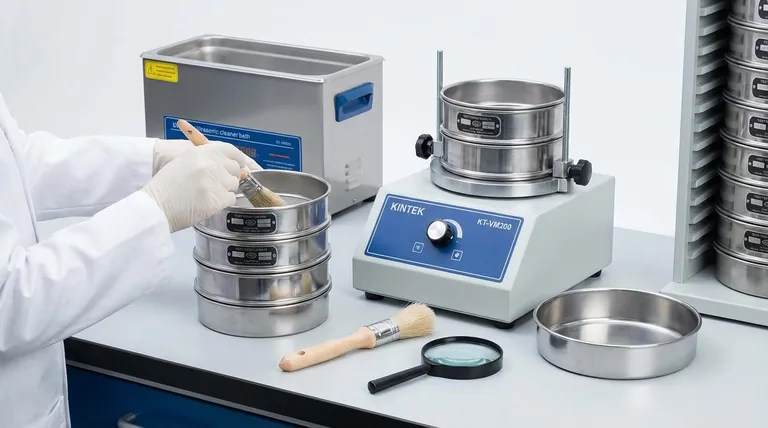
Properly maintaining a test sieve is a critical process that goes beyond simple cleaning. It involves a disciplined approach of gentle handling during use, thorough cleaning between tests, periodic inspection for damage, and correct storage to protect its physical integrity. These steps are essential for extending the life of the sieve and, more importantly, ensuring the continued accuracy of your particle size analysis.
The primary goal of sieve maintenance is not just cleanliness, but preserving the precise, uniform openings of the mesh. A damaged, clogged, or distorted sieve is no longer a calibrated measuring instrument; it is a source of inaccurate and unreliable data.

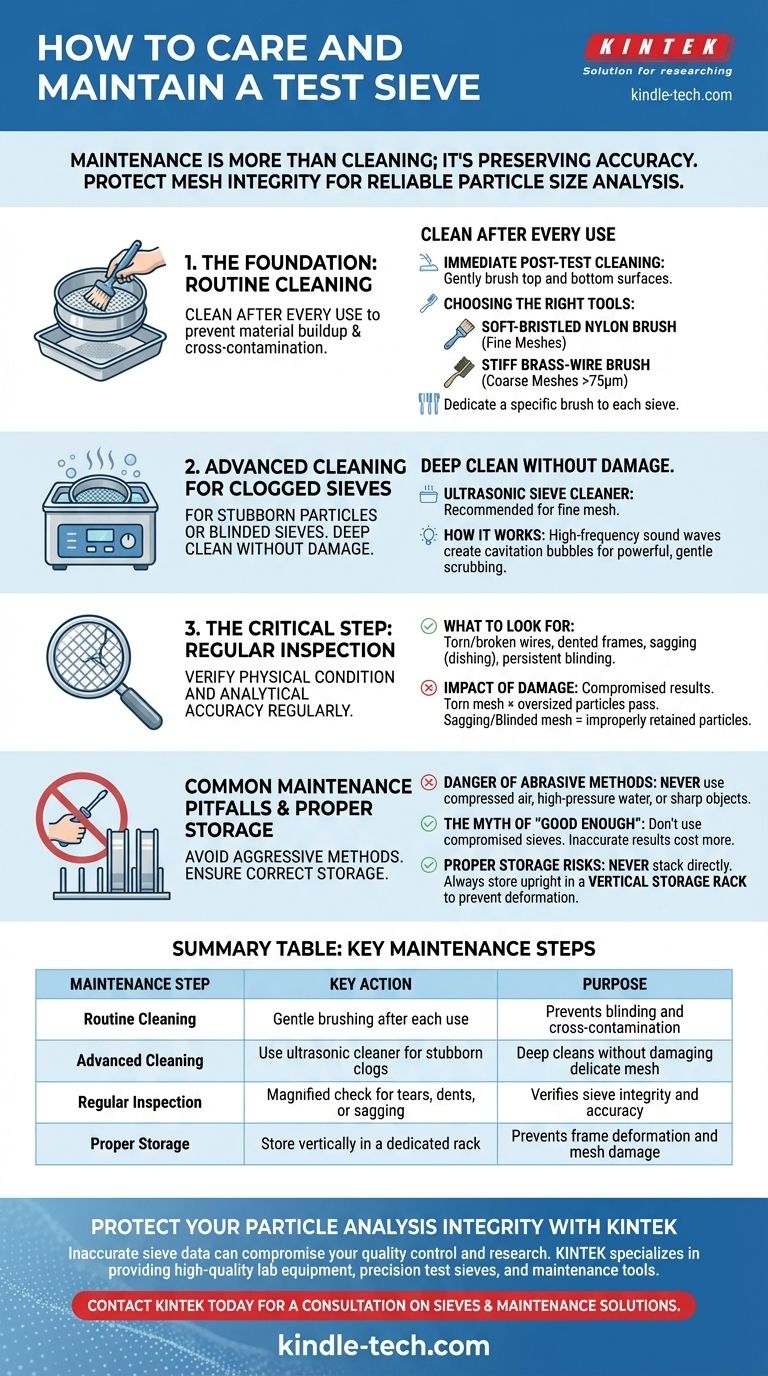
The Foundation: Routine Cleaning
Effective maintenance begins with consistent, proper cleaning after every use. This routine prevents material buildup and cross-contamination between samples.
Immediate Post-Test Cleaning
After each test, the sieve should be cleaned to recover any retained particles. Use a gentle brushing motion on both the top and bottom surfaces of the mesh.
This action prevents fine particles from becoming lodged in the mesh openings, a condition known as blinding.
Choosing the Right Tools
The tool you use is critical. A soft-bristled nylon brush is suitable for most fine meshes, while a slightly stiffer brass-wire brush can be used on coarser meshes (openings of 75µm and larger).
To prevent damage and cross-contamination, it is best practice to dedicate a specific, correctly-sized brush to each sieve in your set.
Advanced Cleaning for Clogged Sieves
For stubborn particles or thoroughly blinded sieves that cannot be cleared with simple brushing, a more robust cleaning method is required.
When to Use an Ultrasonic Cleaner
An ultrasonic sieve cleaner is the most effective and recommended method for deep cleaning. It is particularly useful for fine mesh sieves where brushing alone is often insufficient and risks damaging the delicate wires.
How Ultrasonic Cleaning Works
These devices use high-frequency sound waves to create microscopic cavitation bubbles in a cleaning solution. The collapse of these bubbles generates a gentle but powerful scrubbing action that dislodges particles from the mesh without causing physical damage.
The Critical Step: Regular Inspection
A sieve can be perfectly clean but still be unsuitable for use. Regular inspection is a non-negotiable step to verify the sieve's physical condition and analytical accuracy.
What to Look For
Using a magnifier or a specialized sieve inspection tool, carefully examine the mesh for any signs of wear or damage. Pay close attention to torn or broken wires, dented frames, and any noticeable sagging or stretching of the mesh (dishing).
Also, check for persistent blinding, where particles are permanently wedged in the openings even after cleaning.
The Impact of a Damaged Sieve
A compromised sieve directly leads to compromised results. Torn mesh allows oversized particles to pass through, while sagging or blinded mesh can improperly retain undersized particles. Either flaw invalidates the test data.
Common Maintenance Pitfalls to Avoid
Aggressive or improper maintenance techniques can damage a sieve more quickly than the testing process itself. Understanding what not to do is as important as knowing what to do.
The Danger of Abrasive Methods
Never use compressed air, high-pressure water, or sharp objects like screwdrivers to dislodge particles. These methods can easily stretch, tear, or distort the delicate woven wire mesh, rendering the sieve useless.
The Myth of "Good Enough"
Continuing to use a sieve with minor sags, a few broken wires, or a small dent is a false economy. The cost of inaccurate results—from failed quality control to invalid research—far outweighs the cost of replacing a single compromised sieve.
Improper Storage Risks
Never stack sieves directly on top of one another. The weight can cause the frame to deform and the mesh to sag. Always store sieves upright in a vertical storage rack to protect both the frame and the mesh surface from damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance protocol should align with the precision your work demands. A disciplined approach ensures your equipment remains a reliable instrument.
- If your primary focus is routine production quality control: Emphasize consistent post-test brushing and proper vertical storage to maximize sieve lifespan and consistency.
- If your primary focus is high-precision analysis or certification: Implement a strict schedule of magnified inspections and consider investing in an ultrasonic cleaner to ensure the highest level of cleanliness and accuracy.
- If you suspect inaccurate or inconsistent results: Your first troubleshooting step should be a thorough inspection of every sieve in your stack for damage, distortion, or blinding.
By treating your sieves as the precision instruments they are, you protect the integrity of every analysis you perform.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Routine Cleaning | Gentle brushing after each use | Prevents blinding and cross-contamination |
| Advanced Cleaning | Use ultrasonic cleaner for stubborn clogs | Deep cleans without damaging delicate mesh |
| Regular Inspection | Magnified check for tears, dents, or sagging | Verifies sieve integrity and accuracy |
| Proper Storage | Store vertically in a dedicated rack | Prevents frame deformation and mesh damage |
Protect Your Particle Analysis Integrity with KINTEK
Inaccurate sieve data can compromise your quality control and research. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including precision test sieves and maintenance tools like ultrasonic cleaners, to ensure your particle size analysis remains reliable.
Let our experts help you maintain your analytical standards. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation on the right sieves and maintenance solutions for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance



















