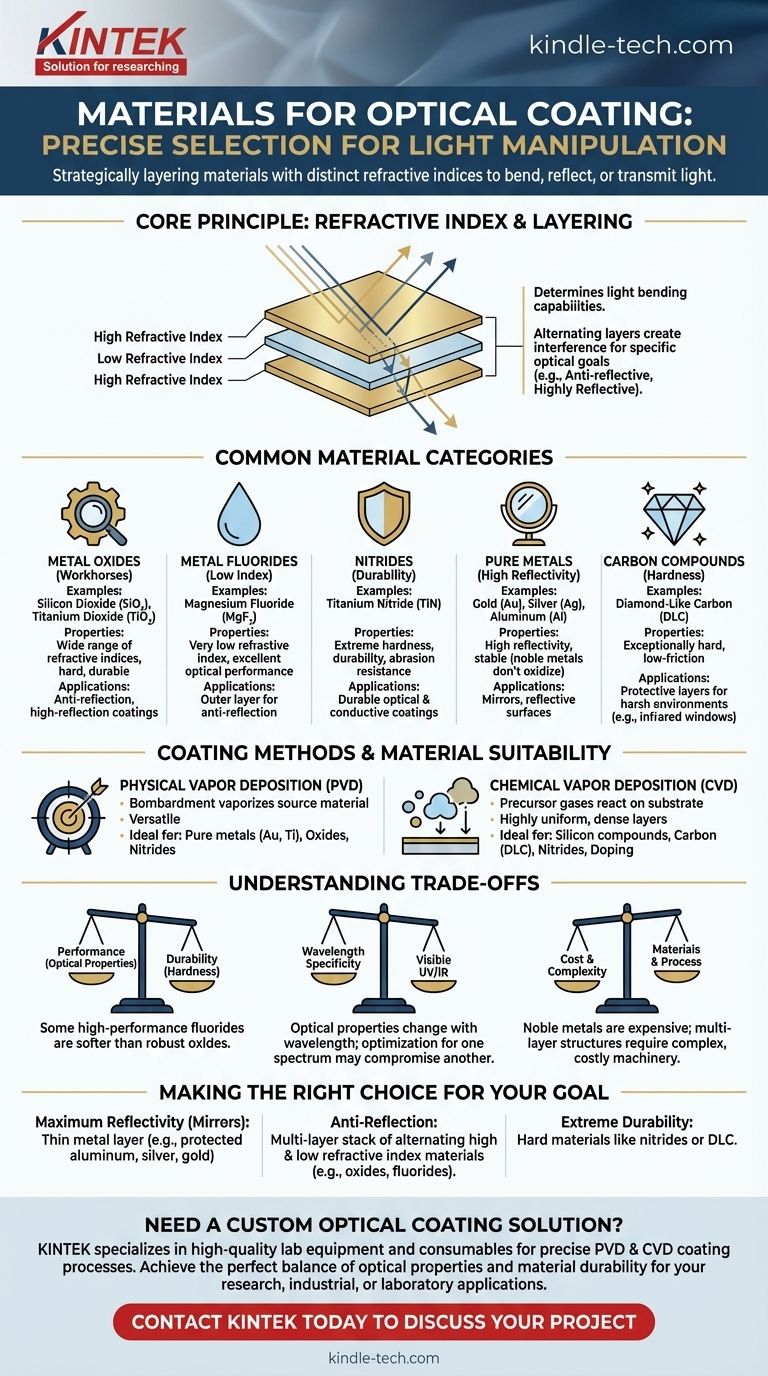
In short, optical coatings are made from a precise selection of materials, including metal oxides (like silicon compounds), nitrides (like titanium nitride), fluorides, pure metals (like gold), and specialized forms of carbon. The specific material is chosen based on its optical properties—primarily its refractive index—and its compatibility with the chosen deposition process, such as Physical or Chemical Vapor Deposition.
The crucial insight is that optical coating isn't about a single "best" material. It's about strategically layering different materials with distinct refractive indices to bend, reflect, or transmit light in a highly controlled way to achieve a specific goal.

The Core Principles of Material Selection
To understand why certain materials are used, you must first understand the goal of an optical coating. The primary purpose is to manipulate how light interacts with a surface.
The Central Role of Refractive Index
The single most important property of an optical coating material is its refractive index. This value determines how much the material bends light.
By stacking ultra-thin layers of materials with alternating high and low refractive indices, we can create interference effects. These effects allow us to design coatings that are anti-reflective, highly reflective, or that pass or block specific wavelengths of light.
Durability and Environment
The material must also be able to withstand its operational environment. Factors like hardness, resistance to abrasion, and stability across temperature and humidity ranges are critical for long-term performance.
Common Material Categories for Optical Coatings
Materials used for optical coatings generally fall into a few key families, each with distinct properties.
Metal Oxides
Oxides are the workhorses of the optical coating industry. They offer a wide range of refractive indices and are generally hard and durable.
Materials like silicon compounds (e.g., Silicon Dioxide, SiO₂) provide a low refractive index, while others like Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) provide a high refractive index.
Metal Fluorides
Fluorides, such as Magnesium Fluoride (MgF₂), are prized for having a very low refractive index. This makes them exceptionally useful as the outer layer in anti-reflection coatings. While sometimes softer than oxides, their optical performance is excellent.
Nitrides
Nitrides are known for their extreme hardness and durability. Titanium nitride (TiN), for example, is often used for coatings that must withstand significant physical abrasion while maintaining specific optical or conductive properties.
Pure Metals
Metals are used when the goal is high reflectivity. A thin layer of metal can create an excellent mirror.
Gold (Au), silver (Ag), and aluminum (Al) are the most common choices. As noted, noble metals from the platinum group are also used because they do not easily oxidize, ensuring the reflective surface remains stable over time.
Carbon Compounds
Specialized forms of carbon, particularly Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC), create exceptionally hard and low-friction surfaces. These are often used as a protective outer layer for optics used in harsh environments, such as infrared windows exposed to the elements.
How Coating Methods Influence Material Choice
The manufacturing process itself dictates which materials can be used effectively. The two dominant methods are Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD techniques, which include sputter coating, involve physically bombarding a source material (the "target") to vaporize it, allowing it to deposit onto the substrate.
This method is highly versatile and works exceptionally well for a wide range of materials, including pure metals like gold and titanium, as well as oxides and nitrides.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD uses precursor gases that react on the substrate surface to form the desired coating. This process is ideal for creating highly uniform and dense layers.
It is particularly well-suited for materials like silicon compounds, carbon (DLC), and nitrides. CVD also allows for advanced techniques like doping, where other elements are introduced to fine-tune the coating's properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no single material that is perfect for every application. Every choice involves balancing competing factors.
Performance vs. Durability
The materials with the most desirable optical properties might not be the most durable. For example, some fluorides offer an excellent refractive index for anti-reflection but are softer and more susceptible to damage than robust metal oxides.
Wavelength Specificity
A material's optical properties, particularly its transparency and refractive index, change with the wavelength of light. A coating designed for visible light will perform poorly in the ultraviolet (UV) or infrared (IR) spectrum, and vice-versa.
Cost and Complexity
Material cost varies dramatically. Noble metals like gold and platinum are inherently expensive. Furthermore, creating a high-performance coating with dozens of alternating layers requires complex machinery and precise control, adding significantly to the final cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application dictates the ideal material composition.
- If your primary focus is maximum reflectivity (mirrors): Your best choice will be a thin layer of metal like protected aluminum, silver, or gold.
- If your primary focus is anti-reflection: You will need a multi-layer stack of alternating high and low refractive index materials, such as metal oxides and fluorides.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability: You should look to hard materials like nitrides (titanium nitride) or a protective Diamond-Like Carbon outer layer.
Ultimately, selecting the right materials for an optical coating is a deliberate engineering decision that balances optical physics with real-world physical demands.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Oxides | Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂), Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) | Wide range of refractive indices, hard, durable | Anti-reflection, high-reflection coatings |
| Metal Fluorides | Magnesium Fluoride (MgF₂) | Very low refractive index, excellent optical performance | Outer layer for anti-reflection coatings |
| Nitrides | Titanium Nitride (TiN) | Extreme hardness, durability, abrasion resistance | Durable optical and conductive coatings |
| Pure Metals | Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Aluminum (Al) | High reflectivity, stable (noble metals) | Mirrors, reflective surfaces |
| Carbon Compounds | Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) | Exceptionally hard, low-friction | Protective layers for harsh environments |
Need a Custom Optical Coating Solution?
Choosing the right materials is critical for your optical application's performance and durability. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for precise coating processes, including PVD and CVD systems. Our expertise ensures you achieve the perfect balance of optical properties and material durability for your specific needs—whether for research, industrial, or specialized laboratory applications.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your optical coating challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tube Racks
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of quartz glass? Essential for Extreme-Temperature and UV Applications
- What is the use of quartz in the glass industry? Essential for High-Performance Fused Quartz Glass
- Why is a PTFE plate selected as the casting substrate for solid polymer electrolytes? Ensure Damage-Free Release
- What is optical quartz? The Ultimate Material for UV and High-Temp Optics
- What is the temperature range of quartz glass? Master Its Thermal Limits for Demanding Applications



















