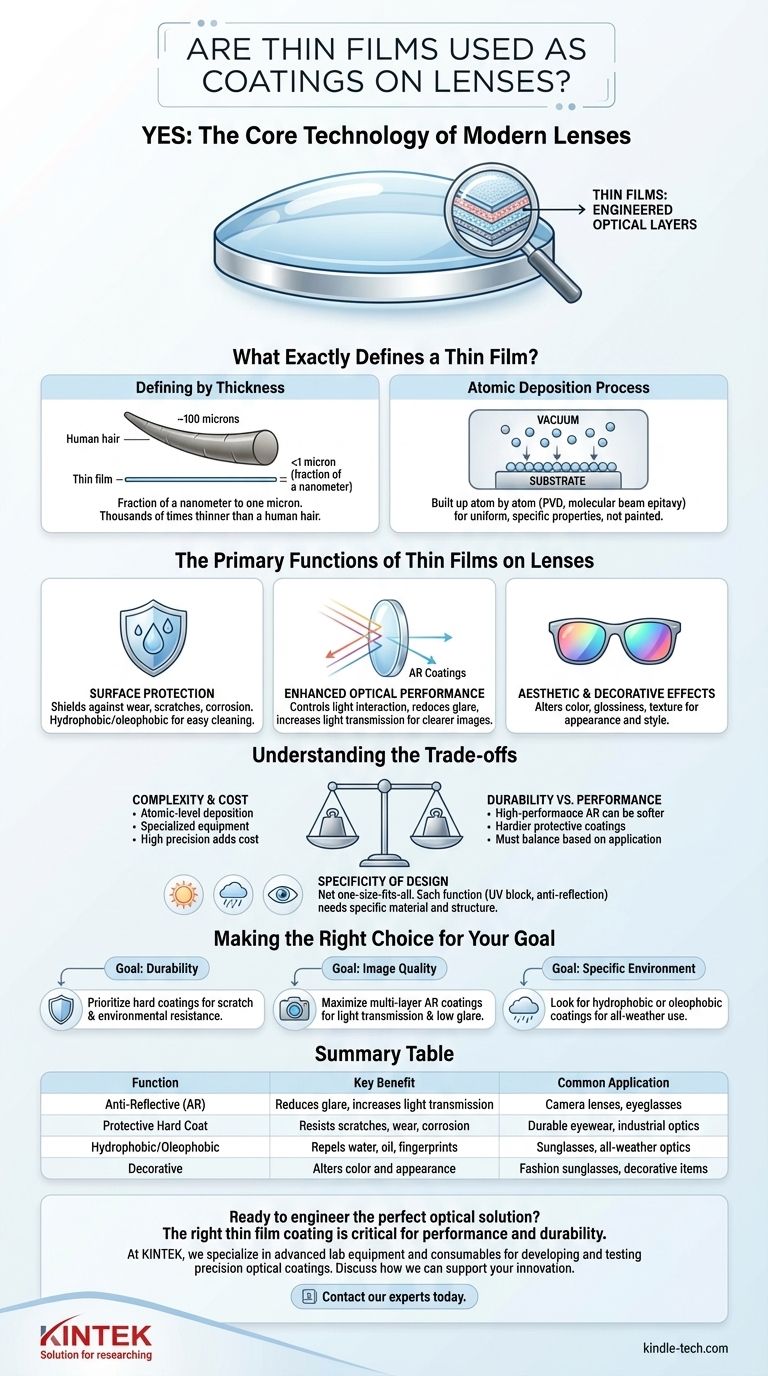
Yes, thin films are fundamental to modern lenses—they are the technology behind the coatings that protect the glass and enhance its optical properties. These precisely engineered layers, often thinner than a wavelength of light, are not just a surface treatment but an integral part of the lens's design and function.
The term 'lens coating' is functionally synonymous with 'optical thin film'. These microscopically thin layers are precisely engineered to manipulate light and protect the lens surface, making them a critical component rather than a simple add-on.
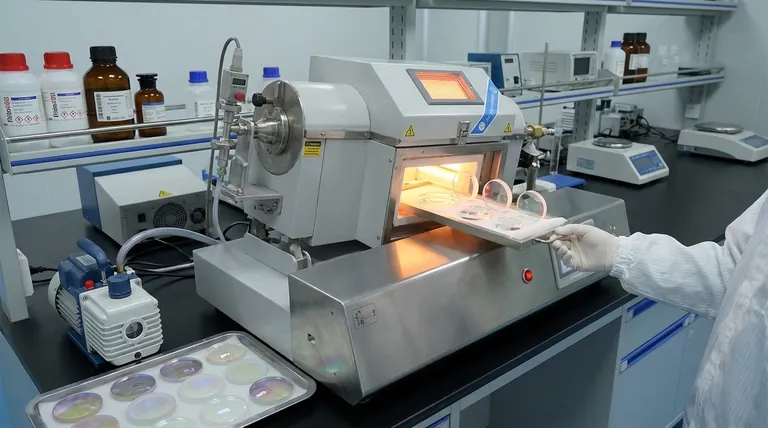

What Exactly Defines a Thin Film?
Defining by Thickness
A thin film is a layer of material ranging from a fraction of a nanometer up to one micron in thickness. To put this in perspective, a single thin film layer can be thousands of times thinner than a human hair.
This microscopic scale is the key differentiator from "thick coatings" like paint.
The Atomic Deposition Process
Thin films are not painted or sprayed on. Instead, they are built up on a surface, known as a substrate, by depositing individual atoms or molecules.
This precise process is why thin films can achieve such uniform and specific properties. Common industrial methods for this include Physical Vapour Deposition (PVD) and molecular beam epitaxy.
The Primary Functions of Thin Films on Lenses
Surface Protection
One of the most straightforward roles of a thin film on an optical element is protection. Hard coatings are designed to shield the underlying glass from wear, scratches, and corrosion.
Specialized films can also be hydrophobic (repelling water) or oleophobic (resisting fingerprints and oils), making the lens easier to clean and maintain.
Enhanced Optical Performance
This is the most critical function for high-performance optics like camera lenses or eyeglasses. Thin films are engineered to control how light interacts with the lens surface.
By applying multiple layers with different refractive indices, engineers can create anti-reflective (AR) coatings that dramatically reduce glare and increase the amount of light that passes through the lens, resulting in a clearer, higher-contrast image.
Aesthetic and Decorative Effects
Thin films can also be used to alter the visual properties of a surface. They can change a material's color, glossiness, and texture.
This is common in sunglasses, where coatings create a mirrored or colored appearance, and can also be used for purely decorative purposes on other products.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Complexity and Cost
The atomic-level deposition processes required to create high-quality thin films are complex and require specialized equipment. This precision adds significant cost and complexity to the manufacturing of an optical element.
Durability vs. Performance
There is often a trade-off between optical performance and physical durability. The most effective multi-layer anti-reflective coatings can be softer and more susceptible to scratching than simpler, hardier protective coatings.
Engineers must balance these priorities based on the lens's intended application.
Specificity of Design
A thin film is not a one-size-fits-all solution. A coating designed to block UV light is fundamentally different from one designed to reduce reflections in the visible spectrum. Each function requires a specific material and structure, and combining multiple functions into one coating stack is a significant engineering challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal thin-film coating is entirely dependent on the primary goal of the optical system.
- If your primary focus is durability: Seek out lenses that emphasize their protective "hard coatings," designed to resist scratches and environmental damage.
- If your primary focus is image quality: Prioritize lenses with advanced, multi-layer anti-reflective (AR) coatings to maximize light transmission and minimize glare.
- If your primary focus is a specific environment: Look for specialized films, such as hydrophobic or oleophobic coatings for all-weather use.
Understanding that these coatings are engineered thin films moves you from seeing a lens as simple glass to appreciating it as a sophisticated optical instrument.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Reflective (AR) | Reduces glare, increases light transmission | Camera lenses, eyeglasses |
| Protective Hard Coat | Resists scratches, wear, and corrosion | Durable eyewear, industrial optics |
| Hydrophobic/Oleophobic | Repels water, oil, and fingerprints | Sunglasses, all-weather optics |
| Decorative | Alters color and appearance for aesthetics | Fashion sunglasses, decorative items |
Ready to engineer the perfect optical solution for your application? The right thin film coating is critical for performance and durability. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for developing and testing precision optical coatings. Whether you're designing camera lenses, specialized eyewear, or industrial optics, our expertise can help you achieve superior clarity and protection. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's innovation in optical thin films.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
People Also Ask
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- How many types of vapor phase deposition techniques are present? PVD vs. CVD Explained
- What is deposition in environmental chemistry? Understanding How Air Pollution Harms Ecosystems
- How many types of sputtering are there? A Guide to DC, RF, and Advanced Techniques
- What is the principle of reactive sputtering? Create High-Performance Ceramic Coatings



















