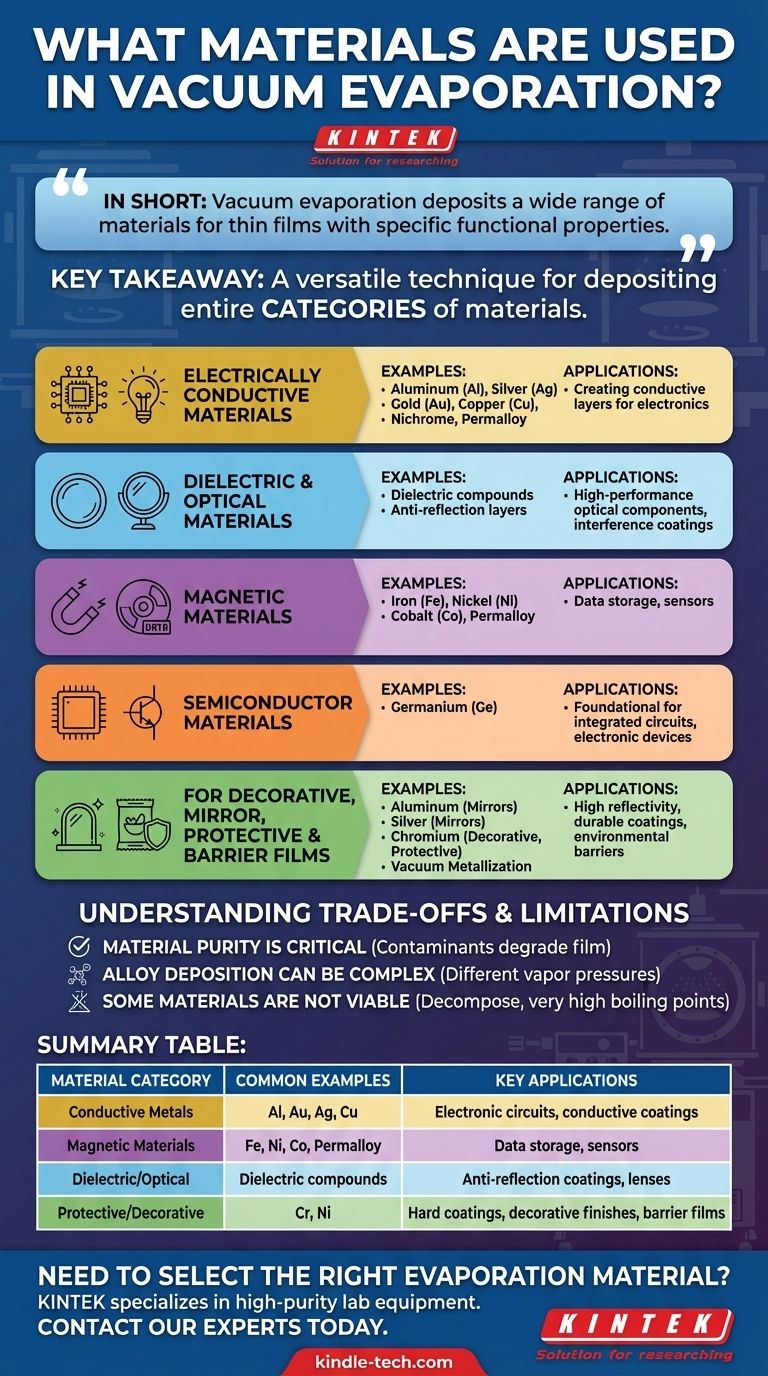
In short, vacuum evaporation can be used to deposit a wide range of materials, including common metals like Aluminum, Gold, Silver, Nickel, and Chromium. The full list is extensive, encompassing various pure metals, alloys, and even semiconductor and dielectric compounds, chosen specifically for the final application.
The key takeaway is not a specific list of materials, but the understanding that vacuum evaporation is a versatile technique for depositing entire categories of materials—conductive, magnetic, dielectric, and more—to create thin films with specific functional properties.
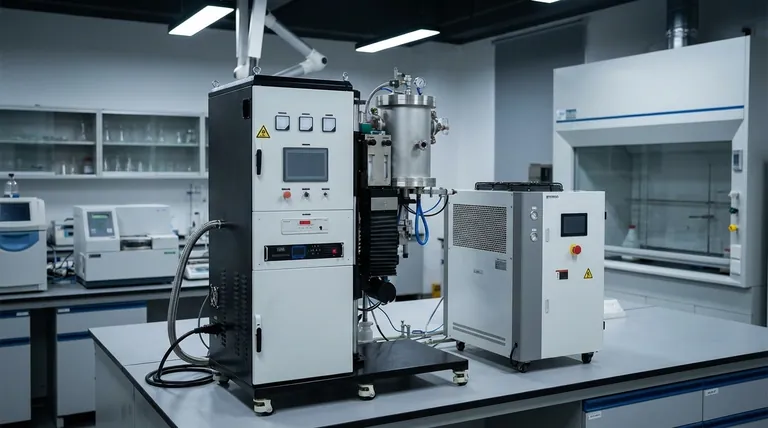

A Closer Look at Evaporation Materials by Category
Vacuum evaporation is fundamentally a process of heating a source material in a vacuum until it vaporizes and then condenses onto a cooler substrate. The suitability of a material is therefore determined by its thermal properties and the desired characteristics of the resulting thin film.
Electrically Conductive Materials
Many of the most common applications for vacuum evaporation involve creating conductive layers for electronics.
Pure metals like Aluminum (Al), Silver (Ag), Gold (Au), and Copper (Cu) are frequently used due to their excellent conductivity. Alloys such as Nichrome and Permalloy are also common.
Dielectric and Optical Materials
This process is crucial for manufacturing high-performance optical components like lenses and mirrors.
While the references highlight metals, the process also deposits dielectric materials. These are used to create optical interference coatings, such as anti-reflection layers, which require precise control over the film's refractive index.
Magnetic Materials
For applications in data storage and sensors, specific magnetic materials are required.
Metals such as Iron (Fe), Nickel (Ni), and Cobalt (Co), along with magnetic alloys like Permalloy, can be deposited to create thin films with specific magnetic properties.
Semiconductor Materials
Vacuum evaporation is a foundational technology in the fabrication of integrated circuits and other electronic devices.
Materials like Germanium (Ge) can be deposited to form the semiconductor layers that are the building blocks of transistors and other microelectronic components.
The Role of Application in Material Selection
The choice of material is always dictated by the end goal. A material is not chosen simply because it can be evaporated, but because it provides a necessary function.
For Decorative and Mirror Coatings
The goal here is high reflectivity across a desired spectrum.
Aluminum is extremely common for mirrors due to its high reflectivity and low cost. Silver offers even better reflectivity but can tarnish. Chromium is often used for a durable, shiny decorative finish.
For Protective and Barrier Films
In this context, the film must provide a robust barrier against environmental factors.
Metals deposited onto flexible plastics, a process often called vacuum metallization, can create a permeation barrier against oxygen and moisture for food packaging. Chromium is also valued for creating hard, corrosion-resistant coatings.
For Electronic Components
Here, electrical performance is the most critical factor.
Gold is often chosen for contact points due to its high conductivity and extreme resistance to corrosion. Copper and Aluminum are used to create the conductive pathways within integrated circuits.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While versatile, vacuum evaporation is not a universal solution, and material selection involves important considerations.
Material Purity is Critical
The source material must be exceptionally pure. Any contaminants present in the source will be vaporized and deposited along with the primary material, degrading the performance of the final film.
Alloy Deposition Can Be Complex
Evaporating alloys can be challenging. The different elements within an alloy often have different vapor pressures, meaning one may evaporate faster than the other. This can result in a thin film whose composition does not match the source alloy.
Some Materials Are Not Viable
This technique is not suitable for all materials. Compounds that decompose when heated cannot be deposited. Likewise, materials with extremely high boiling points (like tungsten or tantalum) are very difficult to evaporate using standard thermal methods and often require more advanced techniques like electron-beam evaporation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's primary requirement will determine the best material for the job.
- If your primary focus is high conductivity: Gold, Silver, Copper, and Aluminum are the industry standards for electronic applications.
- If your primary focus is optical performance: Highly reflective metals like Aluminum and Silver are ideal for mirrors, while specialized dielectric materials are needed for anti-reflection coatings.
- If your primary focus is durability or corrosion resistance: Chromium and Nickel provide hard, protective surfaces suitable for both functional and decorative purposes.
Ultimately, selecting a material for vacuum evaporation is a deliberate choice driven by the functional demands of the final product.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Conductive Metals | Aluminum (Al), Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Copper (Cu) | Electronic circuits, conductive coatings |
| Magnetic Materials | Iron (Fe), Nickel (Ni), Cobalt (Co), Permalloy | Data storage, sensors |
| Dielectric/Optical | Various dielectric compounds | Anti-reflection coatings, optical lenses |
| Protective/Decorative | Chromium (Cr), Nickel (Ni) | Hard coatings, decorative finishes, barrier films |
Need to select the right evaporation material for your specific application?
KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables for vacuum evaporation processes. Whether you're developing advanced electronics, optical coatings, or durable protective layers, our expertise ensures you get the materials and support you need for superior thin-film performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials
- What are the factors influencing shrinkage during sintering? Control Dimensional Changes for Precision Parts
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















