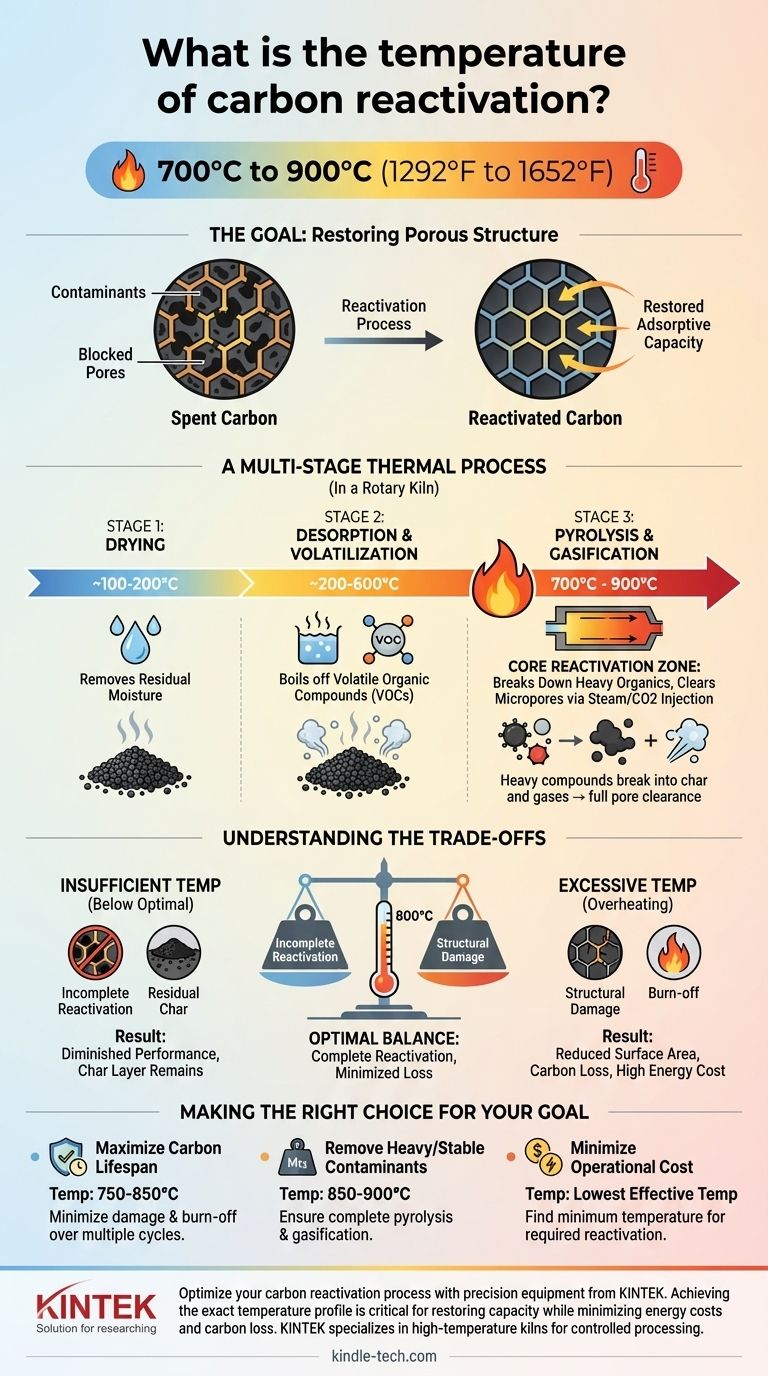
The reactivation of spent activated carbon typically occurs within a high-temperature range of 700°C to 900°C (1292°F to 1652°F). This controlled thermal process, usually conducted in a slowly rotating kiln, is designed to vaporize and destroy the organic contaminants that have been adsorbed onto the carbon, thereby restoring its porous structure and adsorptive capacity for reuse.
Reactivation is not simply a matter of high heat; it is a precisely controlled, multi-stage process. The target temperature range is critical for ensuring complete contaminant destruction without structurally damaging the carbon itself, balancing performance restoration against material degradation.
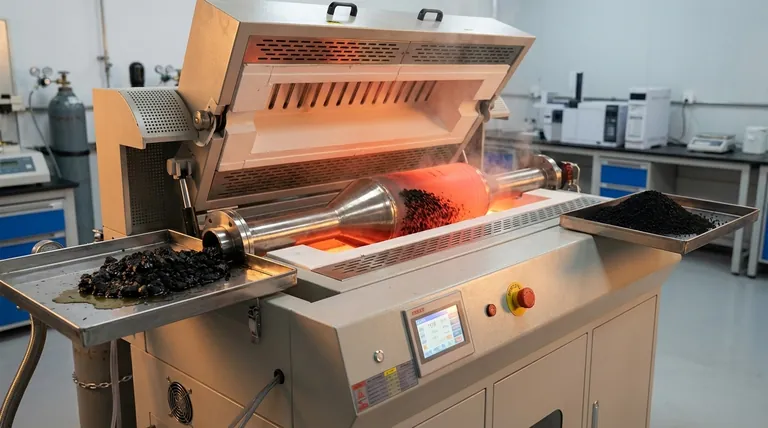

The Goal: Restoring Porous Structure
Why Reactivation is Necessary
Activated carbon works by adsorbing contaminants onto its vast internal surface area, which is composed of millions of microscopic pores. Over time, these pores become saturated, and the carbon is considered "spent" or exhausted.
Reactivation is a cost-effective and environmentally sustainable alternative to disposal. The goal is to carefully strip away the adsorbed contaminants, clearing the pores and making the carbon effective once again.
The Role of High Temperature
The bonds holding organic contaminants to the carbon surface can be strong. High thermal energy is required to break these bonds, volatilize the compounds, and then break them down further into elemental carbon (char) and simple gases.
A Multi-Stage Thermal Process
The journey through a reactivation kiln is not uniform. The temperature range of 700°C to 900°C represents the final and most critical stage of a process that begins at much lower temperatures.
Stage 1: Drying (Approx. 100-200°C)
As the spent carbon enters the kiln, the initial heat drives off any residual water. This is a crucial first step to ensure uniform heating in the subsequent stages.
Stage 2: Desorption & Volatilization (Approx. 200-600°C)
As the temperature rises, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that were adsorbed by the carbon begin to boil off. These vaporized contaminants are carried away in the kiln's gas stream.
Stage 3: Pyrolysis & Gasification (700-900°C)
This is the core reactivation zone. Heavier, less volatile organic compounds that remain on the carbon are broken down through pyrolysis.
At these high temperatures, and often with the injection of an oxidizing agent like steam or carbon dioxide, the residual carbon char from pyrolysis is gasified. This final step clears the micropores, fully restoring the carbon's adsorptive properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the precise temperature within the 700-900°C range is a balancing act with significant consequences.
The Risk of Insufficient Temperature
Operating below the optimal temperature will result in incomplete reactivation. Some of the heavier organic compounds may not fully pyrolyze, leaving a layer of char that continues to block the carbon's pores and diminish its performance.
The Risk of Excessive Temperature
Overheating can be just as damaging. Excessively high temperatures can begin to destroy the delicate pore structure of the activated carbon itself, permanently reducing its surface area and capacity. This also increases the amount of carbon that is oxidized and lost in the process, known as "burn-off."
The Cost Factor
Higher temperatures require more energy, directly increasing operational costs. The goal is to find the lowest possible temperature that achieves complete reactivation for the specific contaminants involved, thereby minimizing both energy consumption and carbon loss.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal temperature depends on the nature of the contaminants and your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing carbon lifespan: Operate at the lower end of the effective range (e.g., 750-850°C) to minimize structural damage and burn-off over multiple reactivation cycles.
- If your primary focus is removing highly stable or heavy contaminants: You will likely need to use the higher end of the temperature range (e.g., 850-900°C) to ensure complete pyrolysis and gasification.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational cost: The key is to find the minimum effective temperature that provides the required level of reactivation for your specific application, avoiding unnecessary energy expenditure.
Ultimately, precise temperature control is the key to successfully and economically extending the life of your activated carbon media.
Summary Table:
| Reactivation Stage | Temperature Range | Key Process |
|---|---|---|
| Drying | 100°C - 200°C | Removes residual moisture |
| Desorption & Volatilization | 200°C - 600°C | Boils off volatile organic compounds (VOCs) |
| Pyrolysis & Gasification | 700°C - 900°C | Core reactivation: Breaks down heavy organics and clears pores |
Optimize your carbon reactivation process with precision equipment from KINTEK.
Achieving the exact temperature profile between 700°C and 900°C is critical for restoring adsorptive capacity while minimizing energy costs and carbon loss. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature kilns and lab furnaces designed for controlled thermal processing, helping you maximize carbon lifespan and operational efficiency.
Let our experts help you balance performance and cost-effectiveness.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your reactivation needs
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic



















