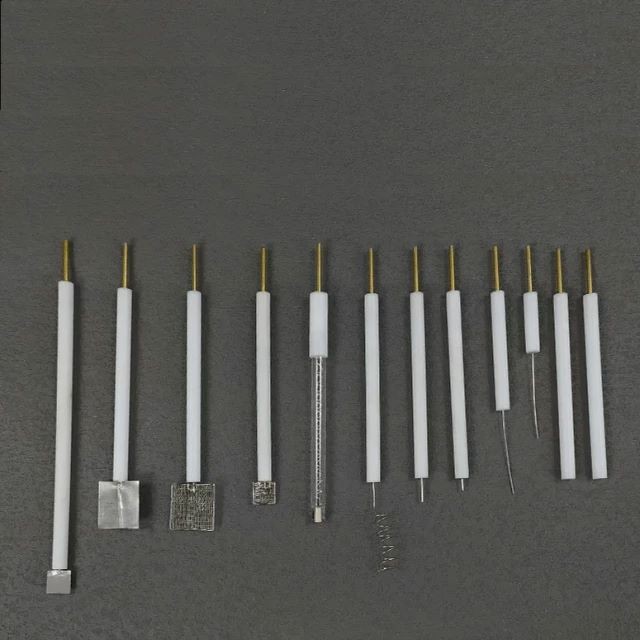

Electrochemical Consumables
Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
Item Number : ELPA
Price varies based on specs and customizations
$25.90 / set
- Features
- Corrosion Resistant
- Applicable temperature range
- 0 ~ 80℃
- Wire diameter
- 0.5 / 1mm
Shipping:
Contact us to get shipping details Enjoy On-time Dispatch Guarantee.
Why Choose Us
Easy ordering process, quality products, and dedicated support for your business success.
Introduction
Auxiliary electrodes are often fabricated from electrochemically inert materials such as gold, platinum, or carbon. The material used to make an auxiliary electrode must be an inert material like graphite or a noble metal such as gold, carbon, or platinum. The purpose of the auxiliary electrode is to provide a pathway for current to flow in the electrochemical cell without passing significant current through the reference electrode.
The Platinum Auxiliary Electrode is ideal for electrochemical experiments, featuring complete models constructed with high-quality materials. It is not only safe and durable, but also customizable to meet your specific needs.
Technical specifications
Platinum Wire Ring Electrode

| Features | Corrosion Resistant |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 80℃ |
| Wire diameter | 0.5 / 1mm |
| Material | pure platinum |
| Customize material (gold, silver, platinum, copper) and rod length to your needs. | |
Platinum wire electrode
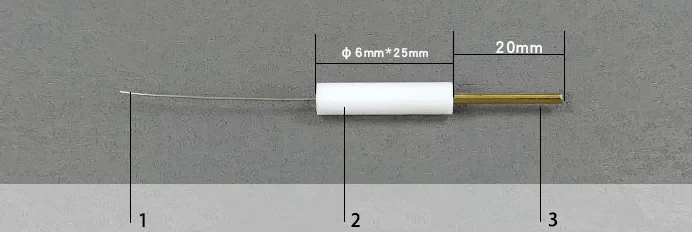
| Features | Corrosion Resistant |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 80℃ |
| Wire diameter | 0.5 / 1mm |
| Material | PTFE Rod + Platinum Wire |
| Customize material (gold, silver, platinum, copper) and rod length to your needs. | |
60 mesh platinum mesh electrode

| Features | Corrosion Resistant |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 80℃ |
| Size | 5*5~ 50*50mm |
| Material | PTFE Rod + Platinum Mesh |
| Pure platinum wire braided mesh electrode, high purity and large surface area. | |
Platinum column electrode
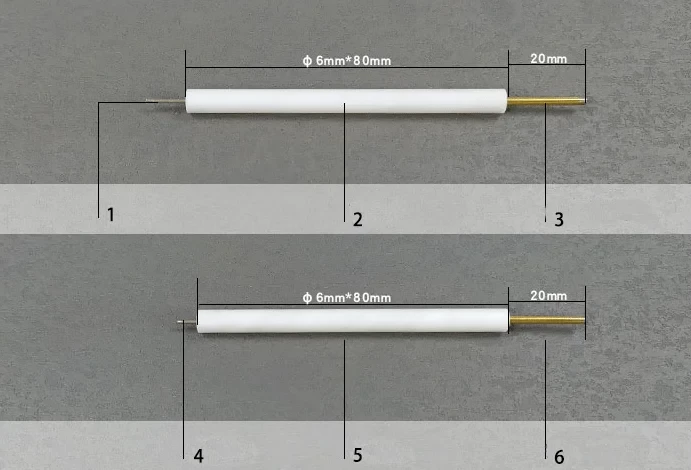
| Features | Corrosion Resistant |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 80℃ |
| Wire diameter | 1mm ~ 2mm |
| Material | PTFE Rod + Platinum |
| Customize material (gold, silver, platinum, copper) and rod length to your needs. | |
Detail & Parts










Features
The Platinum Auxiliary Electrode is an essential component for any electrochemistry setup. It provides a stable and inert surface for the transfer of electrons between the working electrode and the solution, ensuring accurate and reliable measurements.
- High surface area: The platinum gauze working electrode has a high surface area, which allows for a greater current flow and faster electron transfer, making it ideal for bulk electrolysis.
- Inert material: Platinum is an inert material, which means that it will not react with the solution or the working electrode, ensuring that the measurements are not affected by any chemical reactions.
- Corrosion-resistant: Platinum is a corrosion-resistant metal, which means that it will not corrode or degrade over time, ensuring a long lifespan for the electrode.
- Durable: Platinum is a durable material, which means that it can withstand repeated use and harsh conditions, making it an excellent choice for demanding applications.
- Versatile: The Platinum Auxiliary Electrode can be used in a wide range of applications, including electrochemistry, electroplating, and corrosion testing, making it a valuable tool for any laboratory.
Applications
Platinum auxiliary electrodes are widely used in various electrochemical applications, including:
- Electrochemical cells: As the counter electrode in electrochemical cells, facilitating electron transfer and maintaining charge balance.
- Voltammetry: As the counter electrode in cyclic voltammetry (CV) experiments, allowing for the study of electrochemical processes and determination of redox potentials.
- Electrolysis: As the counter electrode in electrolysis experiments, providing electrons for reduction reactions and ensuring efficient current flow.
- Fuel cells: As the counter electrode in fuel cells, facilitating electron transfer and enhancing cell efficiency.
- Solar cells: As the counter electrode in dye-synthesized TiO2 solar cells, improving ionic diffusion and enabling higher current output.
- Sputtering: As the target material in sputtering processes, producing thin platinum films with high electro-catalytic properties and low resistance.
Designed for You
KinTek provide deep custom made service and equipment to worldwide customers, our specialized teamwork and rich experienced engineers are capable to undertake the custom tailoring hardware and software equipment requirements, and help our customer to build up the exclusive and personalized equipment and solution!
Would you please drop your ideas to us, our engineers are ready for you now!
Trusted by Industry Leaders

FAQ
What Is The Purpose Of A Platinum Auxiliary Electrode?
What Are The Benefits Of Using A Platinum Auxiliary Electrode?
How Do I Choose The Right Platinum Auxiliary Electrode?
What Is An Electrode In Electrochemistry?
What Is The Function Of Auxiliary Electrode?
What Are The 3 Electrodes In Electrochemistry?
What Is The Difference Between Auxiliary And Reference Electrode?
What Are The Different Types Of Electrochemical Electrodes?
What Materials Are Commonly Used For Auxiliary Electrodes?
What Materials Are Commonly Used For Electrochemical Electrodes?
How Do Auxiliary Electrodes Affect The Performance Of An Electrochemical Cell?
What Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting An Electrochemical Electrode?
Why Are Auxiliary Electrodes Necessary In Electrochemical Systems?
How Can Electrochemical Electrodes Be Used In Various Applications?
Are There Any Limitations Or Considerations When Using Auxiliary Electrodes?
4.8 / 5
The Platinum Auxiliary Electrode from KINTEK SOLUTION is an excellent choice for any electrochemistry lab. It's made with high-quality materials and is very durable.
4.7 / 5
I've been using the Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for a few months now and I'm very impressed with its performance. It's very accurate and provides consistent results.
4.9 / 5
The Platinum Auxiliary Electrode is a great value for the price. It's very affordable and provides excellent performance.
4.6 / 5
I'm very happy with the Platinum Auxiliary Electrode. It's easy to use and provides very accurate results.
4.8 / 5
The Platinum Auxiliary Electrode is a very versatile tool. It can be used for a variety of electrochemical experiments.
4.7 / 5
I would highly recommend the Platinum Auxiliary Electrode to anyone who is looking for a high-quality and affordable electrode.
4.9 / 5
The Platinum Auxiliary Electrode is a must-have for any electrochemistry lab. It's a great investment that will provide years of reliable service.
4.6 / 5
I'm very impressed with the Platinum Auxiliary Electrode. It's very well-made and provides very accurate results.
4.8 / 5
The Platinum Auxiliary Electrode is a great choice for anyone who is looking for a high-performance electrode.
4.7 / 5
I would highly recommend the Platinum Auxiliary Electrode to anyone who is looking for a reliable and affordable electrode.
4.9 / 5
The Platinum Auxiliary Electrode is a great value for the price. It's very affordable and provides excellent performance.
4.6 / 5
I'm very happy with the Platinum Auxiliary Electrode. It's easy to use and provides very accurate results.
REQUEST A QUOTE
Our professional team will reply to you within one business day. Please feel free to contact us!
Related Products

Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
Elevate your experiments with our Platinum Sheet Electrode. Crafted with quality materials, our safe and durable models can be tailored to fit your needs.

Platinum Sheet Electrode for Battery Lab Applications
Platinum sheet is composed of platinum, which is also one of the refractory metals. It is soft and can be forged, rolled and drawn into rod, wire, plate, tube and wire.

Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
Upgrade your electrochemical experiments with our Platinum Disc Electrode. High-quality and reliable for accurate results.

Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
Looking for a Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode? Our complete models are made of high-quality materials, ensuring durability and safety. Customization options available.

Anion Exchange Membrane for Laboratory Use
Anion exchange membranes (AEMs) are semipermeable membranes, usually made of ionomers, designed to conduct anions but reject gases such as oxygen or hydrogen.

High Purity Gold Platinum Copper Iron Metal Sheets
Elevate your experiments with our high-purity sheet metal. Gold, platinum, copper, iron, and more. Perfect for electrochemistry and other fields.

Ultra-Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Electrode Lead for High-Precision Applications
Discover the Ultra-Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange, perfect for high-precision applications. Ensure reliable connections in ultra-vacuum environments with advanced sealing and conductive technology.

RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
Elevate your electrochemical research with our Rotating Disk and Ring Electrodes. Corrosion resistant and customizable to your specific needs, with complete specifications.

Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
An evaporation crucible for organic matter, referred to as an evaporation crucible, is a container for evaporating organic solvents in a laboratory environment.

Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
Discover our high-quality Multifunctional Electrolytic Cell Water Baths. Choose from single or double-layer options with superior corrosion resistance. Available in 30ml to 1000ml sizes.
Related Articles

Comprehensive Guide to Reference Electrodes: Types, Applications, and Selection Criteria
Explore the world of reference electrodes with our detailed guide. Learn about different types, their applications, and how to select the right one for your needs. Ideal for researchers and lab technicians.

Advanced Techniques in Coating Evaluation Using Electrolytic Cells
Explore the comprehensive guide on coating evaluation using electrolytic cells, covering electroplating, sol-gel methods, and wet chemical techniques. Enhance your understanding of metal coating properties and applications.

Understanding Saturated Calomel Reference Electrodes: Composition, Uses, and Considerations
Explore the detailed guide on saturated calomel reference electrodes, including their composition, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Ideal for researchers and lab technicians.

Understanding Quartz Electrolytic Cells: Applications, Mechanisms, and Advantages
Explore the detailed workings, applications, and benefits of quartz electrolytic cells in various industries. Learn how these cells facilitate precise chemical reactions and their role in high-purity metal production.

Electrode Materials for Rotating Ring-Disk Electrodes
Rotating ring-disk electrodes (RRDEs) are used in a wide range of applications, from fuel cells to sensors, and they require careful selection of electrode materials for optimal performance.

A Comprehensive Guide to Reference Electrodes
Reference electrodes are used in electrochemical measurements to establish a stable potential against which the potential of the working electrode can be measured.

A Beginner's Guide to Understanding Reference Electrodes in Electrochemistry
Reference electrodes provide a stable and known potential that other electrodes can be compared to, allowing for accurate measurements of electrochemical reactions.

AgAgCl Reference Electrode Working Principle and Applications
Ag/AgCl reference electrode is a widely used reference electrode due to its stable potential and long-term stability.

Electrolytes and Electrochemical Electrodes
Electrolytes and electrodes play an essential role in electrochemistry. Electrolytes are substances that conduct electricity when dissolved in water or melted.

How to Choose the Right Reference Electrode for Your Application
When it comes to measuring the electrical potential of a solution accurately, a reference electrode is an essential tool in the laboratory. It provides a stable and consistent reference point for other electrodes to measure against, ensuring accurate and reliable results.

The Future of Electrochemical Electrodes
The latest trends and developments in electrode materials and their implications for the future of electrochemistry.

A Guide to Choosing the Right Reference Electrode for Your ISE Analysis
Reference electrodes are an essential component of any electrochemical measurement.