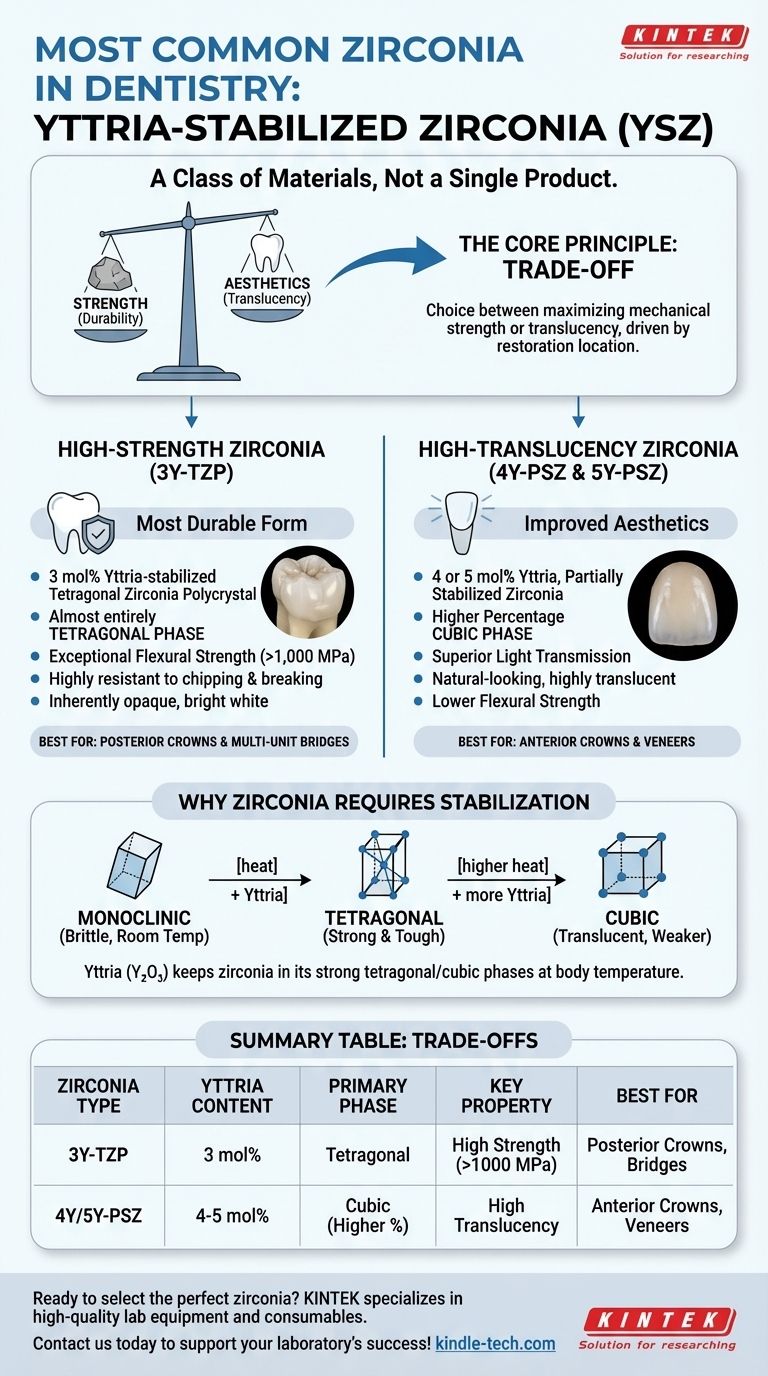
The most common type of zirconia used in dentistry is not a single material but a class of materials known as Yttria-stabilized Zirconia (YSZ). This material is broadly categorized into two main forms based on its composition and resulting properties: high-strength opaque zirconia, prized for its durability, and high-translucency aesthetic zirconia, valued for its natural appearance. The specific clinical need dictates which version is the appropriate choice.
The core principle to understand is that all dental zirconia involves a trade-off. The choice is always between maximizing mechanical strength for durability or maximizing translucency for aesthetics, a decision driven by the location of the restoration in the mouth.

Why Zirconia Requires Stabilization
To understand the different types of zirconia, we must first understand its basic material science. Zirconia is an allotropic material, meaning it can exist in different crystal structures at different temperatures.
The Unstable Nature of Pure Zirconia
At room temperature, pure zirconia has a monoclinic crystal structure, which is not suitable for dental applications due to its brittleness. When heated, it transforms into a much stronger and tougher tetragonal phase, and at even higher temperatures, a cubic phase.
The Role of Yttria (Y₂O₃)
The goal is to keep zirconia in its strong tetragonal phase even after it cools to body temperature. This is achieved by adding a stabilizing oxide, most commonly yttrium oxide (yttria). This process creates Yttria-stabilized Zirconia (YSZ), the foundational material for all modern dental zirconia restorations.
The Two Primary Classes of Dental Zirconia
The amount of yttria added directly controls the final properties of the zirconia. This has led to two distinct classes used for different clinical purposes.
High-Strength Zirconia (3Y-TZP)
This is the original and most durable form of dental zirconia, often referred to as 3Y-TZP (3 mol% Yttria-stabilized Tetragonal Zirconia Polycrystal). It contains the lowest amount of yttria needed for stabilization.
Its structure is almost entirely the tough tetragonal phase. This gives it exceptional flexural strength (often over 1,000 MPa) and fracture toughness, making it incredibly resistant to chipping and breaking under heavy chewing forces.
High-Translucency Zirconia (4Y-PSZ & 5Y-PSZ)
To improve aesthetics, manufacturers developed zirconia with higher concentrations of yttria, typically 4Y (4 mol%) or 5Y (5 mol%). This material is often called Partially Stabilized Zirconia (PSZ).
Increasing the yttria introduces a higher percentage of the cubic phase into the crystal structure. The cubic phase is weaker than the tetragonal phase, but its symmetrical structure allows more light to pass through, creating a highly translucent, natural-looking material ideal for visible front teeth.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength vs. Esthetics
The choice between zirconia types is a clinical judgment based on a fundamental compromise between mechanical performance and visual appearance.
Yttria Content Dictates Everything
The central rule is simple: as yttria content increases, translucency increases, but flexural strength and fracture toughness decrease. A 5Y zirconia can look remarkably like a natural tooth but may only have half the flexural strength of a 3Y zirconia.
Opaque vs. Natural Appearance
High-strength (3Y) zirconia is inherently opaque and bright white. While it can be colored, it lacks the depth and vitality of a natural tooth, making it a less ideal choice for the anterior (front) of the mouth. High-translucency (5Y) zirconia, in contrast, allows light to interact with it similarly to natural enamel, providing a superior aesthetic outcome.
Matching Material to Clinical Need
This trade-off directly translates to clinical use. The immense chewing forces on posterior teeth (molars) demand the uncompromising strength of 3Y zirconia. Conversely, the high aesthetic demands for anterior teeth (incisors) favor the natural look of 5Y zirconia, where biting forces are much lower.
Making the Right Choice for Your Restoration
Selecting the correct zirconia is about aligning the material's properties with the clinical demands of the specific restoration.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability: For posterior crowns and multi-unit bridges, choose a high-strength 3Y-TZP zirconia for its superior fracture resistance.
- If your primary focus is optimal aesthetics: For anterior crowns and veneers, choose a high-translucency 4Y-PSZ or 5Y-PSZ zirconia to achieve the most natural-looking result.
- If your primary focus is a balanced solution: Consider newer multi-layered zirconia discs, which combine high-strength material in the core with a more aesthetic, translucent layer on the surface.
Understanding the direct relationship between yttria content, crystal structure, and clinical performance is the key to leveraging zirconia effectively in modern dentistry.
Summary Table:
| Zirconia Type | Yttria Content | Primary Phase | Key Property | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Y-TZP | 3 mol% | Tetragonal | High Strength (>1000 MPa) | Posterior Crowns, Bridges |
| 4Y/5Y-PSZ | 4-5 mol% | Cubic (Higher %) | High Translucency | Anterior Crowns, Veneers |
Ready to select the perfect zirconia for your dental lab's needs? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for dental laboratories. Whether you require materials for high-strength posterior restorations or aesthetic anterior solutions, our expertise ensures you get the right tools for superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Aluminum Nitride (AlN) Ceramic Sheet
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of dental furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Dental Lab
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- How long does it take to make zirconia teeth? From Same-Day to 2 Weeks
- How is zirconia sintered? A Guide to the High-Temperature Transformation Process
- How hot does a dental sintering furnace get? Unlock the Key to Perfect Restorations
- What is the furnace in which ceramics are fired? A Guide to Choosing the Right Kiln for Your Project
- What does sintering do to zirconia? Unlock Its Full Strength and Aesthetic Potential
- What is the sintering time for zirconia crowns? Master the Trade-Off Between Speed and Strength















