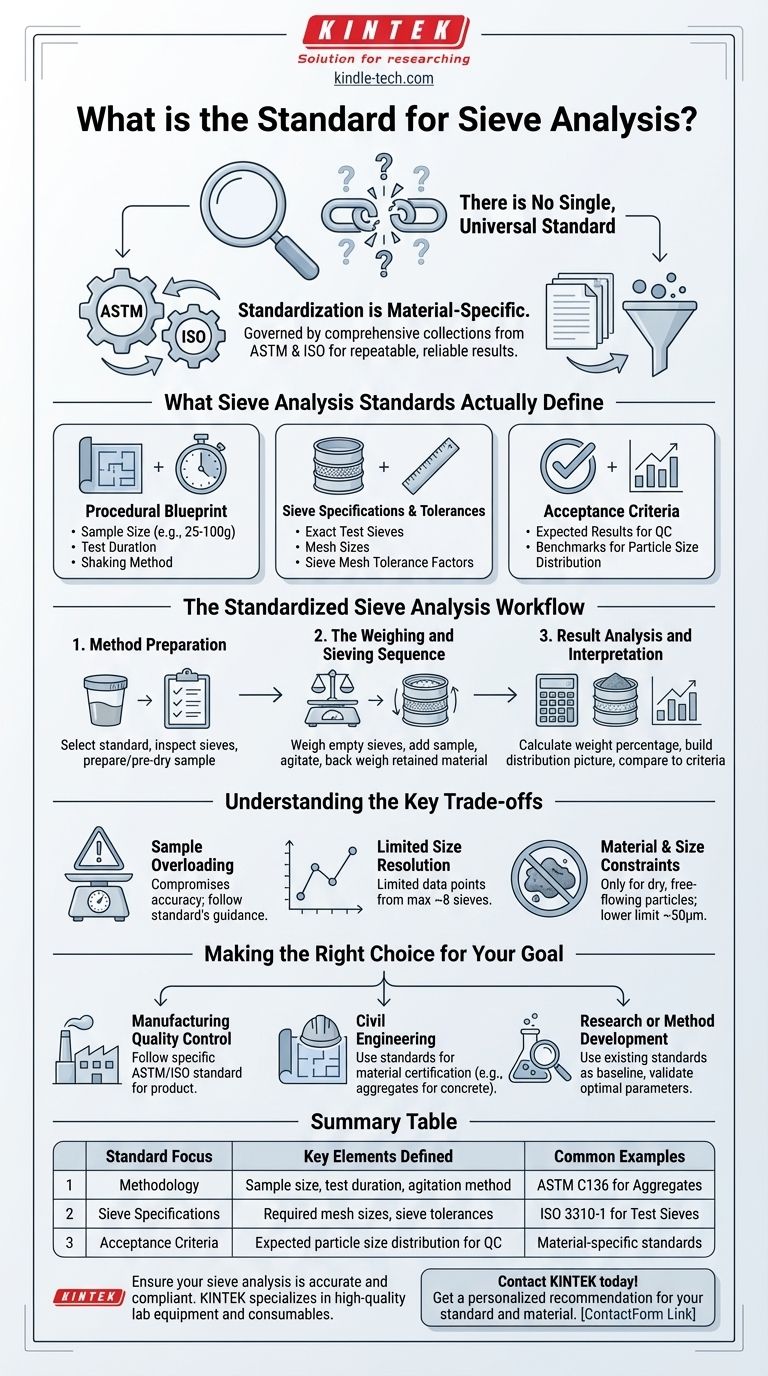
The fundamental truth of sieve analysis is that there is no single, universal standard. Instead, standardization is achieved through a comprehensive collection of material-specific standards published by organizations like the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These documents provide the precise methodology for testing a particular material to ensure results are repeatable and reliable.
The core principle is not to find one master standard, but to identify the specific ASTM or ISO standard that governs your exact material. This standard acts as the definitive procedural guide for achieving accurate and compliant particle size analysis.
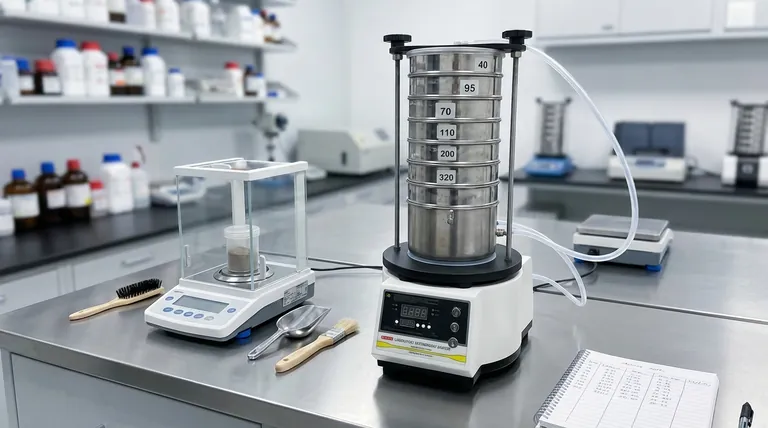

What Sieve Analysis Standards Actually Define
Standards exist to eliminate variability. For sieve analysis, this means controlling every critical step of the process to ensure that a test performed in one lab yields the same results as a test performed in another.
The Procedural Blueprint
A standard provides a detailed recipe for the test. It dictates the entire methodology, including the required sample size, which is typically between 25 and 100 grams to avoid inaccurate results.
It also specifies the test duration and the shaking method (whether manual or with a mechanical shaker), leaving no room for procedural guesswork.
Sieve Specifications and Tolerances
The standard will list the exact test sieves required for a particular material, defining the specific mesh sizes needed to build the sieve stack.
Crucially, standards also establish tolerance factors for the sieve mesh weave itself. This ensures that a "test grade" sieve from any manufacturer performs uniformly, which is vital for consistency.
Acceptance Criteria
For quality control applications, the standard defines the expected results. It provides the benchmarks for the particle size distribution, allowing you to determine if a batch of material meets the required specifications for its intended use, such as for concrete aggregate or asphalt mixes.
The Standardized Sieve Analysis Workflow
While specific details vary by standard, the overall process they define follows a consistent and logical sequence to ensure data integrity.
1. Method Preparation
Before the test begins, the standard guides the initial setup. This includes formally selecting the appropriate standard method, choosing and inspecting the correct sieves, and preparing the material sample, which may involve pre-drying or conditioning.
2. The Weighing and Sieving Sequence
The procedure begins by precisely weighing each empty sieve and the bottom pan. The prepared sample is then placed in the top sieve.
The entire sieve stack is agitated for the specified duration. Afterward, the process of "back weighing" begins, where the material retained on each individual sieve is carefully weighed and recorded.
3. Result Analysis and Interpretation
The final step is to calculate the results. This involves determining the weight percentage of particles retained on each sieve, allowing you to build a clear picture of the material's particle size distribution and compare it against the acceptance criteria.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
While highly reliable, the standardized sieve analysis method has inherent limitations that are critical to understand.
The Risk of Sample Overloading
Using a sample that is too large is a common and critical error. It prevents individual particles from having a fair chance to pass through the mesh, which compromises the accuracy of the results.
The standard often provides guidance, but it may be necessary to test smaller, divided samples to find the optimal weight that produces consistent results.
Limited Size Resolution
A standard sieve stack is typically limited to a maximum of about eight sieves. This means your final particle size distribution curve is based on only a handful of data points, which may not be sufficient for highly detailed analysis.
Material and Size Constraints
Sieve analysis is only effective for dry, free-flowing particles. It cannot be used for wet materials or those that clump together. Furthermore, it has a practical lower measurement limit of around 50 micrometers (µm).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct approach depends entirely on your specific application and the material you are analyzing.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing quality control: Identify the specific ASTM or ISO standard for your product (e.g., ASTM C136 for Aggregates) and follow its procedure exactly.
- If your primary focus is civil engineering: Use the standards required for material certification to ensure aggregates are suitable for concrete, asphalt, or drainage applications.
- If your primary focus is research or method development: Use existing, related standards as a baseline, but run validation tests to determine the optimal sample size and duration for your unique material.
By understanding that standardization is about a repeatable process rather than a single document, you can ensure the integrity of your particle size analysis.
Summary Table:
| Standard Focus | Key Elements Defined | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Methodology | Sample size, test duration, agitation method | ASTM C136 for Aggregates |
| Sieve Specifications | Required mesh sizes, sieve tolerances | ISO 3310-1 for Test Sieves |
| Acceptance Criteria | Expected particle size distribution for QC | Material-specific standards |
Ensure your sieve analysis is accurate and compliant.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your particle size analysis needs. Our range of test sieves and shakers are designed to meet rigorous ASTM and ISO standards, helping you achieve reliable, repeatable results for quality control, research, and material certification.
Let our experts help you select the right equipment for your specific standard and material. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance



















