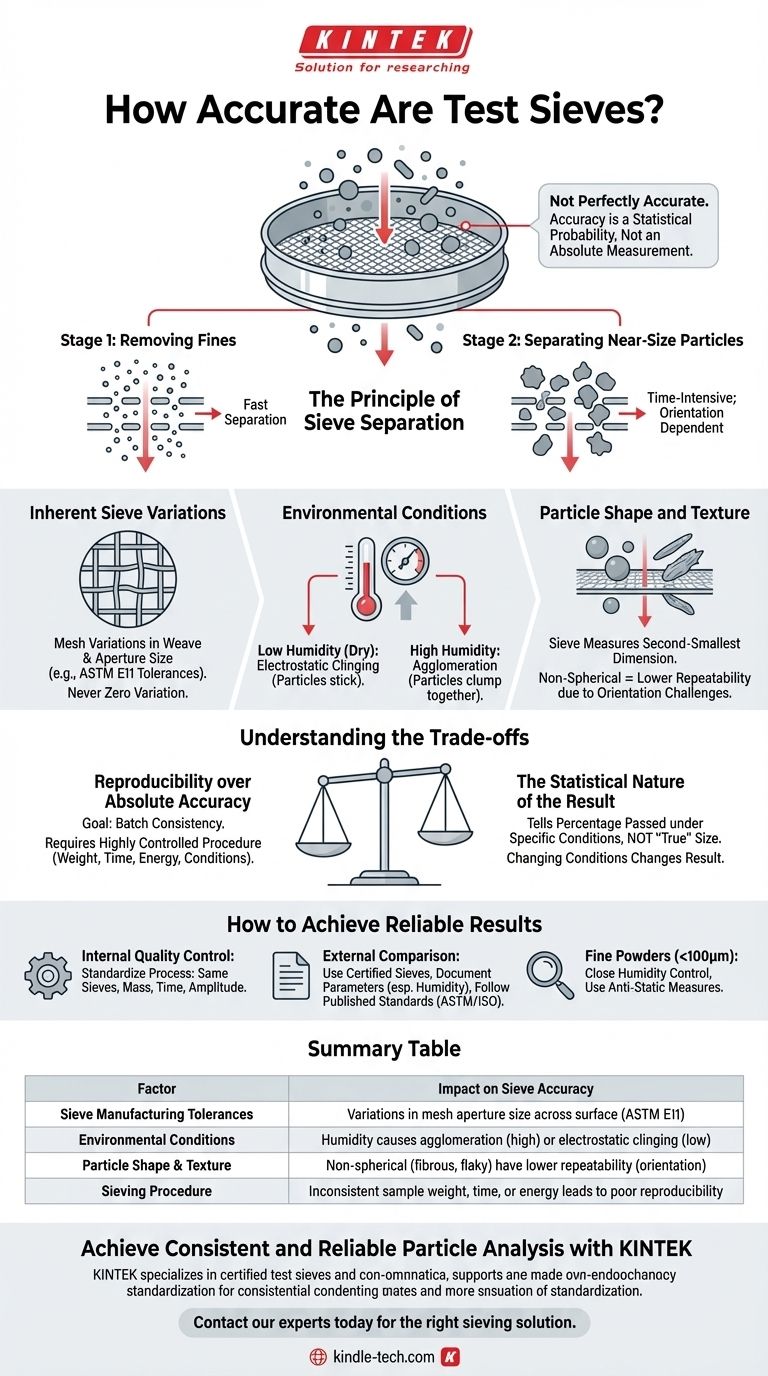
In reality, a test sieve is not a perfectly accurate instrument. Its accuracy is not a single value but a function of the sieve’s manufacturing tolerances, the environmental conditions of the test, and the physical properties of the material being measured. While a high-quality sieve provides a reliable basis for measurement, variations in its mesh and external factors will always introduce a degree of uncertainty.
The core issue is that a sieve analysis provides a statistical probability, not an absolute measurement. The "accuracy" of your result depends less on the sieve in isolation and more on your ability to control the numerous variables that influence whether a particle passes through an aperture.
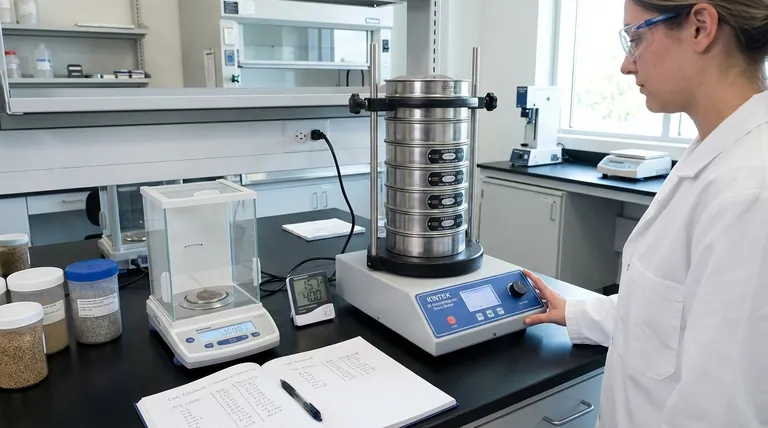

The Principle of Sieve Separation
To understand the limits of accuracy, we must first understand how a sieve functions. The process isn't as simple as just filtering out large particles.
Stage 1: Removing Fines
The first and fastest part of the process is removing all particles that are significantly smaller than the sieve's mesh openings. These pass through quickly with minimal agitation.
Stage 2: Separating Near-Size Particles
The real challenge, and the source of most variability, is the separation of particles that are very close to the size of the mesh openings. For these particles to pass, they must be presented to an aperture at the correct orientation and with enough opportunities to do so, which takes time and energy.
Key Factors That Influence Sieve Accuracy
The final result of a sieve analysis is influenced by several factors, some inherent to the equipment and others related to the environment and procedure.
Inherent Sieve Variations
No sieve mesh is perfectly uniform. The manufacturing process, even under tight controls, results in variations in the weave and thus a distribution of aperture sizes across the sieve surface.
Standards like ASTM E11 define acceptable tolerances for this variation, but it is never zero. This means one certified sieve will produce slightly different results from another, even when testing the same material under identical conditions.
Environmental Conditions
The surrounding environment can dramatically alter test results, especially with fine powders.
The most significant factor is relative humidity. Very dry conditions (low humidity) can generate strong electrostatic charges, causing fine particles to cling to each other and to the sieve mesh, preventing them from passing through.
Conversely, high humidity can cause hygroscopic (water-absorbing) particles to agglomerate or clump together, effectively making them larger and skewing the results toward the coarse side.
Particle Shape and Texture
Sieves measure particles based on their second-smallest dimension. An elongated or flat particle may fail to pass through a mesh opening that it could easily fit through if it were oriented differently (e.g., end-on).
Therefore, a sieve analysis of spherical particles will be inherently more repeatable than one for fibrous or flaky materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thinking of a sieve as a "pass/fail" gauge is a common mistake. It is a tool for characterizing a population of particles, and this comes with inherent limitations.
Reproducibility over Absolute Accuracy
For most industrial applications, reproducibility is more important than absolute accuracy. The goal is to ensure that Batch B has the same particle size distribution as Batch A.
Achieving this requires a highly controlled and documented procedure where sample weight, sieving time, energy, and ambient conditions are kept constant for every test.
The Statistical Nature of the Result
A sieve analysis does not tell you the "true" size of every particle. It tells you what percentage of a bulk sample, by weight, passed through a statistically defined set of apertures under specific test conditions.
Changing any of those conditions—using a different sieve, running the test for longer, or performing it on a more humid day—will change the result.
How to Achieve Reliable Results
Your approach should be dictated by your ultimate goal. By controlling for the known variables, you can produce data that is reliable and fit for its purpose.
- If your primary focus is internal quality control: Standardize your entire process—use the same set of matched sieves, a consistent sample mass, and a fixed sieving time and amplitude.
- If your primary focus is comparing results with an external lab or supplier: Use certified test sieves, document all test parameters (especially humidity), and adhere strictly to a published standard method (e.g., ASTM or ISO).
- If your primary focus is analyzing fine powders (<100 microns): Pay extremely close attention to humidity control and consider using anti-static measures to ensure particles can move freely.
Understanding these variables transforms sieving from a frustrating exercise into a powerful and dependable analytical tool.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Sieve Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Sieve Manufacturing Tolerances | Variations in mesh aperture size across the sieve surface, as defined by standards like ASTM E11. |
| Environmental Conditions | Humidity can cause particle agglomeration (high) or electrostatic clinging (low), skewing results. |
| Particle Shape & Texture | Non-spherical particles (e.g., fibrous, flaky) have lower repeatability due to orientation challenges. |
| Sieving Procedure | Inconsistent sample weight, time, or energy leads to poor reproducibility between tests. |
Achieve Consistent and Reliable Particle Analysis with KINTEK
Understanding the variables that affect test sieve accuracy is the first step. The next is ensuring your lab is equipped with high-quality, certified sieves and follows best-practice procedures to control these factors.
KINTEK specializes in supplying precision lab equipment and consumables for all your particle analysis needs. We provide certified test sieves and the support you need to standardize your process for superior reproducibility in quality control.
Let us help you enhance your lab's efficiency and data reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the right sieving solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are sieve analysis used for? A Guide to Particle Size Distribution Testing
- What are the limitations of sieve analysis? A Guide to Choosing the Right Particle Analysis Method
- How do you calculate sieve analysis in a lab report? A Step-by-Step Guide to Accurate Particle Size Distribution
- How is a test sieve calibrated? Ensure Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- What is the purpose of using a 40-mesh sieve for kaolin catalyst carriers? Optimizing Uniformity and Activity
- What is the primary purpose of using laboratory standard sieves? Optimize Composting Pre-treatment for Pig Manure
- What were possible sources of error in sieve analysis? Avoid These Common Pitfalls for Accurate Results
- What size sieves are used in sieve analysis? A Guide to Mesh, Frame, and Standard Selection



















