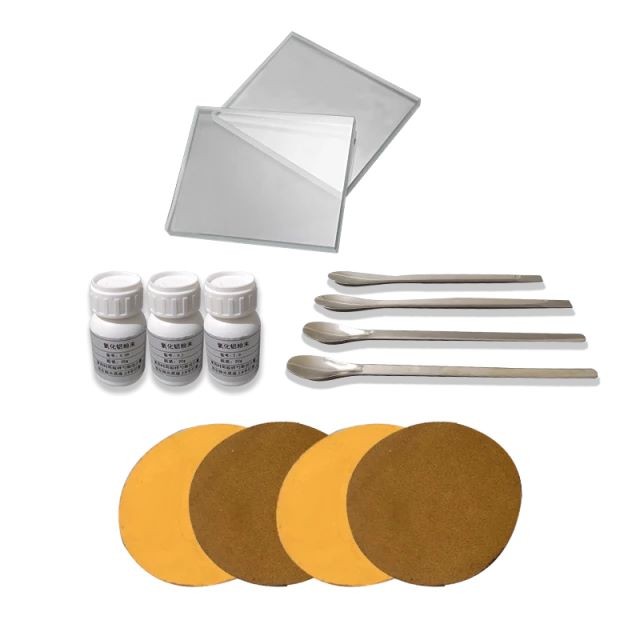

Electrochemical Consumables
Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
Item Number : ELMP
Price varies based on specs and customizations
$69.00 / set
Shipping:
Contact us to get shipping details Enjoy On-time Dispatch Guarantee.
Why Choose Us
Easy ordering process, quality products, and dedicated support for your business success.
Polishing Materials for Electrodes in Electrochemical Experiments
Electrode Polishing and Testing Instructions
- Prepare electrode polishing materials. Remove the backing adhesive from the chamois polishing cloth and affix it to the electrode polishing plate. Pour polishing powder (1.0/0.5/0.3/0.05um) in reverse order onto the polishing cloth and moisten it with distilled water to form a paste.
- Place the electrode vertically on the polishing pad and polish by drawing "8" shapes, clockwise or counterclockwise circles, or horizontal strokes. It is important to ensure that the electrode is perpendicular to the polishing cloth. After polishing, rinse the electrode surface clean with distilled water.
- Choose cyclic voltammetry on the electrochemical workstation and test the electrode in a standard solution of potassium ferrocyanide. If the peak position difference is within 80mv, the electrode can be considered qualified.
- Take two clean beakers and place a dry ethanol (a) and a secondary deionized water (b) in them. Place the tested electrode in the two solutions in order (a, b) and clean it with ultrasonic waves for no more than 60 seconds. Remove the electrode and blow it dry before use.
- If the electrode needs modification, invert it on the electrode drying stand and apply drops.
Detail & Parts
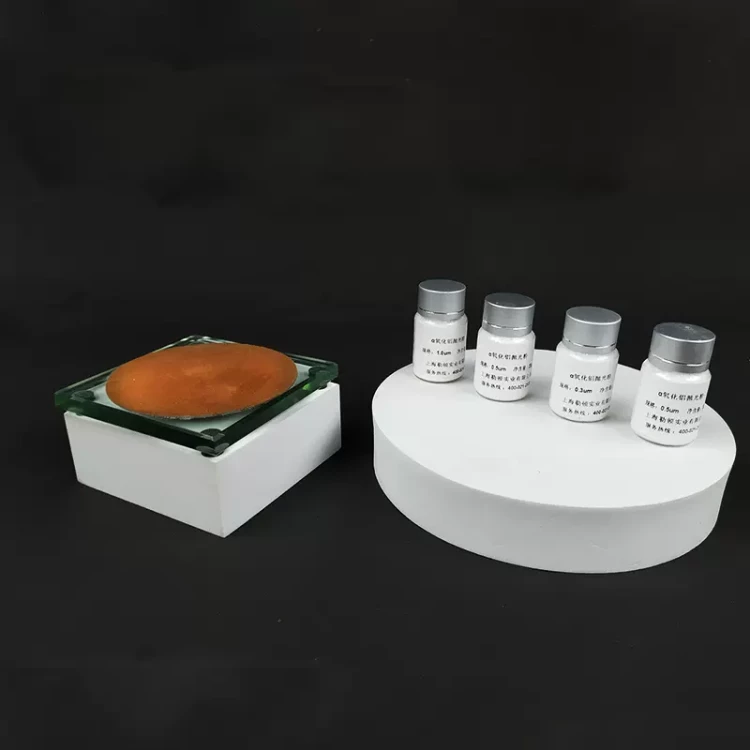
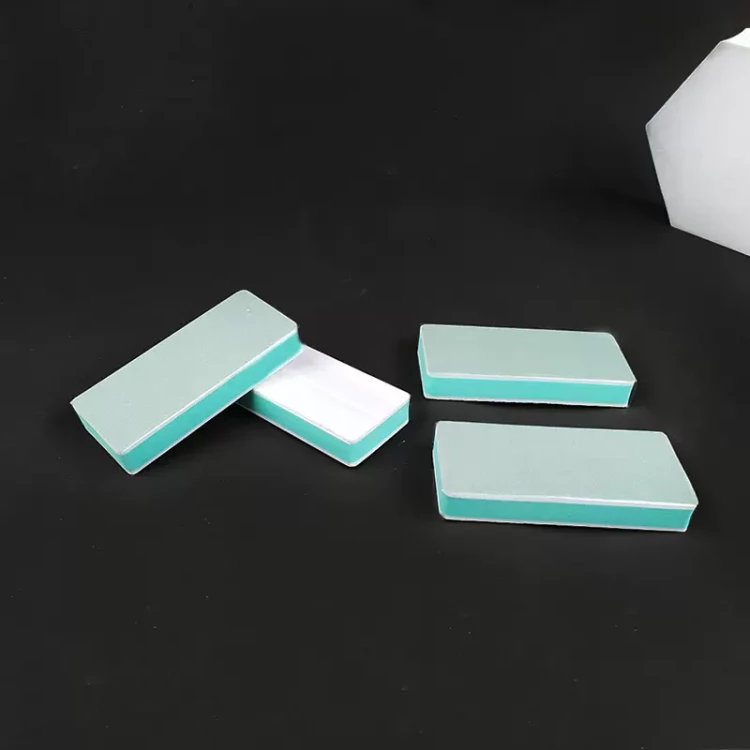




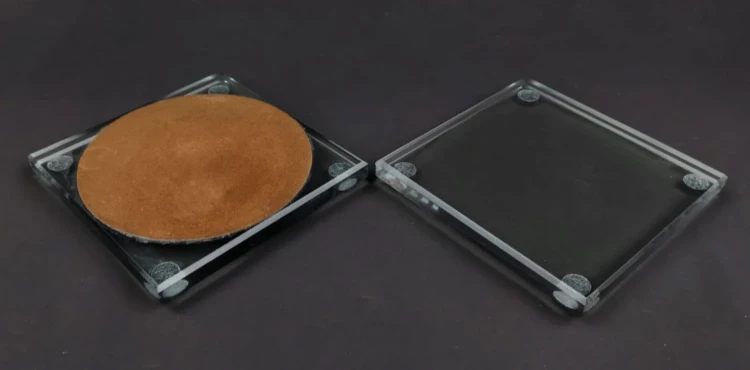
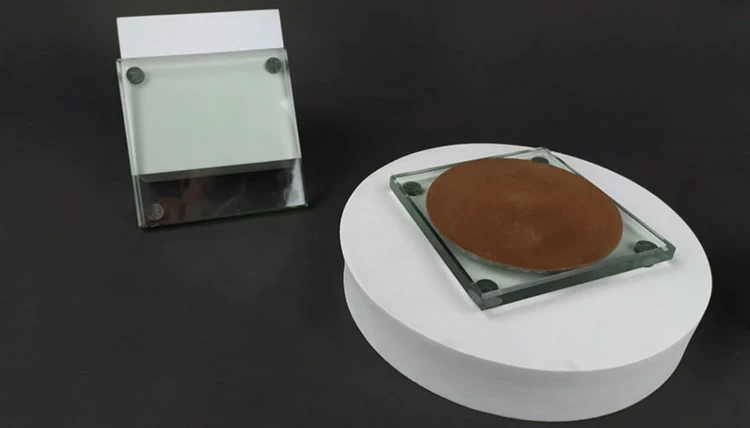

Disc Electrode Polishing Steps
0.05um alumina powder is the most suitable for polishing disk-shaped electrodes. However, if scratches are found on the electrode, you need to use 1.0um, 0.3um, and 0.05um alumina powder in sequence to polish the electrode. After each polishing step, check the electrode surface, which should be flat and neat. Also, use the same alumina powder for polishing. If 1.0um alumina powder cannot remove scratches, you should first use 1200-grit metallographic sandpaper to polish and then use 0.05um alumina powder. The electrode surface will have a mirror-like luster.
Nylon polishing cloth and silk velvet cloth are used with 1.0um alumina powder, and the polishing flannel (coffee-colored) is prepared for 0.3um and 0.05um alumina powder. The back of the cloth has stickiness. Tear off the covering layer on the stickiness and press the polishing cloth tightly onto the dry and clean glass pad. Ensure that there are no bubbles between the glass pad and the polishing cloth. Before polishing, sprinkle a small amount of alumina powder on the polishing cloth and moisten it with distilled water. When polishing, hold the electrode vertically and steadily (not too hard). If the polishing cloth becomes dry, add distilled water and continue polishing.
Before using smaller alumina powder, thoroughly clean the electrode and wash your hands with water. If you accidentally sprinkle large powder on the small powder polishing cloth, you will not achieve the effect that small powder can achieve. Be careful when holding dry powder. Do not put large powder into small powder bottles. Do not exchange powder bottle caps at will. Use different spoons for different bottles when taking alumina powder from the bottle.
Designed for You
KinTek provide deep custom made service and equipment to worldwide customers, our specialized teamwork and rich experienced engineers are capable to undertake the custom tailoring hardware and software equipment requirements, and help our customer to build up the exclusive and personalized equipment and solution!
Would you please drop your ideas to us, our engineers are ready for you now!
Trusted by Industry Leaders

FAQ
What Is An Electrode In Electrochemistry?
What Are The Materials Used In Electrochemical Cell?
What Are The 3 Electrodes In Electrochemistry?
What Are The Examples Of Electrochemical Material?
What Are The Different Types Of Electrochemical Electrodes?
What Materials Are Commonly Used For Electrochemical Electrodes?
What Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting An Electrochemical Electrode?
How Can Electrochemical Electrodes Be Used In Various Applications?
4.9 / 5
These polishing materials greatly enhance the quality of my experiments. The electrodes are polished to a mirror-like finish, resulting in more accurate and reproducible results.
4.7 / 5
I've been using these materials for a few months now and am thoroughly impressed with their durability. They last much longer than other brands I've tried, saving me both time and money.
4.8 / 5
The polishing materials are incredibly easy to use. The instructions are clear and concise, making the process hassle-free. I highly recommend these materials to anyone looking for a reliable and efficient way to polish their electrodes.
4.6 / 5
The fast delivery of these materials was a lifesaver. I needed them urgently for a project and was thrilled when they arrived the next day. The quality is excellent, and I'm very satisfied with my purchase.
4.9 / 5
These polishing materials are worth every penny. They produce a superior finish on my electrodes, and I've noticed a significant improvement in the performance of my electrochemical experiments.
4.7 / 5
I'm very impressed with the technological advancements in these polishing materials. They're designed to minimize contamination and ensure the highest level of accuracy in my experiments. Highly recommended!
4.8 / 5
These materials are an absolute game-changer for my lab. They've streamlined our electrode polishing process, saving us valuable time and resources. The results are consistently excellent, and we're thrilled with the investment.
4.6 / 5
I've been using these polishing materials for over a year now, and they've never let me down. They're incredibly durable and maintain their effectiveness even after multiple uses. Highly recommend!
4.9 / 5
These polishing materials are a must-have for any electrochemist. They're incredibly easy to use, and the results are consistently outstanding. I've seen a noticeable improvement in the quality of my data since switching to these materials.
REQUEST A QUOTE
Our professional team will reply to you within one business day. Please feel free to contact us!
Related Products

Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
High-quality graphite electrodes for electrochemical experiments. Complete models with acid and alkali resistance, safety, durability, and customization options.

Gold Electrochemical Sheet Electrode Gold Electrode
Discover high-quality gold sheet electrodes for safe and durable electrochemical experiments. Choose from complete models or customize to meet your specific needs.

Gold Disc Electrode
Looking for a high-quality gold disc electrode for your electrochemical experiments? Look no further than our top-of-the-line product.

Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
Optimize your electrochemical experiments with our Platinum Auxiliary Electrode. Our high-quality, customizable models are safe and durable. Upgrade today!

Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
Upgrade your electrochemical experiments with our Platinum Disc Electrode. High-quality and reliable for accurate results.

Electrode Fixture for Electrochemical Experiments
Upgrade your experiments with our customizable Electrode Fixtures. High-quality materials, acid and alkali resistant, and safe and durable. Discover our complete models today.

RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
Elevate your electrochemical research with our Rotating Disk and Ring Electrodes. Corrosion resistant and customizable to your specific needs, with complete specifications.

Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
Looking for corrosion-resistant coating evaluation electrolytic cells for electrochemical experiments? Our cells boast complete specifications, good sealing, high-quality materials, safety, and durability. Plus, they're easily customizable to meet your needs.

Flat Corrosion Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Discover our flat corrosion electrolytic cell for electrochemical experiments. With exceptional corrosion resistance and complete specifications, our cell guarantees optimal performance. Our high-quality materials and good sealing ensure a safe and durable product, and customization options are available.

Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
Looking for a reliable quartz electrochemical cell? Our product boasts excellent corrosion resistance and complete specifications. With high-quality materials and good sealing, it's both safe and durable. Customize to meet your needs.

Optical Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Upgrade your electrolytic experiments with our Optical Water Bath. With controllable temperature and excellent corrosion resistance, it's customizable for your specific needs. Discover our complete specifications today.

Super Sealed Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Super-sealed electrolytic cell offers enhanced sealing capabilities, making it ideal for experiments that require high airtightness.

Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Gold Plating Tungsten Molybdenum Crucible for Evaporation
These crucibles act as containers for the gold material evaporated by the electron evaporation beam while precisely directing the electron beam for precise deposition.

Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible enables precise co-deposition of various materials. Its controlled temperature and water-cooled design ensure pure and efficient thin film deposition.

Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
High-purity and smooth conductive boron nitride crucible for electron beam evaporation coating, with high temperature and thermal cycling performance.

Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Tungsten Crucible and Molybdenum Crucible for High Temperature Applications
Tungsten and molybdenum crucibles are commonly used in electron beam evaporation processes due to their excellent thermal and mechanical properties.

Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
Looking for a high-quality gas diffusion electrolysis cell? Our liquid flow reaction cell boasts exceptional corrosion resistance and complete specifications, with customizable options available to suit your needs. Contact us today!
Related Articles

Understanding Electrodeposition with Electrochemical Electrodes
Electrodeposition is a process of depositing a metal or a non-metallic material onto a surface by applying an electric current.

How to Make Your Own Ag/AgCl Reference Electrode for Electrochemical Experiments
A reference electrode is an electrode with a stable and well-defined potential that is used as a reference point to measure the potential of other electrodes. Reference electrodes are commonly used in electrochemical experiments to determine the potential difference between two electrodes.

Comprehensive Guide to Rotating Disk Electrode (RDE) in Electrochemical Studies
Explore the detailed workings, applications, and significance of Rotating Disk Electrodes (RDE) in electrochemical research. Discover how RDEs are used in fuel cells, catalyst development, and more.

Electrode Materials for Rotating Ring-Disk Electrodes
Rotating ring-disk electrodes (RRDEs) are used in a wide range of applications, from fuel cells to sensors, and they require careful selection of electrode materials for optimal performance.

Electrochemical Electrodes in Chemical Analysis
Electrochemical electrodes are essential tools used in many chemical analysis techniques and experiments. These electrodes are devices that allow us to measure the electrical potential difference in a chemical reaction.

How to Choose the Right Electrochemical Electrode
The choice of electrode material can have a significant impact on the performance of the electrochemical system.

Electrolytes and Electrochemical Electrodes
Electrolytes and electrodes play an essential role in electrochemistry. Electrolytes are substances that conduct electricity when dissolved in water or melted.

Advanced Techniques in Coating Evaluation Using Electrolytic Cells
Explore the comprehensive guide on coating evaluation using electrolytic cells, covering electroplating, sol-gel methods, and wet chemical techniques. Enhance your understanding of metal coating properties and applications.

Electrochemical Consumables: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials, Applications, and Selection
Discover the world of electrochemical consumables, including types of electrodes (working, auxiliary, and reference) and electrolytes, as well as factors to consider when selecting materials for your electrochemical experiments or applications.

A Beginner's Guide to Understanding Reference Electrodes in Electrochemistry
Reference electrodes provide a stable and known potential that other electrodes can be compared to, allowing for accurate measurements of electrochemical reactions.

The Future of Electrochemical Electrodes
The latest trends and developments in electrode materials and their implications for the future of electrochemistry.

A Comprehensive Guide to Reference Electrodes
Reference electrodes are used in electrochemical measurements to establish a stable potential against which the potential of the working electrode can be measured.