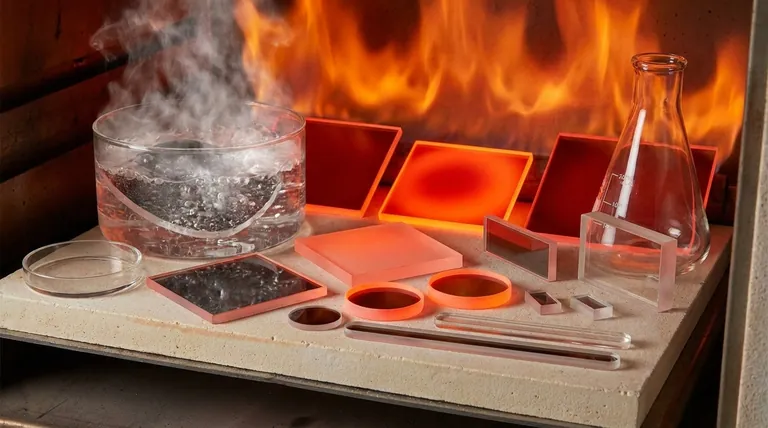
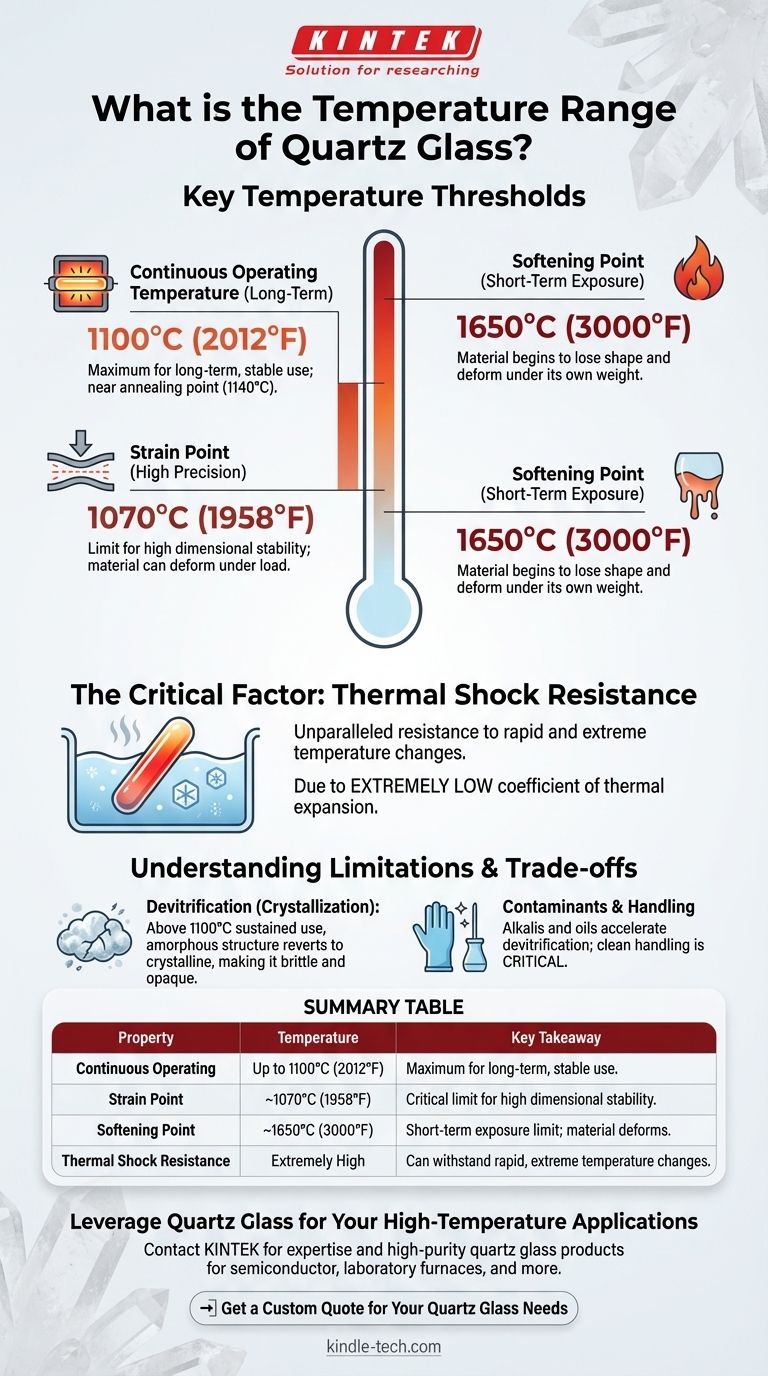
The thermal performance of quartz glass is defined by several key temperature points, not a single range. For practical, long-term use, transparent fused quartz can operate continuously at temperatures up to approximately 1100°C (2012°F). However, it can withstand much higher temperatures for short periods before it begins to soften and deform.
The crucial takeaway is to distinguish between the continuous service temperature and the softening point. While quartz excels at sustained high-heat applications, its true defining characteristic is an unparalleled resistance to thermal shock—the ability to withstand rapid and extreme temperature changes that would shatter ordinary glass.

Key Thermal Properties of Quartz Glass
To use quartz effectively, you must understand three critical temperature thresholds. These points define the material's behavior under thermal load.
Continuous Operating Temperature
The maximum temperature for long-term, continuous use is around 1100°C (2012°F). Beyond this point, the material may begin a slow process of structural change.
This temperature is near the annealing point (approx. 1140°C), where internal stresses within the glass can be relieved over time.
Strain Point
The strain point, typically around 1070°C (1958°F), is a more conservative limit for high-precision applications.
Above this temperature, the material can begin to internally deform under load over extended periods, making it a critical design constraint for applications requiring high dimensional stability.
Softening Point
The softening point is significantly higher, at approximately 1650°C (3000°F). This is the temperature at which quartz begins to lose its shape and deform under its own weight.
This is considered a short-term exposure limit, not a viable operating temperature for any component that needs to maintain its structure.
The Critical Factor: Thermal Shock Resistance
While its heat tolerance is impressive, the most exceptional thermal property of quartz is its resistance to thermal shock.
What is Thermal Shock?
Thermal shock occurs when a material experiences a rapid change in temperature, causing different parts of it to expand or contract at different rates. This creates immense internal stress that can cause brittle materials, like regular glass, to crack.
Why Quartz Excels
Quartz has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts very little when heated or cooled.
Because it barely changes size with temperature, no significant internal stress builds up. This allows it to endure temperature changes that would destroy most other ceramics.
Practical Implications
This property allows a red-hot quartz tube to be plunged into cold water without cracking. This makes it indispensable for applications involving rapid heating and cooling cycles, such as in semiconductor manufacturing and laboratory equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Despite its strengths, quartz glass is not without its operational limits. Understanding these is key to preventing material failure.
The Process of Devitrification
At sustained temperatures above 1100°C, quartz begins a process called devitrification. The amorphous, glassy structure slowly reverts to a crystalline state (cristobalite).
This crystallization makes the material opaque and, more importantly, severely degrades its mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance. It becomes brittle and prone to failure.
The Role of Contaminants
Devitrification is accelerated by the presence of surface contaminants, particularly alkalis like sodium and potassium. Even oils from fingerprints can speed up this process at high temperatures.
For this reason, handling quartz components with clean gloves is a standard and critical practice in high-temperature applications.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
While thermally robust, it's essential to remember that quartz is still a glass. At ambient temperatures, it is a brittle material susceptible to fracture from mechanical shock or impact.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires matching its properties to your specific operational needs.
- If your primary focus is long-term, stable operation: Design your system to stay below the strain point, keeping the continuous service temperature at or below 1100°C (2012°F).
- If you need to withstand rapid, extreme temperature changes: Quartz is an ideal choice due to its near-zero thermal expansion, far superior to other glasses or ceramics.
- If you require short-term exposure to very high heat: You can push towards the softening point (around 1650°C or 3000°F), but understand this risks deformation and accelerates material degradation through devitrification.
Understanding these distinct thermal limits is the key to successfully leveraging quartz glass in demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Property | Temperature | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Operating Temperature | Up to 1100°C (2012°F) | Maximum for long-term, stable use. |
| Strain Point | ~1070°C (1958°F) | Critical limit for high dimensional stability. |
| Softening Point | ~1650°C (3000°F) | Short-term exposure limit; material deforms. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Extremely High | Can withstand rapid, extreme temperature changes. |
Leverage Quartz Glass for Your High-Temperature Applications
Understanding the precise thermal limits of quartz glass is critical for the success and safety of your laboratory processes. Whether you need components for semiconductor manufacturing, laboratory furnaces, or any application requiring superior thermal performance, KINTEK has the expertise and high-purity quartz glass products you need.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements. Our team will help you select the right materials to ensure durability, efficiency, and reliability in your most demanding thermal environments.
➡️ Get a Custom Quote for Your Quartz Glass Needs
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- 400-700nm Wavelength Anti Reflective AR Coating Glass
- Zinc Selenide ZnSe Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer and Lens
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature of quartz glass? Master Its High-Temp Limits & Applications
- What are the thermal properties of quartz? Unlocking Extreme Temperature Stability for Your Lab
- Does quartz have a high melting point? Discover Its Superior High-Temperature Performance
- How does quartz differ from glass? A Guide to Material Selection for Performance
- What is the high temperature of quartz? Key Thresholds for Crystalline vs. Fused Silica













