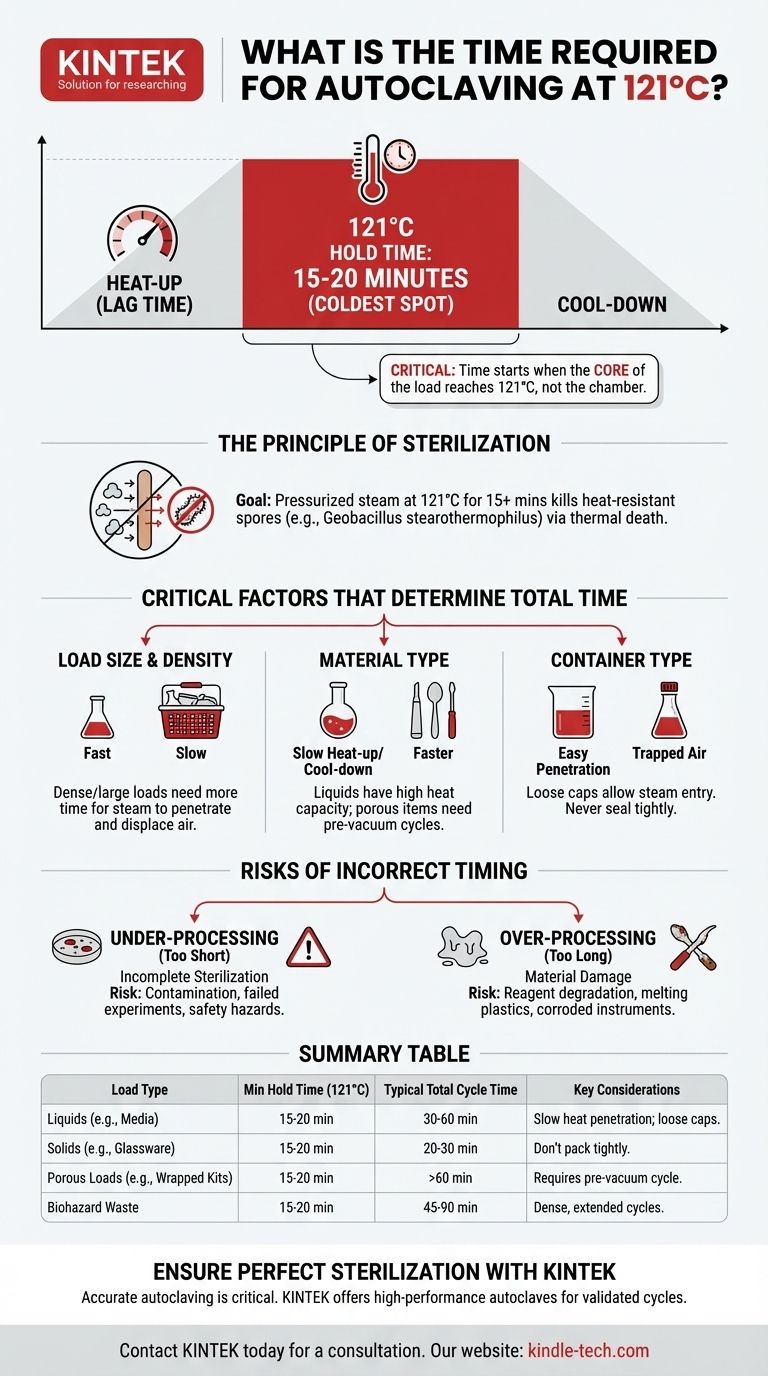
For standard sterilization, the minimum required time for autoclaving at 121°C (250°F) under 15 psi of pressure is 15 to 20 minutes. However, this is the holding time after the material being sterilized has reached 121°C, not the total cycle time. The total time is almost always longer and depends entirely on the size and type of the load.
The critical mistake is assuming the 15-minute timer starts when the autoclave chamber reaches 121°C. The true requirement is that the coldest spot within your load must be held at 121°C for at least 15 minutes to guarantee sterilization.

The Principle of Sterilization Time
The goal of autoclaving is to use pressurized steam to achieve a temperature high enough to kill the most heat-resistant microorganisms, specifically bacterial spores like Geobacillus stearothermophilus. The 121°C for 15 minutes standard is based on the thermal death time required for these organisms.
It's About Penetration, Not Just Presence
The autoclave chamber might reach 121°C quickly, but steam must displace all the air within the chamber and fully penetrate the items being sterilized.
A dense or large load takes significantly longer for its core to reach the target temperature than a small, simple load. This "heat-up" or "lag" time is the most critical variable in determining your total cycle length.
Critical Factors That Determine Autoclave Time
You cannot rely on a single time setting for all applications. You must adjust the cycle based on what you are sterilizing. Think of it like cooking: a small potato cooks much faster than a large turkey in the same oven.
Factor 1: Load Size and Density
A single small flask of media will heat up far more quickly than a large, tightly packed basket of glassware or biohazard waste.
Dense loads require more time for steam to penetrate and displace trapped air, which acts as an insulator and prevents effective sterilization.
Factor 2: Type of Material Being Sterilized
Liquids, especially large volumes (e.g., >1 liter), have a high heat capacity and take much longer to heat up and cool down than solid instruments.
Porous materials like surgical gowns, animal bedding, or tubing require special cycles (often pre-vacuum) to ensure all air is removed so steam can contact every surface.
Factor 3: Container Type and Capping
A loosely covered, wide-mouthed beaker allows for easy steam penetration.
A flask with a narrow neck and a loose-fitting cap will trap air, significantly slowing heat transfer to the liquid inside. Never seal containers tightly, as this creates a risk of explosion.
The Risks of Incorrect Timing
Setting the wrong cycle time has significant consequences that go beyond a simple failed run. This is where procedural discipline is essential.
Under-processing: The Danger of Incomplete Sterilization
This is the most severe failure. If the core of the load never reaches the required temperature for the minimum time, microorganisms will survive.
This can lead to contaminated experimental results, failed media batches, or, in a clinical setting, a serious patient safety risk.
Over-processing: The Damage to Your Materials
Conversely, running a cycle for too long can be destructive. Excessive heat exposure can cause:
- Degradation of reagents and culture media (e.g., sugar caramelization).
- Melting or warping of plastics like polypropylene.
- Dulling and corrosion of sharp surgical instruments.
How to Determine the Correct Cycle for Your Load
The most reliable method is to validate your specific load using biological indicators or a thermocouple placed at the center of the load. When in doubt, it is safer to err on the side of a longer cycle time.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquids (e.g., media): Plan for significantly longer cycles, often 30-60 minutes for multi-liter volumes, to account for slow heat penetration.
- If your primary focus is solid glassware or unwrapped instruments: A standard 20-30 minute total cycle is often sufficient, but ensure items are not packed tightly together.
- If your primary focus is porous loads (e.g., wrapped kits, tubing): You must use a pre-vacuum cycle, and total times can exceed 60 minutes to ensure complete air removal and steam penetration.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biohazard waste: Use extended cycles (45-90 minutes) because these loads are dense, non-homogenous, and contain trapped air.
Ultimately, you must adapt your autoclave protocol to the specific material you are sterilizing to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Summary Table:
| Load Type | Minimum Hold Time at 121°C | Typical Total Cycle Time | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquids (e.g., Media) | 15-20 minutes | 30-60 minutes | Slow heat penetration; never seal containers tightly. |
| Solids (e.g., Glassware) | 15-20 minutes | 20-30 minutes | Ensure items are not packed tightly together. |
| Porous Loads (e.g., Wrapped Kits) | 15-20 minutes | >60 minutes | Requires pre-vacuum cycle for complete air removal. |
| Biohazard Waste | 15-20 minutes | 45-90 minutes | Dense, non-homogenous load; use extended cycles. |
Ensure Your Lab's Sterilization is Perfect Every Time
Accurate autoclaving is critical for experimental integrity and safety. The right equipment and protocols make all the difference. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab autoclaves and consumables designed for reliable, validated sterilization cycles.
Let us help you achieve guaranteed sterility while protecting your valuable materials. Our experts can assist you in selecting the ideal autoclave for your specific loads—whether you're processing liquids, glassware, or complex porous items.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and ensure your lab's foundation is built on precision and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-pressure autoclave essential for HMF conversion? Achieve Efficient Lignocellulose Synthesis
- What role does a high-pressure autoclave play in Pennisetum alopecuroides pretreatment? Optimize Biomass Breakdown
- What function does a high-pressure laboratory autoclave serve in walnut shell pretreatment? Enhance Biomass Reactivity.
- Why is a Nickel-based alloy typically selected for the high-pressure autoclave? Ensure Safety & Precision in S-CO2 Testing
- How long does an autoclave work? Understand Cycle Times for Effective Sterilization
- How long does autoclave liquid cycle take? The Truth About Sterilization Time & Safety
- What is the size of a laboratory autoclave? A Guide to Choosing the Right Capacity
- Why are high-pressure hydrothermal autoclaves essential for IrRu@Te synthesis? Achieve Peak Catalyst Stability



















