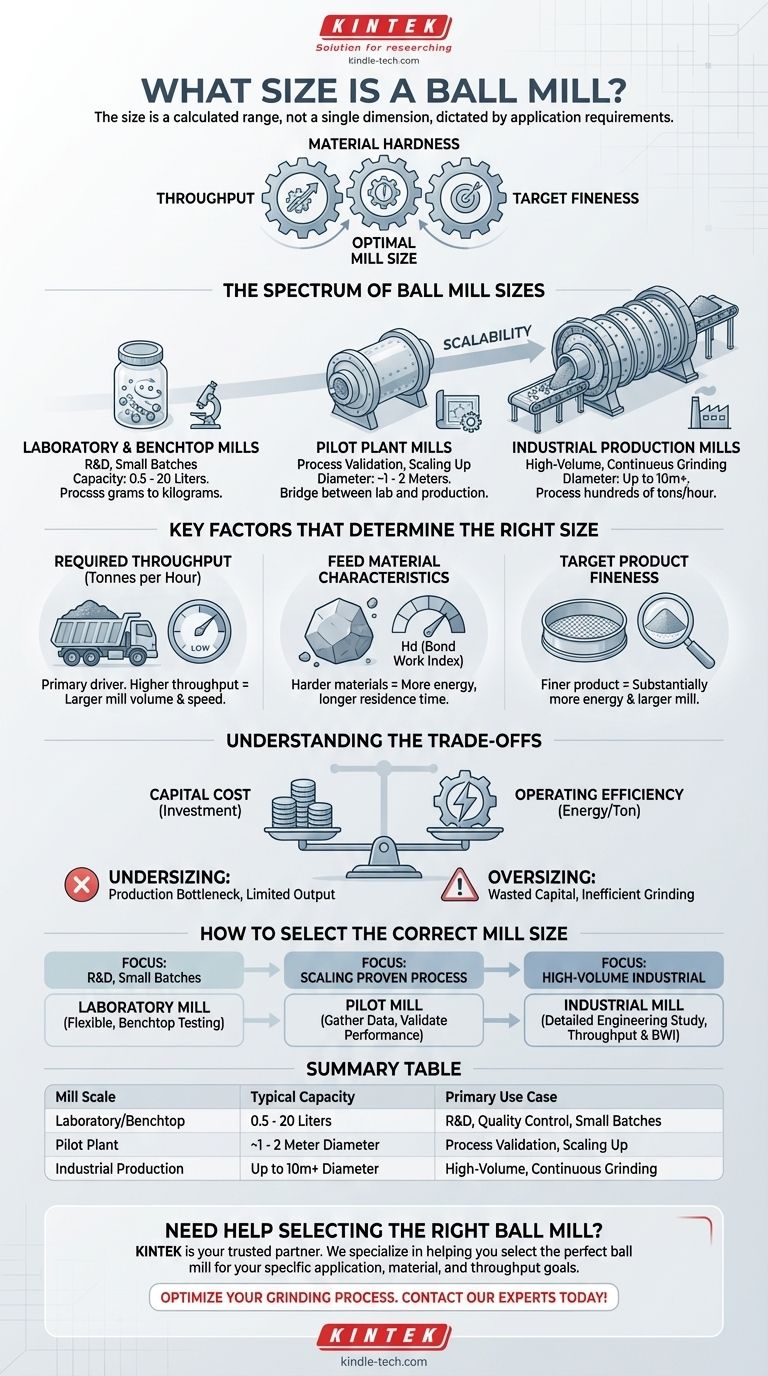
The size of a ball mill is not a single dimension but spans an enormous range, from small laboratory jars that hold a few kilograms to massive industrial grinding mills over 10 meters in diameter. The specific size is dictated entirely by the application's requirements, such as the volume of material to be processed and the desired final particle size.
The most critical insight is that "size" is not just about physical dimensions. It's a calculated parameter based on your required throughput, the hardness of your material, and your target product fineness. Choosing the right size is a direct function of your operational goals.

The Spectrum of Ball Mill Sizes
Ball mills are fundamentally scalable, which is why they are used in applications ranging from small-scale sample preparation to large-scale mining operations. They are generally categorized into three main scales.
Laboratory and Benchtop Mills
These are the smallest units, often designed to sit on a workbench. Their primary purpose is for research and development, quality control, or preparing small test batches of material.
Their capacity is measured in liters, typically ranging from 0.5 to 20 liters. They are designed for processing grams or a few kilograms of material at a time.
Pilot Plant Mills
These mills serve as a bridge between the laboratory and full-scale production. They are used to validate a process, test material behavior at a larger scale, and produce samples for customers before investing in a full-size plant.
Pilot mills are often small-scale versions of industrial designs, with diameters that might range from 1 to 2 meters.
Industrial Production Mills
These are the largest and most common types used in mining, cement production, and other heavy industries. Their goal is continuous, high-volume grinding.
The dimensions of these mills are substantial, with diameters reaching up to 10 meters and lengths exceeding 15 meters. Their power consumption is measured in megawatts, and they are capable of processing hundreds or even thousands of tons of material per hour.
Key Factors That Determine the Right Size
Selecting a ball mill is a technical exercise where the "size" is the output of a calculation based on several critical inputs.
Required Throughput (Tonnes per Hour)
This is often the primary driver for sizing. The internal volume of the mill, combined with its rotational speed and media charge, determines the maximum amount of material it can process in a given period. A higher required throughput directly translates to a larger mill.
Feed Material Characteristics
The hardness and abrasiveness of the material being ground are quantified by metrics like the Bond Work Index (BWI). Harder materials require more energy and a longer residence time inside the mill to be broken down, necessitating a more powerful motor and often a larger mill for a given throughput.
Target Product Fineness
The desired final particle size significantly impacts mill sizing. Grinding material to a very fine powder (e.g., 45 microns) requires substantially more energy and time than producing a coarser product. To achieve a finer grind without sacrificing throughput, a larger and more powerful mill is required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a mill size involves balancing cost, efficiency, and operational flexibility. Making the wrong choice has significant consequences.
Capital Cost vs. Operating Efficiency
Larger mills represent a massive capital investment. However, they can offer better economies of scale, often resulting in a lower energy cost per ton of processed material compared to using multiple smaller mills.
The Danger of Undersizing
An undersized mill is a critical production bottleneck. It will be unable to meet the required throughput or achieve the target product fineness, directly limiting the output of the entire operation.
The Problem with Oversizing
An oversized mill represents wasted capital. Furthermore, running a large mill significantly below its designed capacity can lead to inefficient grinding and higher-than-necessary energy consumption, eroding profitability.
How to Select the Correct Mill Size
The right choice is always the one that is precisely engineered for your specific operational context and material properties.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Select a flexible, benchtop-scale laboratory mill that allows for easy testing of small batches and different grinding media.
- If your primary focus is scaling a proven process: Use a pilot-scale mill to gather data and validate performance before committing to a major capital investment.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production: Your decision must be driven by a detailed engineering study that calculates the required mill size based on throughput targets and the Bond Work Index of your specific material.
Ultimately, selecting the correct ball mill size is a crucial engineering decision that aligns the machine's capabilities with your specific processing mission.
Summary Table:
| Mill Scale | Typical Capacity | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Laboratory/Benchtop | 0.5 - 20 Liters | R&D, Quality Control, Small Batches |
| Pilot Plant | ~1 - 2 Meter Diameter | Process Validation, Scaling Up |
| Industrial Production | Up to 10m+ Diameter | High-Volume, Continuous Grinding |
Need Help Selecting the Right Ball Mill?
Choosing the correct mill size is critical for your lab's efficiency and productivity. An undersized mill becomes a bottleneck, while an oversized one wastes capital and energy.
KINTEK is your trusted partner for all laboratory equipment needs. We specialize in helping you select the perfect ball mill for your specific application, material properties, and throughput goals. Our experts will guide you from benchtop testing to full-scale production, ensuring you get the right equipment for your mission.
Let's optimize your grinding process together. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement
- What is the ball mill based on the principle of? Impact and Attrition for Efficient Grinding
- How do stainless steel grinding jars and balls contribute to mechanical alloying? Optimize HEA Powder Synthesis
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results
- What is the benefit of using tungsten carbide (WC) milling jars and balls? Achieve High-Energy Milling Efficiency



















