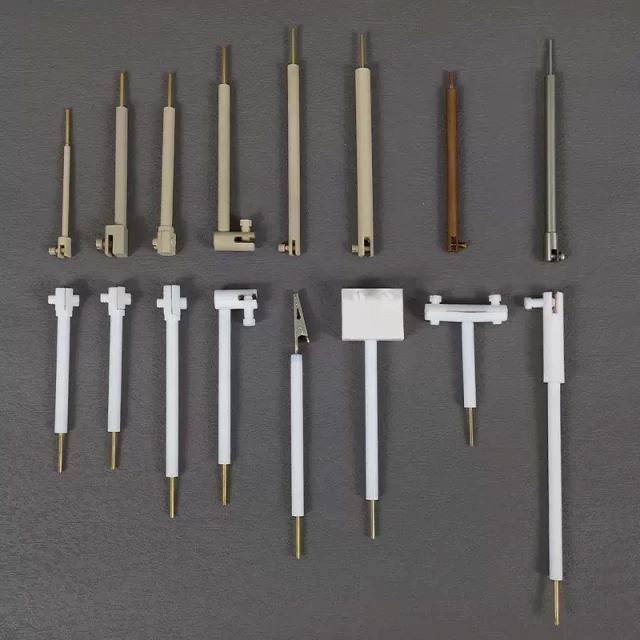

Electrochemical Consumables
Electrode Fixture for Electrochemical Experiments
Item Number : ELEF
Price varies based on specs and customizations
$39.90 / set
- Applicable temperature range
- 0 ~ 60 / 100 / 200 ℃
- Clamping thickness
- 0.1 ~ 5mm
- Material
- Platinum, gold, titanium, stainless steel, copper, etc.
Shipping:
Contact us to get shipping details Enjoy On-time Dispatch Guarantee.
Why Choose Us
Easy ordering process, quality products, and dedicated support for your business success.
Introduction
Working electrode fixtures are designed to hold and position working electrodes in a variety of electrochemical cells. Our Electrode Fixtures are available in complete models, made of high-quality materials with exceptional acid and alkali resistance, ensuring safety and durability. Additionally, they can be customized to meet your specific needs. They offer a number of benefits that make them ideal for use in electrochemical experiments:
- Precise positioning: Working electrode fixtures allow for precise positioning of the working electrode, which is essential for accurate and reproducible measurements.
- Secure hold: Working electrode fixtures securely hold the working electrode in place, even under harsh experimental conditions.
- Variety of materials: Working electrode fixtures are available in a variety of materials, including Teflon, stainless steel, and glass, to meet the needs of different experiments.
- Easy to clean: Working electrode fixtures are easy to clean and maintain, making them ideal for use in a variety of laboratory settings.
- Cost-effective: Working electrode fixtures are a cost-effective way to improve the accuracy and reproducibility of electrochemical experiments.
Technical specifications
Tetrafluoroplatinum electrode holder

| Features | Corrosion Resistant |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 5mm |
| Material | PTFE rod + platinum sheet |
| Two built-in 10*10 and 10*15 (can be customized to clamp 10mm samples) | |
PTFE electrode holder

| Features | Corrosion Resistant |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 5mm |
| Material | PTFE rod + gold sheet |
| Built-in 10*10 (can be customized clip 10mm sample) | |
PTFE sheet electrode holder

| Features | Resistant to slight corrosion |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 5mm |
| Material | PTFE rod + titanium sheet |
| Built-in 10*15 pieces (can be customized to clip 10mm samples) | |
PTFE horizontal platinum sheet electrode holder

| Features | Samples can be placed in parallel |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 3mm |
| Material | PTFE rod + platinum sheet |
| Built-in 10*10 platinum sheet (can be made of gold sheet, sheet, copper sheet, etc.) | |
Simple Working Electrode Clip

| Features | Easy to operate |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 3mm |
| Material | PTFE Rod + Alligator Clip |
| The chuck is made of crocodile clips, easy to use and easy to operate | |
Micro PEEK Platinum Electrode Holder

| Features | High temperature resistance and slight corrosion resistance |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 80℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 3mm |
| Material | PEEK Rod + Platinum Sheet |
| Built-in φ7mm platinum sheet (can be made of gold sheet, sheet, copper sheet, etc.) | |
PEEK Platinum Sheet Electrode Holder

| Features | High temperature resistance and slight corrosion resistance |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 80℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 3mm |
| Material | PEEK Rod + Platinum Sheet |
| Built-in 10*10 platinum sheet (can be made of gold sheet, sheet, copper sheet, etc.) | |
PEEK glassy carbon electrode holder

| Features | Can effectively inhibit the hydrogen evolution reaction |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 65℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 3mm |
| Material | PEEK Rod + Glassy Carbon |
| Built-in 3mm imported glass carbon (note that the working voltage should not exceed 1A) | |
PEEK Full Bore Electrode Holder

| Features | High temperature resistance and slight acid and alkali resistance |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 80℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 3mm |
| Material | PEEK Rod + Platinum |
| Built-in 6*6 and 9*9 platinum sheets (can be customized variable diameter electrode clip 6 to 10) | |
PEEK Transverse Platinum Sheet Electrode Holder

| Features | Can make the sample parallel |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 65℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 3mm |
| Material | PEEK Rod + Glassy Carbon |
| Built-in 9*9 platinum sheet (custom gold sheet, sheet, copper sheet material) | |
316L Stainless Steel Electrode Holder

| Features | Ultra-high temperature resistant and not acid resistant |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 200℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 3mm |
| Material | 316L stainless steel |
| Stainless steel is alkali-resistant, but not acid-resistant, so attention should be paid to the nature of the electrolyte | |
Copper electrode clip

| Features | Ultra-high temperature resistant Slight corrosion temperature range |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 200℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 3mm |
| Material | Copper |
| Stainless steel is alkali-resistant, but not acid-resistant, so attention should be paid to the nature of the electrolyte | |
Wide head electrode clip

| Features | Corrosion resistant large contact area |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 3mm |
| Material | PTFE + platinum sheet |
| Built-in 10*30 platinum sheet (size and material can be customized) | |
T-type electrode clip

| Features | Suitable for soft samples |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 5mm |
| Material | PTFE + platinum sheet |
| Built-in 5*15 platinum (size can be customized, material can be customized) | |
Extended variable diameter electrode clip

| Features | Length and size can be customized |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Clamping thickness | 0.1 ~ 5mm |
| Material | PTFE + copper wire |
| Built-in 0.5mm copper wire (size and material can be customized) | |
Detail & Parts
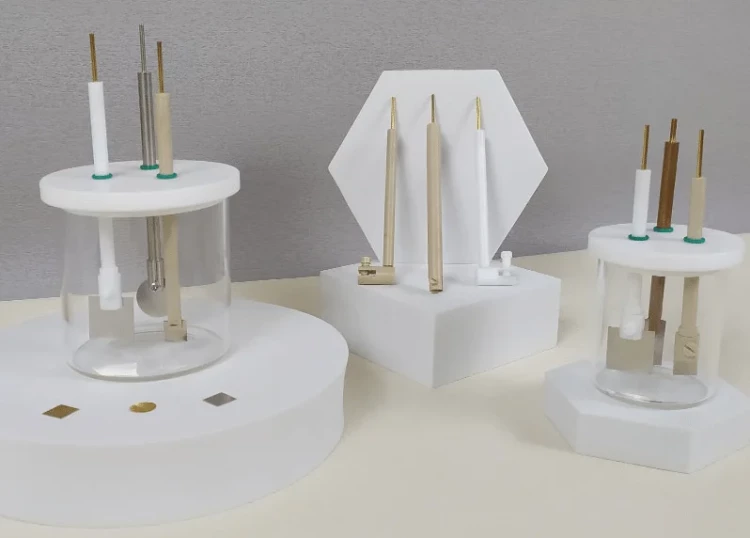



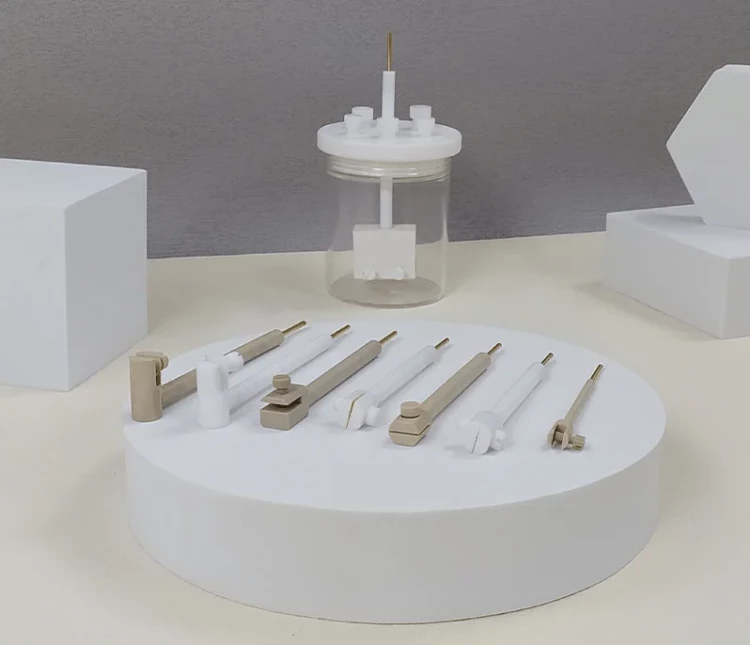
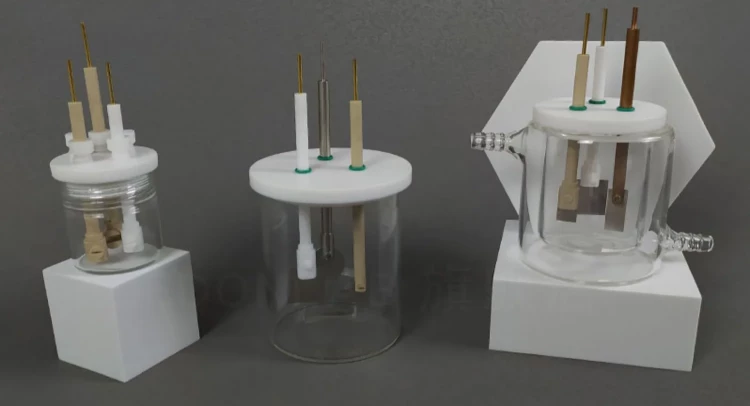
Applications
The working electrode fixture is used in various electrochemical experiments and applications, including:
- Measuring impedance across solution-phase interfaces, such as membranes or liquid-liquid junctions.
- Making accurate measurements of solution resistance or resistance across the surface of materials.
- Studying electrochemical reactions occurring at the working electrode.
- Investigating the behavior of different electrode materials.
- Measuring the rate of solution flow in an experiment.
- Determining the diffusion behavior of the electrode.
Designed for You
KinTek provide deep custom made service and equipment to worldwide customers, our specialized teamwork and rich experienced engineers are capable to undertake the custom tailoring hardware and software equipment requirements, and help our customer to build up the exclusive and personalized equipment and solution!
Would you please drop your ideas to us, our engineers are ready for you now!
Trusted by Industry Leaders

FAQ
What Is The Purpose Of A Working Electrode Fixture?
What Are The Different Types Of Working Electrode Fixtures?
What Are The Factors To Consider When Choosing A Working Electrode Fixture?
How Do I Care For And Maintain A Working Electrode Fixture?
What Is An Electrode In Electrochemistry?
What Is The Function Of Auxiliary Electrode?
What Are The Materials Used In Electrochemical Cell?
What Are The 3 Electrodes In Electrochemistry?
What Is The Difference Between Auxiliary And Reference Electrode?
What Are The Examples Of Electrochemical Material?
What Are The Different Types Of Electrochemical Electrodes?
What Materials Are Commonly Used For Auxiliary Electrodes?
What Materials Are Commonly Used For Electrochemical Electrodes?
How Do Auxiliary Electrodes Affect The Performance Of An Electrochemical Cell?
What Factors Should Be Considered When Selecting An Electrochemical Electrode?
Why Are Auxiliary Electrodes Necessary In Electrochemical Systems?
How Can Electrochemical Electrodes Be Used In Various Applications?
Are There Any Limitations Or Considerations When Using Auxiliary Electrodes?
4.9 / 5
I've never seen an electrode fixture that is as easy to use and operate as KINTEK SOLUTION's. It's a game-changer for my lab.
4.7 / 5
The quality of the electrode fixture is top-notch! I can see that it is made from durable materials and can withstand the demands of our lab.
5.0 / 5
The electrode fixture arrived promptly, and I appreciate the fast delivery. It's a huge time-saver for our laboratory.
4.8 / 5
The electrode fixture is a great investment for our lab. It's corrosion-resistant and can withstand a wide range of temperatures.
4.6 / 5
The fixture is very easy to customize, which makes it suitable for various experiments. I'm impressed with its versatility.
4.9 / 5
The electrode fixture is a great value for money. It's affordable and comes with all the necessary components, making it a cost-effective solution.
5.0 / 5
The electrode fixture is incredibly durable, and I'm confident it will last for years in our lab. It's a worthwhile investment for any laboratory.
4.7 / 5
The fixture is technologically advanced and allows us to conduct precise experiments. It's a valuable addition to our laboratory equipment.
4.8 / 5
The customer service at KINTEK SOLUTION is exceptional. They were very responsive to my inquiries and provided helpful advice.
4.9 / 5
I highly recommend KINTEK SOLUTION's electrode fixture to any laboratory. It's a top-quality product that enhances our experimental capabilities.
5.0 / 5
The electrode fixture is an absolute must-have for any lab. It streamlines our experiments and makes them more efficient.
4.7 / 5
I'm very satisfied with the performance of the electrode fixture. It's a reliable piece of equipment that delivers accurate and consistent results.
4.8 / 5
The electrode fixture is a valuable asset to our lab. It enables us to conduct complex experiments with ease and precision.
4.9 / 5
The fixture is a testament to KINTEK SOLUTION's commitment to innovation. It's a game-changer for our laboratory research.
REQUEST A QUOTE
Our professional team will reply to you within one business day. Please feel free to contact us!
Related Products

Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
High-quality graphite electrodes for electrochemical experiments. Complete models with acid and alkali resistance, safety, durability, and customization options.

Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
Looking for a way to polish your electrodes for electrochemical experiments? Our polishing materials are here to help! Follow our easy instructions for best results.

Gold Electrochemical Sheet Electrode Gold Electrode
Discover high-quality gold sheet electrodes for safe and durable electrochemical experiments. Choose from complete models or customize to meet your specific needs.

Gold Disc Electrode
Looking for a high-quality gold disc electrode for your electrochemical experiments? Look no further than our top-of-the-line product.

Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
Upgrade your electrochemical experiments with our Platinum Disc Electrode. High-quality and reliable for accurate results.

RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
Elevate your electrochemical research with our Rotating Disk and Ring Electrodes. Corrosion resistant and customizable to your specific needs, with complete specifications.

Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
Optimize your electrochemical experiments with our Platinum Auxiliary Electrode. Our high-quality, customizable models are safe and durable. Upgrade today!

Flat Corrosion Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Discover our flat corrosion electrolytic cell for electrochemical experiments. With exceptional corrosion resistance and complete specifications, our cell guarantees optimal performance. Our high-quality materials and good sealing ensure a safe and durable product, and customization options are available.

Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
Looking for a reliable quartz electrochemical cell? Our product boasts excellent corrosion resistance and complete specifications. With high-quality materials and good sealing, it's both safe and durable. Customize to meet your needs.

Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
Looking for corrosion-resistant coating evaluation electrolytic cells for electrochemical experiments? Our cells boast complete specifications, good sealing, high-quality materials, safety, and durability. Plus, they're easily customizable to meet your needs.

Super Sealed Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Super-sealed electrolytic cell offers enhanced sealing capabilities, making it ideal for experiments that require high airtightness.

Optical Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Upgrade your electrolytic experiments with our Optical Water Bath. With controllable temperature and excellent corrosion resistance, it's customizable for your specific needs. Discover our complete specifications today.

Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Gold Plating Tungsten Molybdenum Crucible for Evaporation
These crucibles act as containers for the gold material evaporated by the electron evaporation beam while precisely directing the electron beam for precise deposition.

Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
High-purity and smooth conductive boron nitride crucible for electron beam evaporation coating, with high temperature and thermal cycling performance.

Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Tungsten Crucible and Molybdenum Crucible for High Temperature Applications
Tungsten and molybdenum crucibles are commonly used in electron beam evaporation processes due to their excellent thermal and mechanical properties.

Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
Looking for a high-quality gas diffusion electrolysis cell? Our liquid flow reaction cell boasts exceptional corrosion resistance and complete specifications, with customizable options available to suit your needs. Contact us today!
Related Articles

Comprehensive Guide to Reference Electrodes: Types, Applications, and Selection Criteria
Explore the world of reference electrodes with our detailed guide. Learn about different types, their applications, and how to select the right one for your needs. Ideal for researchers and lab technicians.

Electrode Fixture Guide: Types, Design, and Applications
Discover the comprehensive guide to electrode fixtures, covering various types, design considerations, and their indispensable role in industries like electroplating, welding, and electrochemical cells.

Electrochemical Electrodes in Chemical Analysis
Electrochemical electrodes are essential tools used in many chemical analysis techniques and experiments. These electrodes are devices that allow us to measure the electrical potential difference in a chemical reaction.

Electrolytes and Electrochemical Electrodes
Electrolytes and electrodes play an essential role in electrochemistry. Electrolytes are substances that conduct electricity when dissolved in water or melted.

Understanding Electrodeposition with Electrochemical Electrodes
Electrodeposition is a process of depositing a metal or a non-metallic material onto a surface by applying an electric current.

A Comprehensive Guide to Reference Electrodes
Reference electrodes are used in electrochemical measurements to establish a stable potential against which the potential of the working electrode can be measured.

Innovations in Electrochemical Electrodes Technology
Recent advancements in nanotechnology and materials science have led to significant improvements in electrochemical devices, making them more efficient, durable, and cost-effective.

The Future of Electrochemical Electrodes
The latest trends and developments in electrode materials and their implications for the future of electrochemistry.

AgAgCl Reference Electrode Working Principle and Applications
Ag/AgCl reference electrode is a widely used reference electrode due to its stable potential and long-term stability.

Electrode Materials for Rotating Ring-Disk Electrodes
Rotating ring-disk electrodes (RRDEs) are used in a wide range of applications, from fuel cells to sensors, and they require careful selection of electrode materials for optimal performance.

How to Choose the Right Electrochemical Electrode
The choice of electrode material can have a significant impact on the performance of the electrochemical system.

Reference Electrodes: Calomel, Silver Chloride, and Mercury Sulfate - A Comprehensive Guide
Explore the world of reference electrodes, including calomel, silver chloride, and mercury sulfate. Understand their construction, principles, and applications in electrochemical measurements.