Introduction to Handheld XRF Analyzers
Handheld XRF analyzers have revolutionized the field of elemental analysis, offering a portable and efficient solution across various industries. This comprehensive guide delves into the significance of these devices, their underlying technology, and the myriad ways they enhance accuracy and efficiency. We'll explore the basic principles of X-ray fluorescence (XRF) technology, highlighting its advantages over conventional methods. Whether you're involved in metals inspection, environmental assessments, or precious metals analysis, understanding how handheld XRF analyzers work and how to select the right one for your needs is crucial for maximizing productivity and sustainability. Join us as we uncover the versatile applications and best practices of handheld XRF analyzers, paving the way for smarter, more informed decisions in your field.
How Handheld XRF Analyzers Work
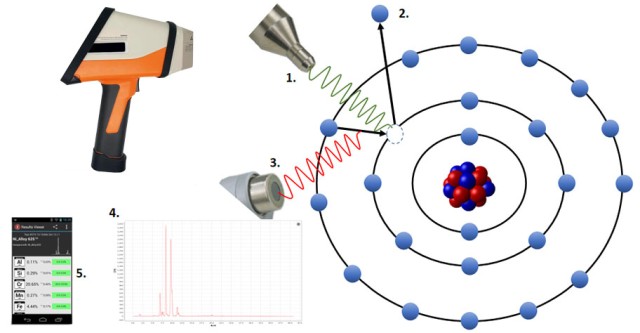
Handheld XRF (X-Ray Fluorescence) analyzers are sophisticated devices used for the rapid and non-destructive analysis of elemental composition in various materials. The technology operates on the principle of XRF, which involves the emission, excitation, and measurement of X-rays to determine the presence and concentration of elements within a sample.
The XRF Process
Emission
The process begins with the handheld XRF analyzer emitting a beam of X-rays towards the sample. This emission is controlled and calibrated to ensure accurate and reliable results. The X-rays are generated by a small, high-performance micro X-ray tube within the analyzer, which is designed to produce a consistent and focused beam.
Excitation
Upon reaching the sample, the emitted X-rays interact with the atoms of the material. These X-rays have sufficient energy to dislodge electrons from the inner shells of the atoms, creating vacancies. This process is known as excitation. When electrons from higher energy levels drop down to fill these vacancies, they release energy in the form of secondary X-rays, which are characteristic of the specific elements present in the sample.
Measurement
The secondary X-rays, or fluorescent X-rays, are then detected by the analyzer's detector, typically a Silicon Drift Detector (SDD). The SDD is capable of measuring the energy and intensity of these X-rays with high precision. Each element emits X-rays at specific energy levels, allowing the analyzer to identify and quantify the elements present in the sample. The data is processed using advanced algorithms to provide a detailed analysis of the elemental composition.
Capabilities and Limitations
Handheld XRF analyzers are versatile tools with a wide range of applications, including material verification, scrap recycling, mining, environmental assessments, and precious metals analysis. They offer several advantages, such as:
- Speed and Efficiency: Results are obtained in seconds, enabling rapid on-site analysis without the need for sample preparation.
- Non-Destructive Testing: The sample remains intact, making it ideal for valuable or irreplaceable materials.
- Wide Elemental Range: Handheld XRF analyzers can detect elements from phosphorus (P) to plutonium (Pu) on the periodic table, covering a broad spectrum of applications.
However, there are limitations to consider:
- Detection Limits: The sensitivity of handheld XRF analyzers is not as high as laboratory-based XRF systems, which can affect the detection of trace elements.
- Elemental Interference: Spectral overlap can lead to false positives or negatives, particularly with elements that have similar energy signatures.
- Radiation Safety: While handheld XRF analyzers are designed to be safe, users must follow proper radiation safety procedures to prevent exposure.
Practical Applications
In the mining industry, handheld XRF analyzers are invaluable for exploration and grade control. They help geologists identify valuable minerals and elements in real-time, guiding drilling and extraction efforts. In environmental assessments, these analyzers are used to detect contaminants in soil, water, and air, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Conclusion
Handheld XRF analyzers represent a significant advancement in portable analytical technology. By understanding the principles of emission, excitation, and measurement, users can harness the full potential of these devices for a variety of applications. While there are limitations to consider, the benefits of rapid, non-destructive analysis make handheld XRF analyzers an essential tool in many industries.
Applications of Handheld XRF Analyzers
Handheld XRF analyzers have revolutionized the way various industries conduct elemental analysis, offering a portable, efficient, and accurate solution for on-site testing. These devices utilize X-ray fluorescence (XRF) technology to determine the elemental composition of materials without damaging the sample, making them indispensable in numerous applications ranging from metals inspection to environmental assessments.
Metals Inspection and Scrap Recycling
In the realm of metals inspection, handheld XRF analyzers are pivotal for ensuring the quality and composition of metal alloys. Industries such as aerospace, military, steel, petrochemical, and pharmaceuticals rely heavily on these devices to verify the elemental makeup of their materials. For instance, during the production of aircraft components, handheld XRF analyzers can quickly identify the alloy grades, ensuring that the correct materials are used to meet stringent safety standards.
Scrap recycling is another significant application area for handheld XRF analyzers. These devices help in the rapid identification and sorting of scrap metals, which is crucial for maximizing the efficiency and profitability of recycling operations. By accurately determining the composition of scrap materials on-site, recyclers can avoid contamination and ensure that the recycled metals meet the required specifications for reuse in various industries.
Mining and Mineral Exploration
The mining industry extensively utilizes handheld XRF analyzers for mineral exploration and ore grade control. These devices enable geologists to perform real-time analysis of rock and soil samples, providing immediate insights into the elemental composition and potential mineral content. This capability is particularly valuable in the early stages of exploration, where rapid assessment of large areas can significantly reduce the time and cost associated with traditional laboratory-based analysis.
In addition, handheld XRF analyzers play a crucial role in optimizing extraction processes and determining ore grades. By providing on-site assay results, these devices help mining companies make informed decisions about the most promising drill locations and extraction methods. This not only enhances productivity but also promotes sustainability by minimizing waste and resource wastage.
Environmental Assessments
Handheld XRF analyzers are instrumental in conducting environmental assessments, particularly in detecting harmful substances in building materials and soil. These devices can identify heavy metal elements such as lead and mercury, which, if present in excess, can pose significant health risks. By enabling timely detection and remediation of contaminated sites, handheld XRF analyzers contribute to safeguarding public health and the environment.
Moreover, these devices are used in environmental monitoring programs to assess the impact of industrial activities on soil and water quality. The ability to perform on-site analysis allows for rapid response to potential contamination events, ensuring that mitigation measures can be implemented promptly to prevent long-term environmental damage.

Precious Metals Analysis
The analysis of precious metals, such as gold, silver, and platinum, is another critical application of handheld XRF analyzers. These devices are widely used in the jewelry industry to verify the purity and authenticity of precious metal alloys. By providing instant results, handheld XRF analyzers help jewelers and assayers to maintain the highest standards of quality and integrity in their products.
In addition, these devices are essential tools for the mining and refining of precious metals. They enable miners to quickly assess the concentration of precious metals in ore samples, guiding extraction processes and ensuring that resources are utilized efficiently. This not only enhances profitability but also promotes responsible mining practices by minimizing waste and environmental impact.
Archaeology and Cultural Relics Protection
Handheld XRF analyzers have found a unique niche in the field of archaeology and cultural relics protection. During archaeological excavations, these devices can quickly obtain elemental composition information from the surface of cultural relics, providing valuable insights into the materials and production techniques used by ancient civilizations. This information is crucial for understanding the historical context and significance of archaeological finds.
Furthermore, handheld XRF analyzers are used in the restoration and preservation of cultural relics. By analyzing the elemental composition and changes in materials, restorers can develop scientifically sound restoration plans and protection measures. This helps to preserve the integrity and historical value of cultural relics, ensuring that they can be appreciated by future generations.
Food Safety Testing
Food safety is a paramount concern, and handheld XRF analyzers play a vital role in ensuring the quality and safety of food products. These devices can rapidly detect the presence of heavy metal elements such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, which, if超标, can pose serious health risks. By enabling timely detection and remediation of contaminated food, handheld XRF analyzers contribute to safeguarding public health.
In addition, these devices are used to detect illegal additives in food production. Handheld XRF analyzers can identify the presence of harmful substances that may be added to food to enhance taste or appearance. By ensuring the safety and integrity of food products, these devices protect consumer rights and promote public confidence in the food supply chain.
Other Fields
Beyond the major application areas mentioned above, handheld XRF analyzers have a wide range of uses in various other fields. For example, in geological exploration, these devices are used to analyze the elemental composition of rocks and soil, providing valuable data for mapping and resource assessment. In the field of jewelry identification, handheld XRF analyzers help in determining the authenticity and value of gemstones by analyzing their elemental composition.

Furthermore, these devices are used in artwork identification, electronic product testing, and many other applications where rapid, non-destructive elemental analysis is required. The versatility and portability of handheld XRF analyzers make them an invaluable tool for professionals in diverse industries, enabling them to make informed decisions and ensure the quality and safety of their products and operations.
In conclusion, handheld XRF analyzers have become indispensable in numerous applications due to their ability to provide rapid, accurate, and non-destructive elemental analysis. From metals inspection and mining to environmental assessments and food safety testing, these devices offer a powerful solution for on-site testing, enhancing productivity, and ensuring the quality and safety of various products and operations.
Best Practices for Using Handheld XRF Analyzers
Handheld X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analyzers are versatile tools used across various industries for rapid and non-destructive elemental analysis. To ensure accurate and reliable results, it is crucial to adhere to best practices in training, calibration, and maintenance. This section delves into these practices, highlighting common mistakes and providing solutions to enhance the performance and longevity of handheld XRF analyzers.
Proper Training and Operator Competency
The accuracy of handheld XRF analyzers heavily relies on the operator's skill and understanding. Proper training is essential to avoid common pitfalls such as improper sample preparation, calibration errors, and inadequate measurement techniques. Operators should be trained to:
- Understand the Instrument: Gain a comprehensive understanding of the XRF analyzer's capabilities and limitations. This includes knowing the types of samples it can analyze and the elements it can detect.
- Prepare Samples Correctly: Clean samples thoroughly to remove any contaminants that could affect the analysis. For instance, solid samples like metals should be filed to ensure a clean surface, while bulk samples like soil should be crushed and placed in cuvettes.
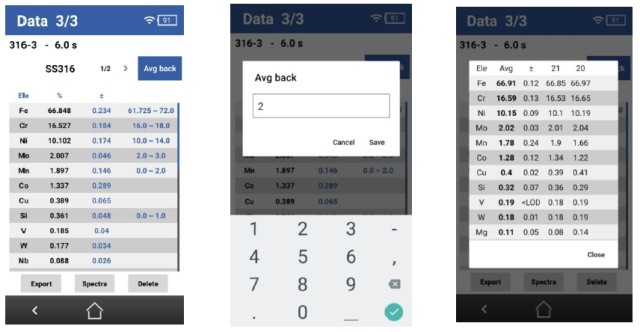
- Calibrate the Instrument: Ensure the XRF analyzer is calibrated for the specific task at hand. Using an incorrect calibration can lead to inaccurate results. Regular recalibration by the manufacturer is recommended to maintain accuracy.
Calibration and Maintenance
Calibration is a critical aspect of using handheld XRF analyzers. It involves setting the instrument to ensure it measures accurately against known standards. Here are some key points to consider:
- Use Appropriate Calibration Standards: Choose between thin film or monolithic standards based on the application. Thin films offer flexibility, while monolithic standards provide robustness and are closer to actual samples.
- Annual Certification: Similar to annual vehicle inspections, XRF instruments should be calibrated annually by the manufacturer. This ensures all components, including the X-ray tube and detector, are functioning correctly.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Operators often encounter several common mistakes that can compromise the accuracy of XRF analysis. Here are some of these mistakes and how to avoid them:
- Improper Sample Preparation: Ensure samples are cleaned and prepared according to the instrument's guidelines. Use appropriate tools like different files for different types of samples to avoid cross-contamination.
- Incorrect Calibration: Always use the correct calibration for the specific analysis. If new tasks arise, send the instrument back to the supplier for recalibration.
- Failure to Replace Protective Cartridges: Replace the protective cartridges regularly to prevent contamination from affecting results. This is especially important when analyzing different types of samples.
- Insufficient Measurement Time: Set adequate measurement time to ensure accurate results. Shorter measurement times can lead to large errors and missed detections of minor elements.
- Neglecting Radiation Safety: Always follow radiation safety protocols. Do not hold samples in hands or point the beam at others. Regular exposure to X-rays, even at low intensities, can be harmful.
Advanced Considerations
For more advanced users, there are additional factors to consider to ensure optimal performance:
- Focus the Sample: Proper focusing keeps a fixed distance between the X-ray tube, sample, and detector, ensuring accurate measurements.
- Place the Sample Correctly: Ensure the sample is placed in the correct direction to avoid errors in multi-layer coating analyses.
Establishing Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
To maintain consistency and accuracy, establish standard operating procedures (SOPs) for using the handheld XRF analyzer. This includes:
- Matrix Matching: Use site-specific certified reference materials (CRMs) for matrix matching.
- Quality Control/Quality Assurance (QC/QA): Perform regular QC/QA checks using blanks, duplicates, and replicates to ensure the accuracy of the results.
Conclusion
Handheld XRF analyzers are powerful tools for elemental analysis, but their effectiveness depends on proper use and maintenance. By adhering to best practices in training, calibration, and maintenance, operators can ensure accurate and reliable results, enhancing the value and utility of handheld XRF analyzers in various applications.
Advanced Features and Software
Modern handheld XRF (X-ray Fluorescence) analyzers are equipped with advanced features and intelligent software solutions that significantly enhance their functionality and ease of use. These innovations not only improve the efficiency of analyses but also extend the capabilities of these devices beyond traditional boundaries.
User-Friendly Interfaces
One of the standout features of contemporary handheld XRF analyzers is their user-friendly interfaces. These interfaces are designed to be intuitive, allowing even minimally trained users to navigate through the menu options and perform complex analyses with ease. The simplicity of use reduces the learning curve and ensures that users can focus on the task at hand rather than struggling with the technology.
Remote Operation Capabilities
Another significant advancement is the ability to operate these analyzers remotely. Through software like SPEK PC, users can control the instrument via WiFi and USB connections, viewing and printing data and reports directly from a connected device. This feature is particularly beneficial in hazardous environments where physical presence near the analyzer might be risky, or in situations where immediate data access is crucial.

Seamless Data Transfer
The integration of WiFi capabilities in handheld XRF analyzers facilitates seamless data transfer. This allows for the remote viewing of sample readings, which is invaluable in field settings where immediate decision-making is required. The ability to quickly share data with team members or stakeholders enhances collaboration and speeds up the decision-making process.
Enhanced Productivity and Sustainability
Handheld XRF analyzers are designed to maximize productivity while promoting sustainability. They enable swift qualitative screenings directly in the field, allowing for the clear demarcation of ore and waste boundaries. This reduces the unpredictability of excavation and minimizes the need for outsourcing samples to external testing labs. Rapid assays help in optimizing drill locations, guiding extraction processes, and determining ore grade, thereby boosting confidence and reducing turnaround times.
Intelligent Software Solutions
The intelligent software solutions provided with these analyzers are tailored to meet specific business needs. Users can customize data fields and user profiles to create workflow solutions that are perfectly aligned with their requirements. The SPEC PC software, for instance, allows for remote operation of the analyzer, enhancing flexibility and convenience.

Applications in Various Fields
Handheld XRF analyzers are versatile tools with applications ranging from mineral exploration and core analysis to geochemical testing and mapping. They are used in mine face or pit-face operations, waste processing, metal recovery, ore grade control, and even in specific mining operations like silver ore mining. The ability to perform these tasks with a compact and portable device makes handheld XRF analyzers indispensable in modern mining and exploration activities.
In conclusion, the advanced features and software of handheld XRF analyzers represent a significant leap forward in the field of analytical technology. These devices not only enhance the speed and accuracy of analyses but also make them more accessible and convenient for a wide range of applications. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative features that will further expand the capabilities of these invaluable tools.
In conclusion, the future of handheld XRF technology is bright, with significant advancements on the horizon. These developments will not only enhance the capabilities of existing applications but also open up new opportunities across a wide range of industries. As technology continues to evolve, handheld XRF analyzers will remain an indispensable tool for fast, accurate, and non-destructive elemental analysis.
Related Products
- XRD Sample Holder X-ray Diffractometer Powder Slide
- Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use