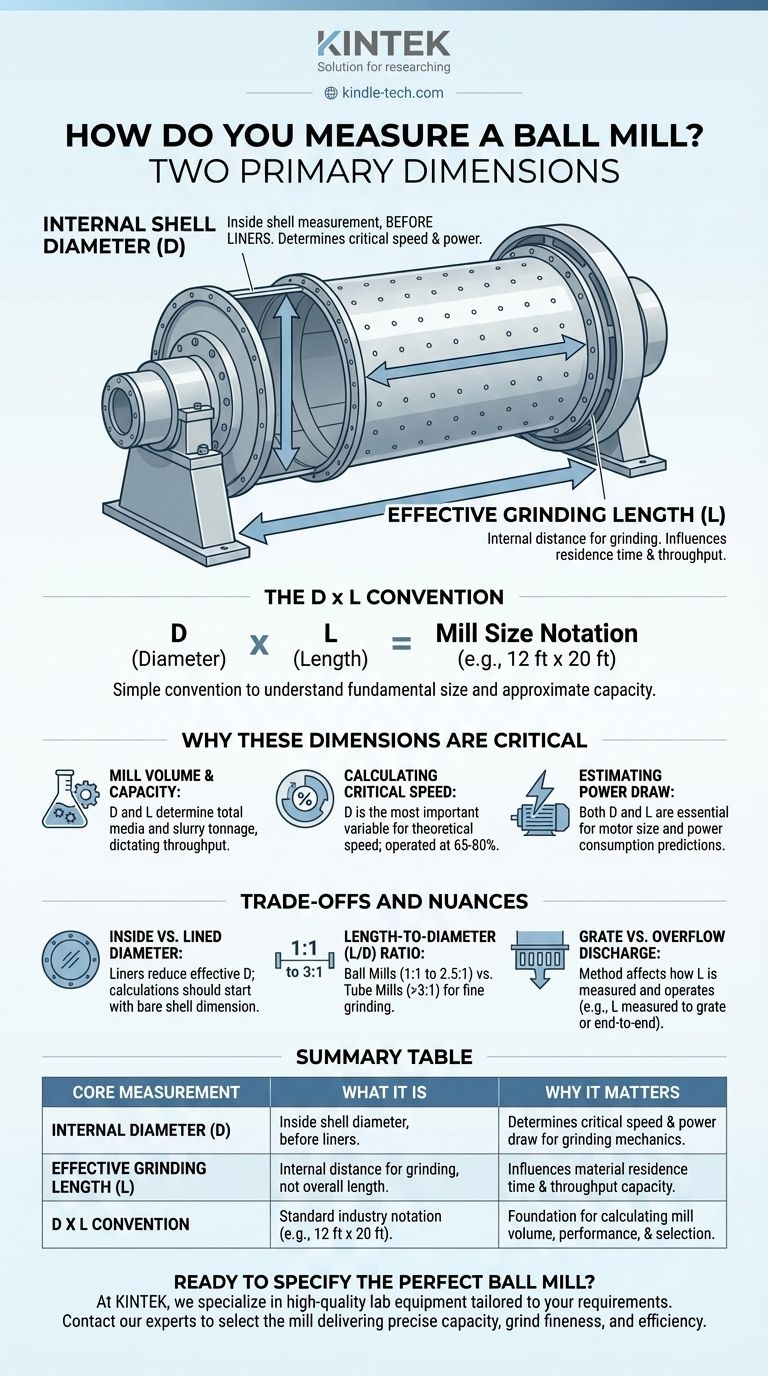
At its core, a ball mill is measured by two primary dimensions. The industry standard is to define a mill's size by its internal shell diameter followed by its effective grinding length. For example, a "12 ft x 20 ft" mill has an internal diameter of 12 feet and an effective grinding length of 20 feet. These two measurements are the foundation for determining the mill's capacity, power draw, and overall performance.
While the question is about "how" to measure a mill, the critical insight is understanding why these specific dimensions matter. The diameter dictates the grinding mechanics and power, while the length influences residence time and throughput, making these figures the language of mill selection and process design.
The Core Measurements: Diameter and Length
Understanding how a ball mill is specified requires knowing precisely what is being measured. The external dimensions are irrelevant; it's the internal working volume that defines the machine's capability.
Defining the Mill's Shell Diameter (D)
The first and most critical measurement is the internal diameter of the cylindrical shell. This measurement is taken from inside the steel shell, before any liners are installed.
This dimension is the primary factor in calculating the mill's critical speed—the theoretical speed at which the grinding media would centrifuge and cease to grind effectively.
Measuring the Effective Grinding Length (L)
The second key dimension is the effective grinding length (EGL). This is not the overall flange-to-flange length of the mill shell.
Instead, it represents the actual internal distance available for grinding. For overflow discharge mills, this is typically measured between the inside faces of the end liners. For grate discharge mills, it's the distance from the inside of the feed end liner to the face of the discharge grate.
The D x L Convention
The standard industry notation is Diameter (D) x Length (L). This simple convention allows engineers and operators to quickly understand the fundamental size and approximate capacity of a mill.
Why These Dimensions Are Critical
The D x L measurements are far more than just physical specs; they are the primary inputs for calculating a mill's operational parameters and performance potential.
Determining Mill Volume and Capacity
The internal volume of the mill is a direct function of its diameter and length. This volume determines the total tonnage of grinding media (balls) and slurry the mill can hold, which in turn dictates its throughput capacity. A larger volume allows for a larger charge and higher production rates.
Calculating Critical Speed
The mill's internal diameter (D) is the most important variable for calculating its critical speed. Mills are operated at a specific percentage of this critical speed (typically 65-80%) to achieve the desired grinding action—either cascading for finer grinding or cataracting for coarser, impact-based grinding.
Estimating Power Draw
Both diameter and length are essential for estimating the motor size and power required to operate the mill. Foundational comminution formulas, like the Bond Work Index equation, rely on these dimensions to predict the energy consumption needed to reduce a specific ore to a desired particle size.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
While D x L is the standard, several practical details can influence a mill's actual performance. Being aware of these is crucial for accurate design and operation.
Inside Diameter vs. Lined Diameter
It is vital to distinguish between the bare shell diameter and the lined diameter. New liners can reduce the effective internal diameter by several inches. As liners wear down, the effective diameter increases, which slightly alters the mill's critical speed and volume. All baseline calculations should start with the bare shell dimension.
The Length-to-Diameter (L/D) Ratio
The ratio of length to diameter is a key design choice.
- Ball Mills typically have an L/D ratio between 1:1 and 2.5:1. This shape promotes a good mix of impact and abrasion grinding.
- Tube Mills, which are used for finer grinding, have a much higher L/D ratio, often 3:1 or greater. The longer length increases particle residence time, ensuring a finer final product.
Grate vs. Overflow Discharge
The method of discharge affects how the length is measured and how the mill operates. A grate discharge mill allows for better slurry level control but requires measuring length to the grate, whereas an overflow mill's length is measured end-to-end. This can slightly alter the effective grinding volume between two mills with the same nominal dimensions.
Matching Mill Size to Your Process Goal
Ultimately, measuring a mill is the first step toward selecting the right one for a specific task. Use the dimensions to guide your decision based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: You will need a mill with a large internal volume, which means prioritizing a larger diameter and/or a longer length.
- If your primary focus is achieving a very fine final grind: The Length-to-Diameter (L/D) ratio becomes critical; a higher ratio (a longer, thinner mill) is often required to increase residence time.
- If your primary focus is process control and power efficiency: The internal diameter is the most influential variable, as it dictates the mill's critical speed and is a primary driver of power consumption.
Understanding these core measurements allows you to move beyond simple dimensions and specify a mill based on its true processing capability.
Summary Table:
| Core Measurement | What It Is | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Diameter (D) | Inside shell diameter, before liners are installed. | Determines critical speed and power draw for grinding mechanics. |
| Effective Grinding Length (L) | Internal distance available for grinding, not overall length. | Influences material residence time and throughput capacity. |
| D x L Convention | Standard industry notation (e.g., 12 ft x 20 ft). | Foundation for calculating mill volume, performance, and selection. |
Ready to specify the perfect ball mill for your lab's grinding needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including ball mills tailored to your specific process requirements. Our experts can help you interpret these critical dimensions to select a mill that delivers the precise capacity, grind fineness, and efficiency your research demands.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and let KINTEK be your partner in achieving superior grinding results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of polyurethane ball mill jars for silicon nitride? Ensure Purity & Prevent Metal Contamination
- Why is a ball mill jar lined with Y-ZrO2 required for Na3PS4 synthesis? Ensuring Purity in Sulfide Electrolytes
- Why are silicon nitride or zirconia preferred for milling iodo-vanadate-lead precursors? Ensure High Purity Results
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement
- How do stainless steel grinding jars and balls contribute to mechanical alloying? Optimize HEA Powder Synthesis



















