The "best" lens coating isn't a single product; it is a combination of treatments customized for your specific visual needs and lifestyle. For nearly everyone, a high-quality anti-reflective (AR) coating serves as the essential foundation. This single treatment provides the most significant and immediate improvement to your visual clarity, comfort, and the appearance of your eyeglasses.
The most effective strategy is to begin with a foundational anti-reflective (AR) package and then layer on specialized treatments like blue light filtering or photochromic tints only if they solve a specific, daily problem you face—such as prolonged screen time or moving between indoors and outdoors.

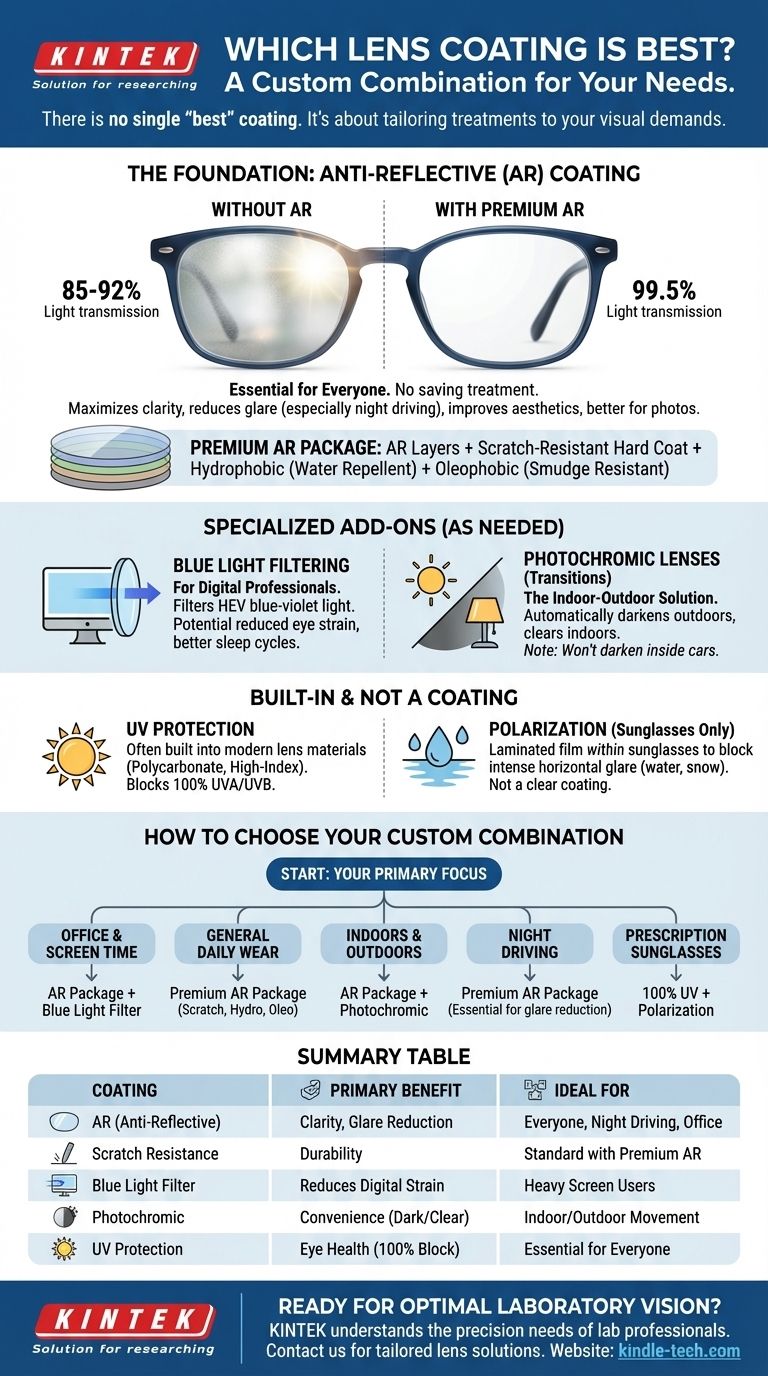
The Foundation: Anti-Reflective (AR) Coating
An anti-reflective (or anti-glare) coating is the single most important upgrade you can choose for your lenses. It is a microscopically thin, multi-layer treatment that eliminates reflections from both the front and back surfaces of the lens.
What AR Coatings Actually Do
Without an AR coating, about 8-15% of light reflects off the surface of a standard plastic lens, never reaching your eye. This creates glare and reduces visual contrast.
AR coatings work by allowing up to 99.5% of available light to pass through the lens and enter your eye. This dramatic increase in light transmission results in clearer, sharper, and more defined vision.
The Practical Benefits: Clarity and Aesthetics
The primary benefit of AR is the reduction of distracting glare. This is especially noticeable when driving at night (reducing halos from headlights) and working under fluorescent lighting.
By eliminating reflections on the front of your lenses, AR coatings also make your glasses more cosmetically appealing. People can see your eyes clearly, making for more natural face-to-face interaction and better appearance in photos.
Why Not All AR is Created Equal
Premium AR coatings are not just a single layer but a complex stack that often includes other valuable properties. These packages typically bundle the anti-reflective layers with a scratch-resistant hard coat, a hydrophobic coat to repel water, and an oleophobic coat to resist oil and smudges, making the lenses much easier to clean.
Specialized Coatings for Specific Needs
Once you have a solid AR foundation, you can consider adding other treatments that solve specific lifestyle challenges.
Scratch Resistance: Protecting Your Investment
Modern lenses are made of plastics that can scratch easily. A scratch-resistant coating is a transparent hard coat applied to the lens surface that makes it more durable for daily handling.
Today, this is less of an optional add-on and more of a standard feature, especially when you purchase an AR coating package.
Blue Light Filtering: For the Digital Professional
These coatings are designed to filter a specific portion of the high-energy visible (HEV) blue-violet light spectrum emitted by digital screens and the sun.
The goal is to potentially reduce digital eye strain and regulate sleep cycles by limiting blue light exposure, particularly in the evening. While the direct medical benefits for eye strain are still debated, many users report increased visual comfort during long hours of computer use.
UV Protection: A Non-Negotiable for Eye Health
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a known contributor to the development of cataracts and other eye diseases. A UV-protective treatment blocks 100% of harmful UVA and UVB rays.
It's important to note that many modern lens materials, such as polycarbonate and high-index plastics, have this UV protection built directly into the lens material itself, making an additional coating redundant. Always confirm this with your optician.
Photochromic Lenses: The Indoor-Outdoor Solution
Commonly known by the brand name Transitions, photochromic lenses automatically darken when exposed to UV light and lighten when indoors.
This offers the convenience of having one pair of glasses that acts as both clear spectacles and sunglasses, ideal for people who are constantly moving between indoor and outdoor environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Choosing coatings involves balancing performance, cost, and practicality. There is no single "perfect" solution.
The Cost vs. Benefit Equation
Premium coatings cost more, but they offer superior performance and durability. A cheap AR coating may be prone to crazing (a web of fine cracks) or peeling within a year, while a high-end one can last the life of your prescription with proper care.
The Myth of the "Do-It-All" Lens
Every specialized coating has limitations. For example, photochromic lenses do not darken inside a car because the windshield blocks the UV rays required to activate the tinting process. For driving in sunny conditions, dedicated sunglasses are superior.
A Note on Polarization
It is crucial to understand that polarization is not a coating for clear, everyday glasses. It is a specialized film laminated within a sunglass lens. Its sole purpose is to block the intense, horizontally-reflected glare from surfaces like water, wet roads, or snow. It is an essential feature for sunglasses but is not applicable to your primary indoor pair.
How to Choose the Right Coatings for Your Glasses
Base your decision on your most common daily activities.
- If your primary focus is office work and screen time: Start with a premium AR coating and strongly consider adding a blue light filter for enhanced visual comfort.
- If your primary focus is general daily wear: A high-quality AR package that includes scratch resistance, hydrophobic, and oleophobic properties is your most effective and practical choice.
- If you frequently move between indoors and outdoors: An AR coating combined with photochromic lenses offers the most convenience and seamless protection.
- If your primary concern is driving, especially at night: A premium AR coating is essential to dramatically reduce distracting and dangerous glare from headlights and streetlights.
- If you are buying prescription sunglasses: Prioritize 100% UV protection and polarization to cut blinding glare and protect your long-term eye health.
By understanding what each coating actually does, you can confidently build a pair of glasses that perfectly serves your vision and your life.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Primary Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Reflective (AR) | Maximizes clarity, reduces glare, improves aesthetics | Everyone; essential for night driving and office work |
| Scratch Resistance | Increases lens durability and longevity | Standard with most premium AR packages |
| Blue Light Filtering | May reduce digital eye strain from screens | Heavy computer and digital device users |
| Photochromic | Lenses darken in sunlight, clear indoors | People frequently moving between indoors and outdoors |
| UV Protection | Blocks 100% of harmful UVA/UVB rays | Often built into lens material; essential for everyone |
Ready to build the perfect pair of glasses for your needs?
The right combination of lens coatings is key to achieving optimal visual clarity, comfort, and protection. At KINTEK, we understand the precise requirements of laboratory professionals, where clear, strain-free vision is critical for accuracy and safety when working with sensitive equipment and consumables.
Let our experts help you select the ideal lens solutions tailored to your specific lab environment and visual demands. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's needs with precision and care.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- What is thin film coating? Transforming Surfaces with Precision Engineering
- What are the applications of semiconductor thin films? Powering the Core of Modern Electronics
- How does thermal vapour deposition work? Master Precise Thin Film Coating with Simple Thermal Energy
- How do optical coatings work? Manipulate Light with Precision Thin Films
- What are the target materials for sputtering? From Metals to Ceramics for Precise Thin Films
- What are some key film characteristics to consider? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition for Peak Performance
- What are the applications of optical coating? Unlock Advanced Light Control for Your Industry
- Which of the following are properties of carbon nanotubes? Unlock Their Unique Electrical, Thermal & Mechanical Strengths














