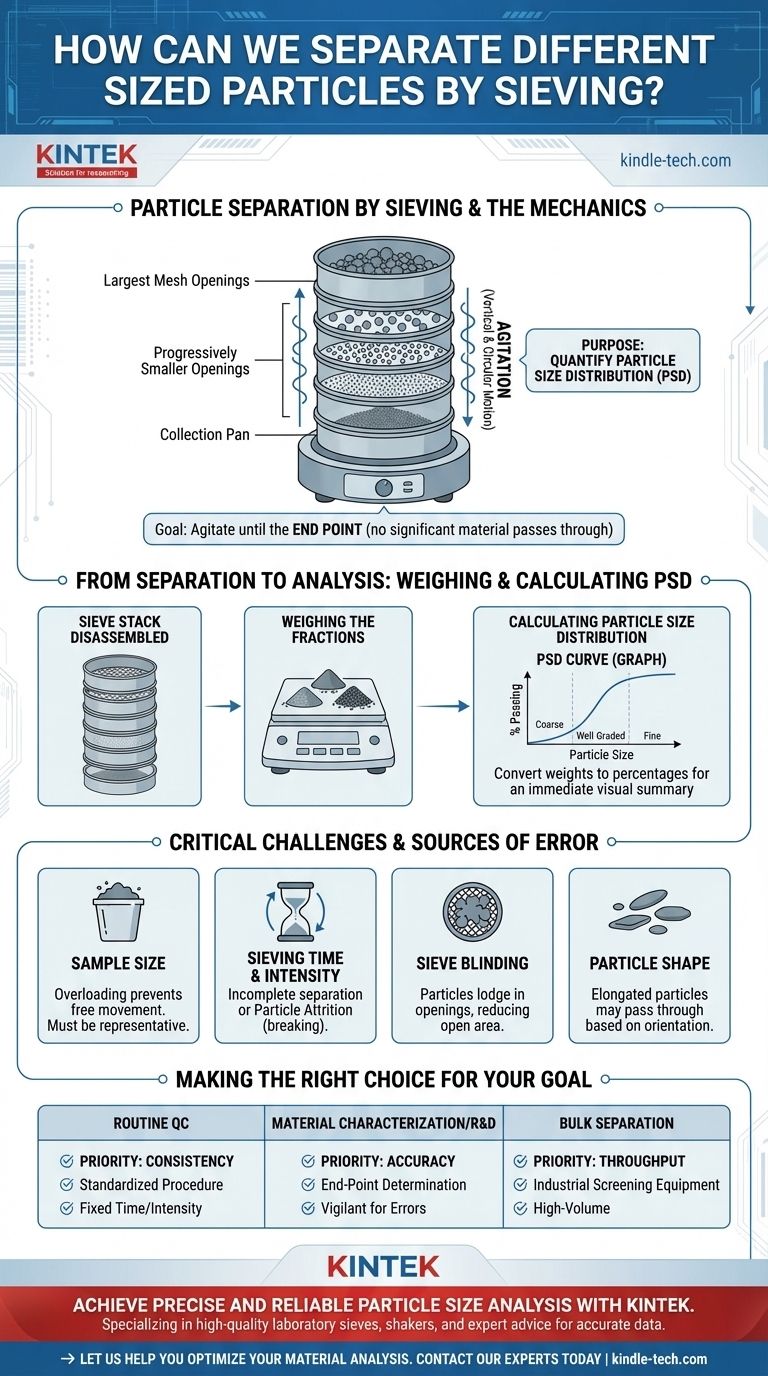
Particle separation by sieving is a mechanical process used to sort granular materials based on size. It is accomplished by passing a sample through a stacked column of sieves—each a screen of a specific mesh size—and using agitation to facilitate the sorting. Smaller particles fall through the mesh openings until they are retained by a sieve with apertures too small for them to pass.
The fundamental purpose of sieving is not merely to sort particles, but to accurately quantify a material's particle size distribution (PSD). This data is critical for quality control, process optimization, and predicting a material's physical behavior.

The Mechanics of Sieve Analysis
Sieve analysis, or a gradation test, is the standard procedure for measuring the particle distribution of a granular sample. The process relies on a few key components and principles working in concert.
The Sieve Stack
A standard analysis uses a "stack" of test sieves. These are arranged vertically with the sieve having the largest mesh openings at the top and each subsequent sieve below it having progressively smaller openings. A solid collection pan is placed at the very bottom to collect the finest particles.
The Role of Agitation
The material sample is placed in the top sieve, and the entire stack is secured in a mechanical sieve shaker. The shaker provides controlled agitation—often a combination of vertical tapping and horizontal circular motion. This movement ensures particles are constantly presented to the mesh surface in different orientations, giving them the maximum opportunity to pass through if they are small enough.
Reaching the 'End Point'
Sieving is not an instantaneous process. The goal is to continue agitation until the "end point" is reached. This is the point at which continued sieving does not result in a significant amount of additional material passing through any of the sieves, ensuring the separation is as complete as possible.
From Separation to Analysis: What the Data Means
Once the agitation is complete, the physical separation is done. The next step is to turn that separation into quantitative, actionable data.
Weighing the Fractions
The sieve stack is carefully disassembled. The material retained on each individual sieve, as well as the material in the bottom pan, is collected and weighed precisely. The sum of these individual weights should closely match the initial total weight of the sample.
Calculating Particle Size Distribution
The weight of the material on each sieve is converted into a percentage of the total sample weight. This data is typically presented in a table or plotted on a graph, creating a particle size distribution curve. This curve provides an immediate visual summary of whether the material is coarse, fine, or well-graded (containing a wide range of sizes).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Sources of Error
While straightforward in principle, accurate sieving requires careful attention to detail. Several factors can compromise the quality of your results.
Sample Size
The sample must be large enough to be statistically representative of the entire batch of material. However, a sample that is too large will overload the sieves, preventing particles from moving freely and finding their way through the mesh.
Sieving Time and Intensity
Insufficient sieving time or intensity will lead to an incomplete separation, with too much coarse material reported. Conversely, excessive agitation time or intensity, especially with brittle materials, can cause particle attrition (breaking particles down), which skews the results toward a finer distribution.
Sieve Blinding
Sieve blinding occurs when particles become lodged in the mesh openings, effectively reducing the open area of the sieve. This is common with particles that are very close in size to the mesh openings and can prevent other, smaller particles from passing through.
Particle Shape
Sieving fundamentally measures a particle's second-largest dimension, as this determines its ability to pass through a square opening. Highly elongated or flat particles may pass through a mesh they would otherwise be retained on if they orient themselves correctly, which can be a source of variability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The rigor you apply to the sieving process should match your ultimate objective.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: Prioritize consistency. Use a standardized procedure with a fixed sample weight, sieving time, and shaker intensity to ensure your results are repeatable and comparable over time.
- If your primary focus is material characterization or R&D: Prioritize accuracy. Perform an end-point determination to establish the optimal sieving time for your specific material and be vigilant about potential errors like attrition or sieve blinding.
- If your primary focus is separating bulk material for use (not analysis): Prioritize throughput. In this case, analytical sieve shakers are less relevant than larger industrial screening equipment designed for high-volume, efficient separation.
Mastering the sieving process transforms it from a simple sorting task into a powerful tool for material insight and process control.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | To quantify a material's particle size distribution (PSD). |
| Process | Passing a sample through a stacked column of sieves with mechanical agitation. |
| Key Components | Sieve stack (largest to smallest mesh), sieve shaker, collection pan. |
| Critical Factors | Sample size, sieving time/intensity, sieve blinding, particle shape. |
| Primary Goal | To achieve a complete separation for accurate, repeatable data. |
Achieve precise and reliable particle size analysis with KINTEK.
Whether your focus is on rigorous R&D, consistent quality control, or high-throughput industrial separation, the right equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory sieves, mechanical sieve shakers, and expert advice to ensure your sieving process delivers accurate and actionable data every time.
Let us help you optimize your material analysis. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect sieving solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research



















