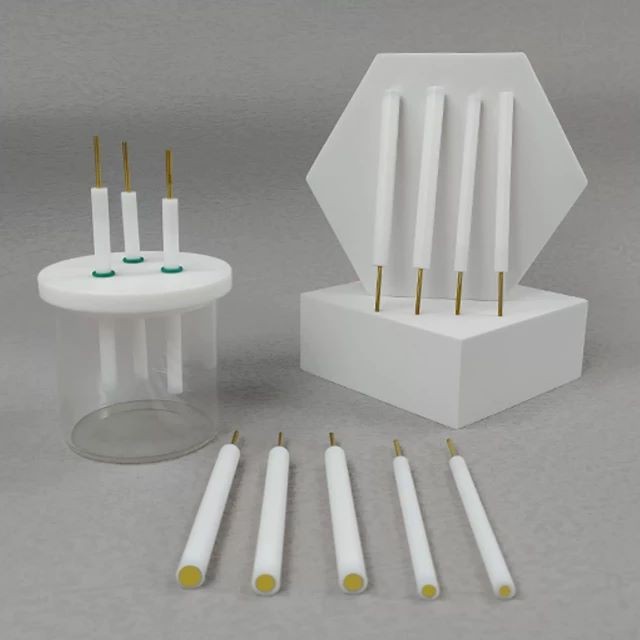

Electrochemical Consumables
Gold Disc Electrode
Item Number : ELEGD
Price varies based on specs and customizations
$59.90 / set
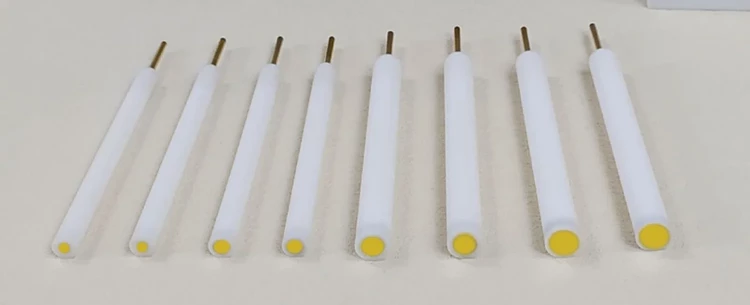
- Specifications
- 0.5 ~ 6mm, can be customized
- Applicable temperature range
- 0 ~ 60℃
- Rod Material
- PTFE
- Guide material
- high purity gold> 99.99%
Shipping:
Contact us to get shipping details Enjoy On-time Dispatch Guarantee.
Why Choose Us
Easy ordering process, quality products, and dedicated support for your business success.
Introduction
In electrochemistry, electrodes are conductors that make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit. They are used in a variety of applications including batteries, electrolysis, and potentiometric analysis. Inert electrodes, such as graphite, platinum, gold, and rhodium, do not participate in chemical reactions and are used to transfer electricity by passing electrons through a solution instead of exchanging ions. Gold electrodes are commonly used in electrochemistry due to their inertness, good conductivity, and resistance to corrosion. They are also used in the fabrication of integrated circuits and other electronic devices.
Technical specifications

| Specifications | 0.5 ~ 6mm, can be customized |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Rod Material | PTFE |
| Guide material | high purity gold> 99.99% |
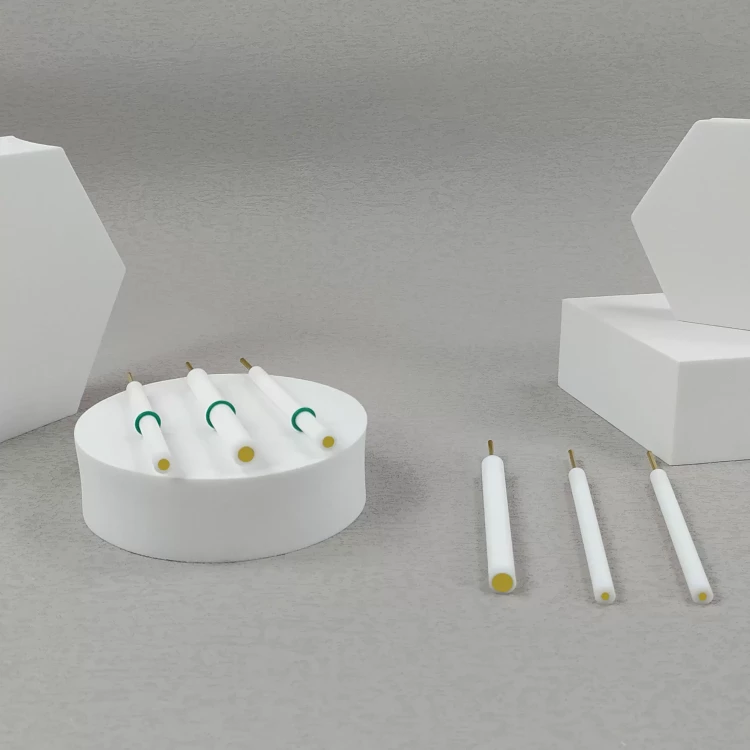
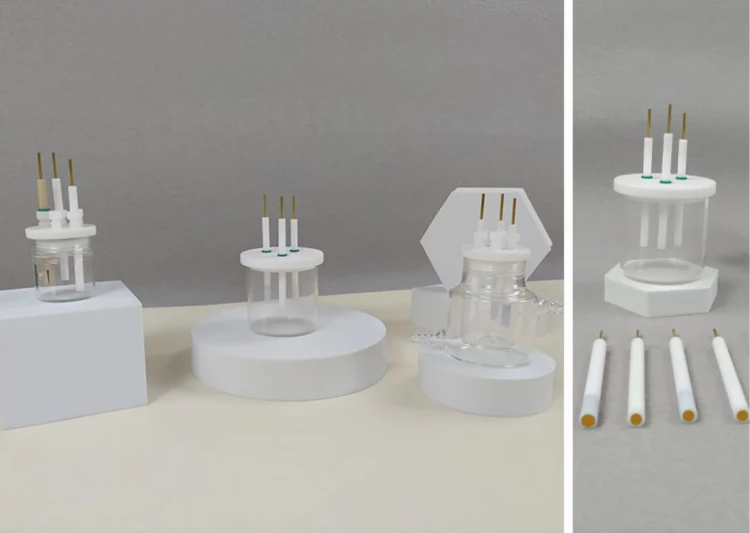
Detail & Parts


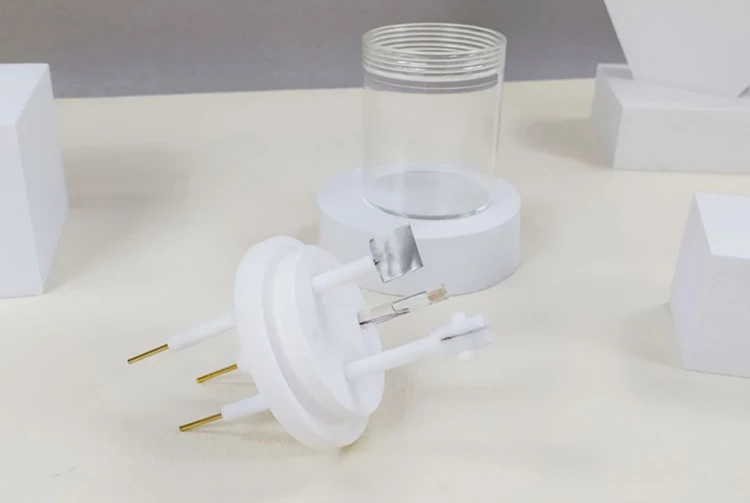
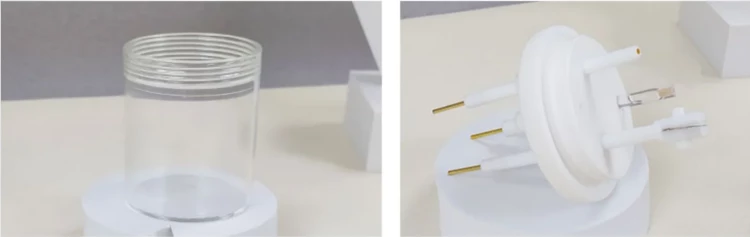

Applications
Electrodes, especially gold electrodes, are widely used in various fields. Some major application areas include:
- Analytical chemistry: Gold electrodes can be used for electrochemical measurements such as potentiometry, voltammetry, and amperometry. They are used for the detection and quantification of a variety of substances, including heavy metals, ions, and organic compounds.
- Battery: Gold electrodes are used as components in different types of batteries, such as lead-acid batteries, zinc-carbon batteries, and lithium-polymer batteries. Their role is to facilitate the flow of electrons and enable the storage and release of electrical energy.
- Electrolysis: During the electrolysis process, the gold electrode acts as an auxiliary electrode. They provide an inert surface for reactions to occur without participating in electrochemical reactions. This allows salts and ores to be converted into metals efficiently.
- Non-aqueous reference electrode: In non-aqueous electrochemistry, gold electrodes can be used as pseudo-reference electrodes. They establish a constant reference potential during experiments and help monitor changes in cell solutions. This application is critical for studying electrochemical reactions in non-aqueous solvents.
Advantages
- Increased masking potential: Gold plating is more compatible with selective plating applications than PVD coating, allowing manufacturers to plate specific areas of a workpiece while leaving others unaffected.
- Lower energy consumption: Gold plating requires a low-voltage electrical current for electrodeposition, consuming less energy compared to PVD, which often occurs at high temperatures. This reduced energy consumption can lower project costs.
- Extended range of applications: Gold, platinum, and glassy carbon (GC) are common electrode materials in RRDEs, but GC is prone to dissolution at high oxidizing potentials, especially in alkaline solutions. Moving to different electrode materials, such as gold, can expand the range of applications for RRDEs.
- Durability and corrosion resistance: PVD Gold Sputtering coating offers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to other gold coating types. Its ability to retain its sheen and withstand contact with the skin and wear makes it ideal for high-end jewelry, ensuring a longer-lasting lifespan.
Designed for You
KinTek provide deep custom made service and equipment to worldwide customers, our specialized teamwork and rich experienced engineers are capable to undertake the custom tailoring hardware and software equipment requirements, and help our customer to build up the exclusive and personalized equipment and solution!
Would you please drop your ideas to us, our engineers are ready for you now!
Trusted by Industry Leaders

FAQ
What Is An Electrode In Electrochemistry?
What Is The Function Of Auxiliary Electrode?
What Are The 3 Electrodes In Electrochemistry?
What Is The Difference Between Auxiliary And Reference Electrode?
What Are The Different Types Of Electrochemical Electrodes?
What Materials Are Commonly Used For Auxiliary Electrodes?
What Materials Are Commonly Used For Electrochemical Electrodes?
How Do Auxiliary Electrodes Affect The Performance Of An Electrochemical Cell?
What Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting An Electrochemical Electrode?
Why Are Auxiliary Electrodes Necessary In Electrochemical Systems?
How Can Electrochemical Electrodes Be Used In Various Applications?
Are There Any Limitations Or Considerations When Using Auxiliary Electrodes?
4.7 / 5
Fast delivery and great quality gold disc electrode. I'm very satisfied with my purchase.
4.8 / 5
The gold disc electrode is a great value for the price. It's well-made and works perfectly.
4.9 / 5
I've been using the gold disc electrode for a few weeks now and I'm very impressed with its durability. It's holding up well to the harsh chemicals I'm using.
5.0 / 5
The gold disc electrode is a great addition to my lab. It's easy to use and gives me accurate results.
4.7 / 5
I'm very happy with the gold disc electrode. It's a great value for the price and it works perfectly.
4.8 / 5
The gold disc electrode is a great investment. It's well-made and it's going to last me for years.
4.9 / 5
I'm very impressed with the gold disc electrode. It's a great value for the price and it works perfectly.
5.0 / 5
The gold disc electrode is a great addition to my lab. It's easy to use and gives me accurate results.
4.7 / 5
I'm very happy with the gold disc electrode. It's a great value for the price and it works perfectly.
4.8 / 5
The gold disc electrode is a great investment. It's well-made and it's going to last me for years.
4.9 / 5
I'm very impressed with the gold disc electrode. It's a great value for the price and it works perfectly.
5.0 / 5
The gold disc electrode is a great addition to my lab. It's easy to use and gives me accurate results.
4.7 / 5
I'm very happy with the gold disc electrode. It's a great value for the price and it works perfectly.
4.8 / 5
The gold disc electrode is a great investment. It's well-made and it's going to last me for years.
4.9 / 5
I'm very impressed with the gold disc electrode. It's a great value for the price and it works perfectly.
5.0 / 5
The gold disc electrode is a great addition to my lab. It's easy to use and gives me accurate results.
4.7 / 5
I'm very happy with the gold disc electrode. It's a great value for the price and it works perfectly.
4.8 / 5
The gold disc electrode is a great investment. It's well-made and it's going to last me for years.
4.9 / 5
I'm very impressed with the gold disc electrode. It's a great value for the price and it works perfectly.
REQUEST A QUOTE
Our professional team will reply to you within one business day. Please feel free to contact us!
Related Products

Gold Electrochemical Sheet Electrode Gold Electrode
Discover high-quality gold sheet electrodes for safe and durable electrochemical experiments. Choose from complete models or customize to meet your specific needs.

Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
Upgrade your electrochemical experiments with our Platinum Disc Electrode. High-quality and reliable for accurate results.

RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
Elevate your electrochemical research with our Rotating Disk and Ring Electrodes. Corrosion resistant and customizable to your specific needs, with complete specifications.

Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
High-quality graphite electrodes for electrochemical experiments. Complete models with acid and alkali resistance, safety, durability, and customization options.

Platinum Sheet Electrode for Battery Lab Applications
Platinum sheet is composed of platinum, which is also one of the refractory metals. It is soft and can be forged, rolled and drawn into rod, wire, plate, tube and wire.

Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Gold Plating Tungsten Molybdenum Crucible for Evaporation
These crucibles act as containers for the gold material evaporated by the electron evaporation beam while precisely directing the electron beam for precise deposition.
Related Articles

Comprehensive Guide to Rotating Disk Electrode (RDE) in Electrochemical Studies
Explore the detailed workings, applications, and significance of Rotating Disk Electrodes (RDE) in electrochemical research. Discover how RDEs are used in fuel cells, catalyst development, and more.

Electrode Materials for Rotating Ring-Disk Electrodes
Rotating ring-disk electrodes (RRDEs) are used in a wide range of applications, from fuel cells to sensors, and they require careful selection of electrode materials for optimal performance.

Comprehensive Guide to Reference Electrodes: Types, Applications, and Selection Criteria
Explore the world of reference electrodes with our detailed guide. Learn about different types, their applications, and how to select the right one for your needs. Ideal for researchers and lab technicians.

Electrochemical Electrodes in Chemical Analysis
Electrochemical electrodes are essential tools used in many chemical analysis techniques and experiments. These electrodes are devices that allow us to measure the electrical potential difference in a chemical reaction.

Understanding Electrodeposition with Electrochemical Electrodes
Electrodeposition is a process of depositing a metal or a non-metallic material onto a surface by applying an electric current.

Understanding Saturated Calomel Reference Electrodes: Composition, Uses, and Considerations
Explore the detailed guide on saturated calomel reference electrodes, including their composition, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Ideal for researchers and lab technicians.

A Comprehensive Guide to Reference Electrodes
Reference electrodes are used in electrochemical measurements to establish a stable potential against which the potential of the working electrode can be measured.

A Beginner's Guide to Understanding Reference Electrodes in Electrochemistry
Reference electrodes provide a stable and known potential that other electrodes can be compared to, allowing for accurate measurements of electrochemical reactions.

Advanced Techniques in Coating Evaluation Using Electrolytic Cells
Explore the comprehensive guide on coating evaluation using electrolytic cells, covering electroplating, sol-gel methods, and wet chemical techniques. Enhance your understanding of metal coating properties and applications.

Reference Electrodes: Calomel, Silver Chloride, and Mercury Sulfate - A Comprehensive Guide
Explore the world of reference electrodes, including calomel, silver chloride, and mercury sulfate. Understand their construction, principles, and applications in electrochemical measurements.

The Future of Electrochemical Electrodes
The latest trends and developments in electrode materials and their implications for the future of electrochemistry.

Electrochemical Consumables: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials, Applications, and Selection
Discover the world of electrochemical consumables, including types of electrodes (working, auxiliary, and reference) and electrolytes, as well as factors to consider when selecting materials for your electrochemical experiments or applications.