To ensure accurate results, you must understand that sieve analysis is affected by the physical limitations of the equipment, the characteristics of the particles themselves, and the specific procedure followed. The number of sieves limits the resolution of your data, the method is generally unsuitable for particles smaller than 50 µm, and it requires a dry, free-flowing sample to work correctly.
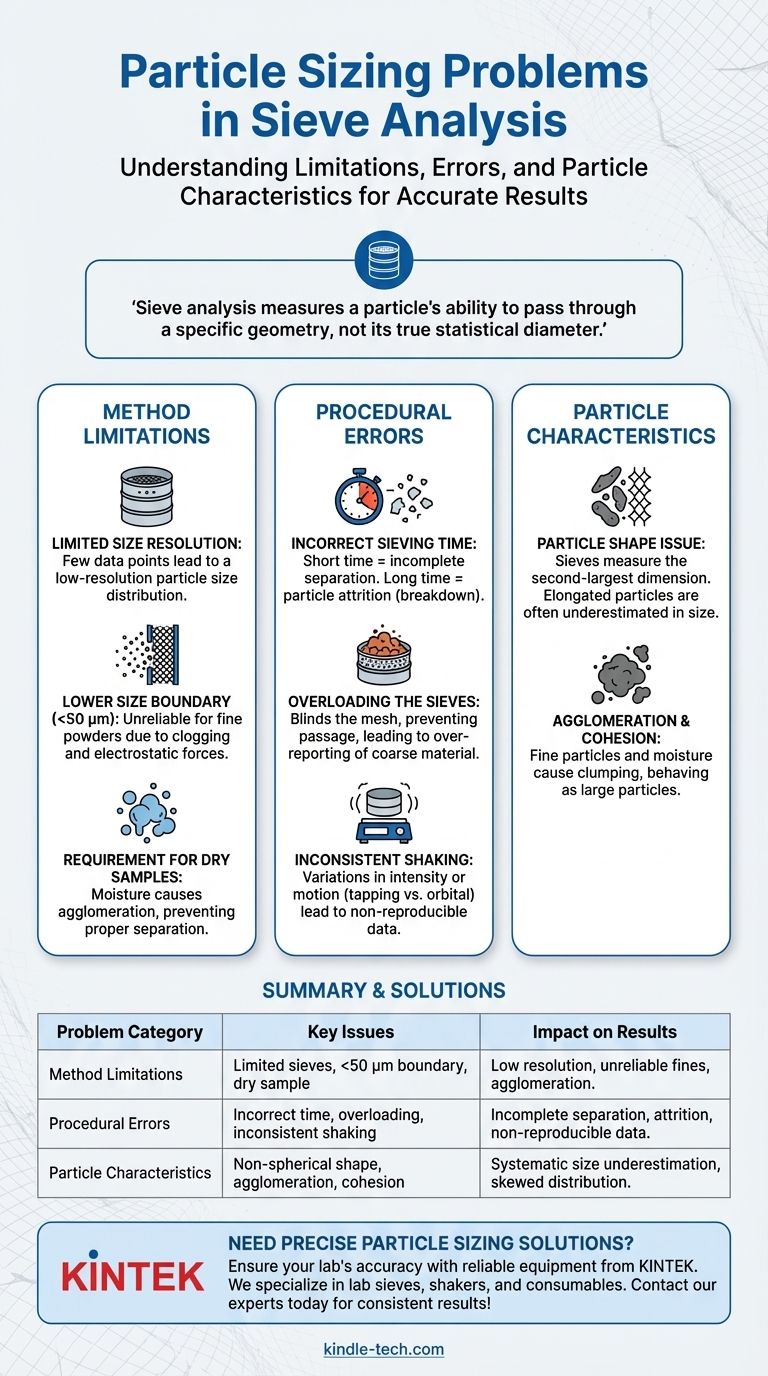
Sieve analysis is a foundational and reliable technique, but its accuracy hinges on a critical understanding: it measures a particle's ability to pass through a specific geometry, not its true statistical diameter. This distinction is the source of most potential problems.

Fundamental Limitations of the Method
Every analytical technique has inherent boundaries. For sieve analysis, these are defined by the equipment and the basic principles of separating particles by size using a mesh.
Limited Size Resolution
A standard stack of sieves typically has a maximum of eight screens. This means your final particle size distribution is based on a very small number of data points, creating a low-resolution picture of the sample.
Lower Size Boundary
The method becomes unreliable for very fine powders. Particles smaller than approximately 50 micrometers (µm) tend to clog the sieve mesh or be influenced by electrostatic forces, preventing them from passing through the apertures correctly.
Requirement for Dry Samples
Traditional sieve analysis is designed for dry, free-flowing powders. The presence of moisture can cause particles to agglomerate (stick together), preventing proper separation and skewing the results toward larger sizes.
Common Procedural Errors
Even with perfect equipment, the way you perform the analysis can introduce significant errors. Consistency is paramount.
Incorrect Sieving Time
Sieving time is a critical variable. If the time is too short, the separation will be incomplete. If it's too long, friable (brittle) particles may break down, a process called attrition, which generates more fine particles and distorts the results.
Overloading the Sieves
Placing too much sample material onto a sieve is a frequent mistake. This blinds the mesh, preventing smaller particles from having a chance to pass through and leading to an over-reporting of coarse material.
Inconsistent Shaking
The energy and motion of the shaker are vital for reproducible results. Variations in shaking intensity or motion (e.g., tapping vs. orbital) between tests will lead to data that cannot be reliably compared.
The Impact of Particle Characteristics
The nature of the particles themselves is often the most overlooked source of error. Sieving assumes ideal, spherical particles, which is rarely the case.
The Problem of Particle Shape
This is the most significant conceptual issue. A sieve measures a particle's second-largest dimension. Elongated or flat particles can pass through apertures end-on or diagonally, meaning the analysis will systematically report them as being smaller than their actual length or volume would suggest.
Agglomeration and Cohesion
Fine particles, especially in humid conditions, can clump together due to static or moisture. These agglomerates behave as a single large particle, failing to pass through the correct, smaller sieve mesh until that cohesion is broken.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Recognizing the limitations of sieve analysis allows you to use it effectively and know when to choose a different method.
Simplicity vs. Precision
Sieve analysis is valued for its simplicity, low cost, and ease of use. This accessibility comes at the cost of the high resolution and detailed shape information provided by more advanced methods like laser diffraction or image analysis.
Throughput vs. Time
While conceptually simple, performing a proper sieve analysis can be a time-consuming and labor-intensive process, especially when cleaning and weighing are considered. This can be a bottleneck in high-throughput environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use your understanding of these potential issues to ensure your results are valid and fit for purpose.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Prioritize absolute consistency in sample mass, sieving time, and shaking energy to ensure your results are reproducible day-to-day.
- If your primary focus is characterizing irregular particles: Acknowledge that sieving will underestimate the size of elongated materials and consider supplementing your analysis with microscopy to understand true particle shape.
- If your primary focus is analyzing powders below 50 µm: Recognize you are at the limit of the technique and switch to a more suitable method like laser diffraction or air jet sieving for reliable data.
By controlling for these variables, sieve analysis becomes a powerful and highly practical tool for particle characterization.
Summary Table:
| Problem Category | Key Issues | Impact on Results |
|---|---|---|
| Method Limitations | Limited sieves, lower size boundary (<50 µm), dry sample requirement | Low resolution, unreliable fines data, agglomeration errors |
| Procedural Errors | Incorrect sieving time, sieve overloading, inconsistent shaking | Incomplete separation, attrition, non-reproducible data |
| Particle Characteristics | Non-spherical shape, agglomeration, cohesion | Systematic underestimation of size, skewed distribution |
Need precise particle sizing solutions? Ensure your lab's accuracy with reliable equipment from KINTEK. We specialize in lab sieves, shakers, and consumables tailored to your sample type—whether for quality control or complex material characterization. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and get a recommendation for consistent, reproducible results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability



















