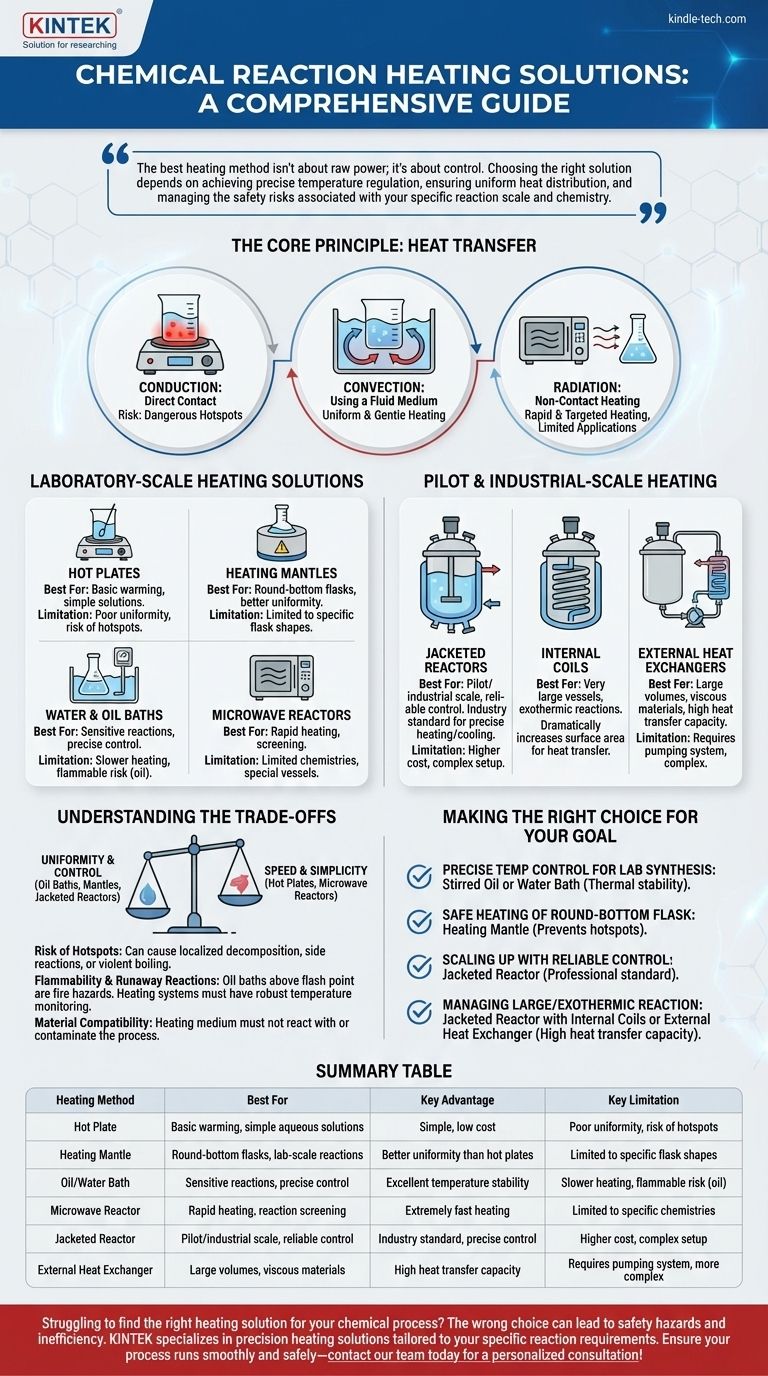
For heating chemical reactions, the solutions range from simple laboratory hot plates and heating mantles to industrial-scale jacketed reactors and external heat exchangers. The choice of equipment is dictated by the reaction's required temperature, the need for precise control, the scale of the operation, and critical safety considerations.
The best heating method isn't about raw power; it's about control. Choosing the right solution depends on achieving precise temperature regulation, ensuring uniform heat distribution, and managing the safety risks associated with your specific reaction scale and chemistry.

The Core Principle: Heat Transfer
To select the right method, you must first understand the fundamental ways heat is transferred. Each heating solution emphasizes one or more of these principles.
Conduction: Direct Contact
Conduction is heat transfer through direct physical contact. A hot plate touching a beaker is a primary example. While simple, it can create dangerous hotspots where the vessel is much hotter than the bulk liquid.
Convection: Using a Fluid Medium
Convection uses a fluid (like oil, water, or steam) to transfer heat. The fluid is heated and then circulates around the reaction vessel, providing much more uniform and gentle heating than direct conduction. This is the principle behind oil baths and jacketed reactors.
Radiation: Non-Contact Heating
Radiation transfers heat via electromagnetic waves, such as infrared or microwaves. This method, used in microwave reactors, can provide extremely rapid and targeted heating but is typically limited to specific applications and vessel types.
Laboratory-Scale Heating Solutions
For reactions typically under a few liters, the equipment prioritizes flexibility and ease of use.
Hot Plates
A hot plate with a magnetic stirrer is the most basic setup. It is best suited for non-critical applications where precise temperature control is not the main goal, such as warming simple aqueous solutions.
Heating Mantles
These are fiberglass shells with embedded heating elements shaped to fit round-bottom flasks. They provide far more uniform heating than a hot plate by increasing the contact surface area, significantly reducing the risk of hotspots and localized boiling.
Water and Oil Baths
An immersion circulator or a simple hot plate is used to heat a bath of water or silicone oil, into which the reaction vessel is placed. This method offers excellent temperature stability and uniformity, making it a gold standard for sensitive reactions requiring precise control.
Microwave Reactors
Specialized laboratory microwave reactors use radiation to rapidly heat polar solvents and reactants. This can accelerate reaction rates dramatically, but it requires specific microwave-transparent vessels and is not suitable for all chemical systems.
Pilot and Industrial-Scale Heating
As reaction volumes increase, safety, efficiency, and uniformity become paramount. The equipment reflects these priorities.
Jacketed Reactors
This is the industry standard for controlled heating and cooling. The reactor is a vessel surrounded by an outer shell, or "jacket." A thermal fluid (like steam, water, or a specialized heat transfer oil) is circulated through the space between the vessel and the jacket to precisely control the internal temperature.
Internal Coils
For very large vessels or reactions that generate significant heat (exothermic), internal coils are often used in addition to a jacket. A thermal fluid flows through these coils, dramatically increasing the available surface area for heat transfer inside the reactor.
External Heat Exchangers
In this setup, the reaction mixture is pumped out of the reactor, through an external heat exchanger, and then back into the vessel. This closed loop allows for immense heating power and is highly effective for managing very large volumes or highly viscous materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single method is universally superior. The choice involves balancing performance with risk.
Uniformity vs. Hotspots
A key danger in heating is the creation of hotspots, which can cause localized decomposition, unwanted side reactions, or violent boiling. A stirred oil bath or heating mantle is far superior to a flat hot plate in preventing hotspots.
Control vs. Speed
An oil bath provides slow, steady, and precise control. A microwave reactor provides immense speed. The choice depends on whether the goal is careful synthesis or rapid screening.
Flammability and Runaway Reactions
Using an oil bath above its flash point creates a significant fire hazard. More importantly, any heating system must be paired with robust temperature monitoring to prevent a runaway reaction, where the reaction rate accelerates uncontrollably.
Material Compatibility
The heating medium must not react with or contaminate the process. Using direct steam injection, for example, is only appropriate for aqueous reactions where dilution by the condensed steam is acceptable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your heating method based on the most critical parameter for your specific process.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature control for a sensitive lab synthesis: A stirred oil or water bath is your most reliable choice for thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is safely heating a round-bottom flask without hotspots: A heating mantle offers a significant safety and performance advantage over a standard hot plate.
- If your primary focus is scaling up a process with reliable control: A jacketed reactor with a dedicated thermal fluid system is the professional standard.
- If your primary focus is managing a large, viscous, or highly exothermic reaction: Combining a jacketed reactor with internal coils or an external heat exchanger provides the necessary heat transfer capacity.
By matching the heating method to your reaction's specific needs, you ensure safe operation, process efficiency, and reproducible results.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Plate | Basic warming, simple aqueous solutions | Simple, low cost | Poor uniformity, risk of hotspots |
| Heating Mantle | Round-bottom flasks, lab-scale reactions | Better uniformity than hot plates | Limited to specific flask shapes |
| Oil/Water Bath | Sensitive reactions requiring precise control | Excellent temperature stability and uniformity | Slower heating, flammable risk (oil) |
| Microwave Reactor | Rapid heating of polar solvents, reaction screening | Extremely fast heating | Limited to specific chemistries and vessels |
| Jacketed Reactor | Pilot/industrial scale, reliable control | Industry standard for precise heating/cooling | Higher cost, complex setup |
| External Heat Exchanger | Large volumes, viscous materials, exothermic reactions | High heat transfer capacity | Requires pumping system, more complex |
Struggling to find the right heating solution for your chemical process? The wrong choice can lead to safety hazards, inconsistent results, and process inefficiency. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision heating solutions tailored to your specific reaction requirements—from reliable heating mantles for your R&D to robust jacketed reactors for scale-up. Our experts can help you select the ideal equipment for precise temperature control, uniform heating, and enhanced safety. Ensure your process runs smoothly and safely—contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
People Also Ask
- Why are high-pressure autoclaves essential for preparing bio-based polyamide curing agents from dimeric acid?
- What roles do autoclaves play in MFI zeolite synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Crystalline Growth
- What is the contribution of a hydrothermal reactor to graded pore construction? Precision Templates for TAS
- What is the function of a constant temperature hydrothermal reactor? Master Coal Fly Ash Activation
- Why are sealed laboratory reaction vessels necessary in the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites? Ensure Purity and Yield



















