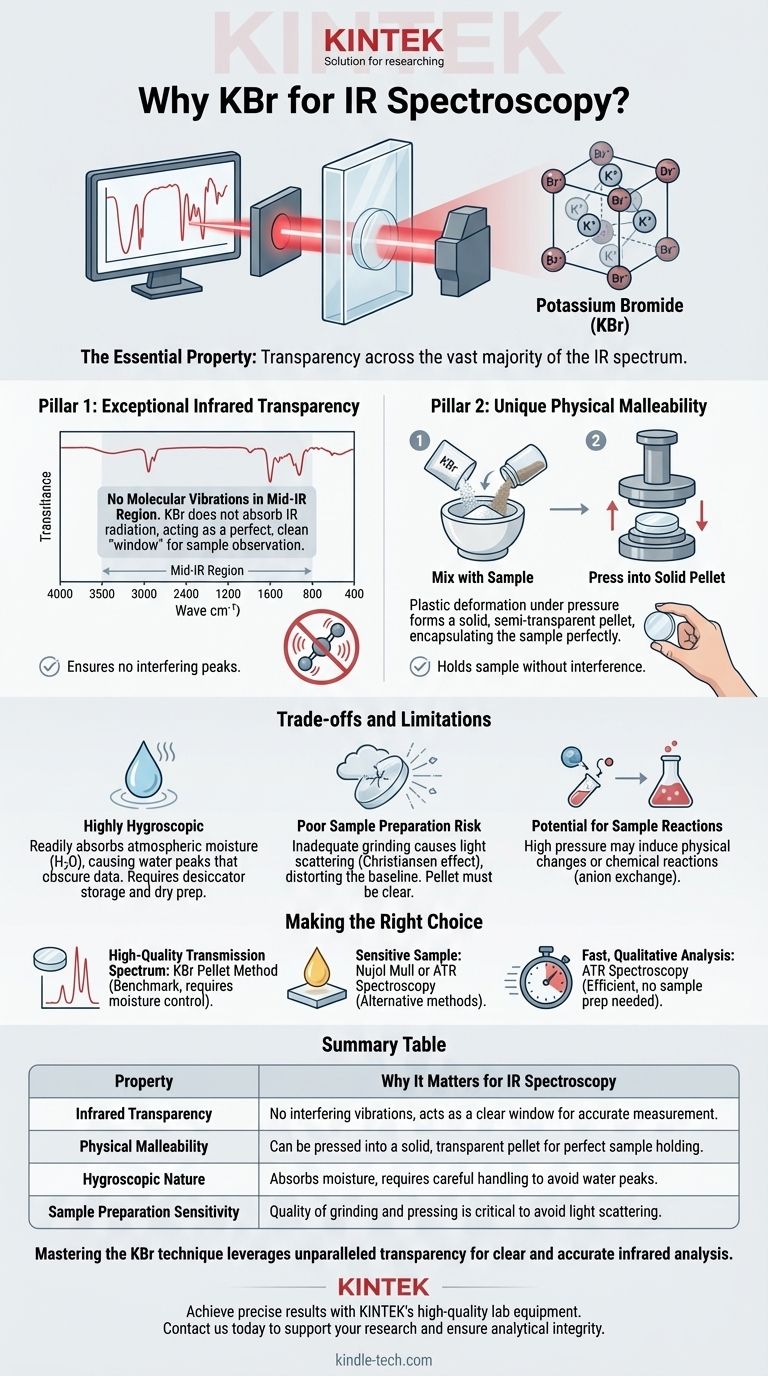
The essential property of Potassium Bromide (KBr) that makes it ideal for infrared (IR) spectroscopy is its transparency across the vast majority of the IR spectrum. This optical clarity, combined with a unique physical property that allows it to form a solid, glass-like pellet under pressure, makes it an excellent medium for holding a sample for analysis without interfering with the measurement.
KBr's value in IR spectroscopy stems from a powerful combination: it is optically invisible in the infrared region and physically malleable, allowing it to form a perfect, non-interfering solid window to hold a sample for analysis.

The Two Pillars of KBr's Suitability
To understand why KBr is a staple in analytical labs, we must look at two distinct but equally important properties: one optical and one physical.
Pillar 1: Exceptional Infrared Transparency
The core purpose of IR spectroscopy is to measure the vibrations of chemical bonds within a sample molecule. Each bond type (like C-H, O-H, C=O) absorbs infrared light at a specific frequency, creating a peak in the spectrum.
KBr is an ionic salt. Its ionic bond (K⁺-Br⁻) has a vibrational frequency that falls far outside the standard mid-infrared region (4000 cm⁻¹ to 400 cm⁻¹) used for analysis.
Because it has no molecular vibrations of its own in this region, KBr does not absorb IR radiation and does not produce any interfering peaks. It acts as a perfect, clean "window" through which the spectrometer can observe the sample's unique spectral fingerprint.
Pillar 2: Unique Physical Malleability
While optical transparency is critical, a material also needs to be a suitable physical matrix for the sample. This is where KBr's second key property comes into play.
When pure, finely ground KBr powder is subjected to immense pressure (typically several tons), it undergoes plastic deformation. The crystalline structure flows and fuses together, forming a solid, semi-transparent disc or "pellet."
This process allows an analyst to intimately mix a tiny amount of powdered sample with the KBr powder. When pressed, the KBr forms a solid pellet that encapsulates the sample particles in a perfectly distributed, IR-transparent medium, ready for analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While KBr is the gold standard for many applications, it is not without its challenges. Acknowledging these limitations is key to generating reliable data.
KBr is Highly Hygroscopic
The most significant drawback of KBr is its hygroscopic nature—it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. Water (H₂O) has very strong and broad absorption bands in the IR spectrum, particularly around 3400 cm⁻¹ (O-H stretching) and 1640 cm⁻¹ (H-O-H bending).
If the KBr or the resulting pellet is exposed to humid air, these water peaks will appear in the spectrum, potentially obscuring important sample peaks and compromising the analysis. This is why KBr must be kept in a desiccator and pellets are often prepared under vacuum or in a dry environment.
The Risk of Poor Sample Preparation
The quality of the final spectrum is highly dependent on the quality of the pellet. If the sample and KBr are not ground into extremely fine particles, light scattering can occur as the IR beam passes through the pellet.
This scattering, known as the Christiansen effect, can distort the baseline of the spectrum and make accurate interpretation difficult. A well-prepared pellet should appear clear or uniformly translucent, not cloudy.
Potential for Sample Reactions
The high pressures used to form the pellet can occasionally induce physical changes (polymorphism) or chemical reactions in the sample. Furthermore, as an alkali halide, KBr can sometimes react with certain types of samples, an effect known as anion exchange, which alters the sample's true spectral signature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Understanding KBr allows you to use it effectively and decide when an alternative method might be more appropriate.
- If your primary focus is a high-quality transmission spectrum of a solid sample: The KBr pellet method remains the benchmark for producing sharp, well-resolved data, provided you take care to avoid moisture.
- If your sample is sensitive to pressure or moisture: Consider an alternative like a Nujol mull (suspending the sample in mineral oil) or Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) spectroscopy.
- If you need a fast, qualitative analysis with minimal sample prep: ATR is often a more efficient choice, as it analyzes the surface of a sample directly without the need for grinding or pressing.
Ultimately, mastering the KBr technique is about controlling these variables to leverage its unparalleled transparency for clear and accurate infrared analysis.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for IR Spectroscopy |
|---|---|
| Infrared Transparency | KBr has no interfering vibrations in the mid-IR region, acting as a clear window for accurate sample measurement. |
| Physical Malleability | Can be pressed into a solid, transparent pellet that holds the sample perfectly for analysis. |
| Hygroscopic Nature | Absorbs moisture easily, which can introduce water peaks; requires careful handling and dry storage. |
| Sample Preparation Sensitivity | Quality of grinding and pressing is critical to avoid light scattering and ensure a clear spectrum. |
Achieve precise and reliable infrared analysis with the right equipment.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for spectroscopy. Our products are designed to help you master sample preparation techniques, like creating perfect KBr pellets, to generate clear, interpretable data.
Let our experts help you select the ideal tools for your laboratory's needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your research and ensure the integrity of your analytical results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- kbr pellet press 2t
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
- XRF & KBR plastic ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why do we use KBr in IR spectroscopy? Achieve Clear, High-Quality Solid Sample Analysis
- Why KBr is used for IR spectroscopy? The Ideal Medium for Solid Sample Analysis
- What are the safety precautions for KBr? Achieve Flawless FTIR Pellet Preparation and Data Accuracy
- What is a KBr pellet? A Guide to Preparing Solid Samples for IR Spectroscopy
- What is KBr disc method in IR spectroscopy? A Guide to Solid Sample Analysis



















