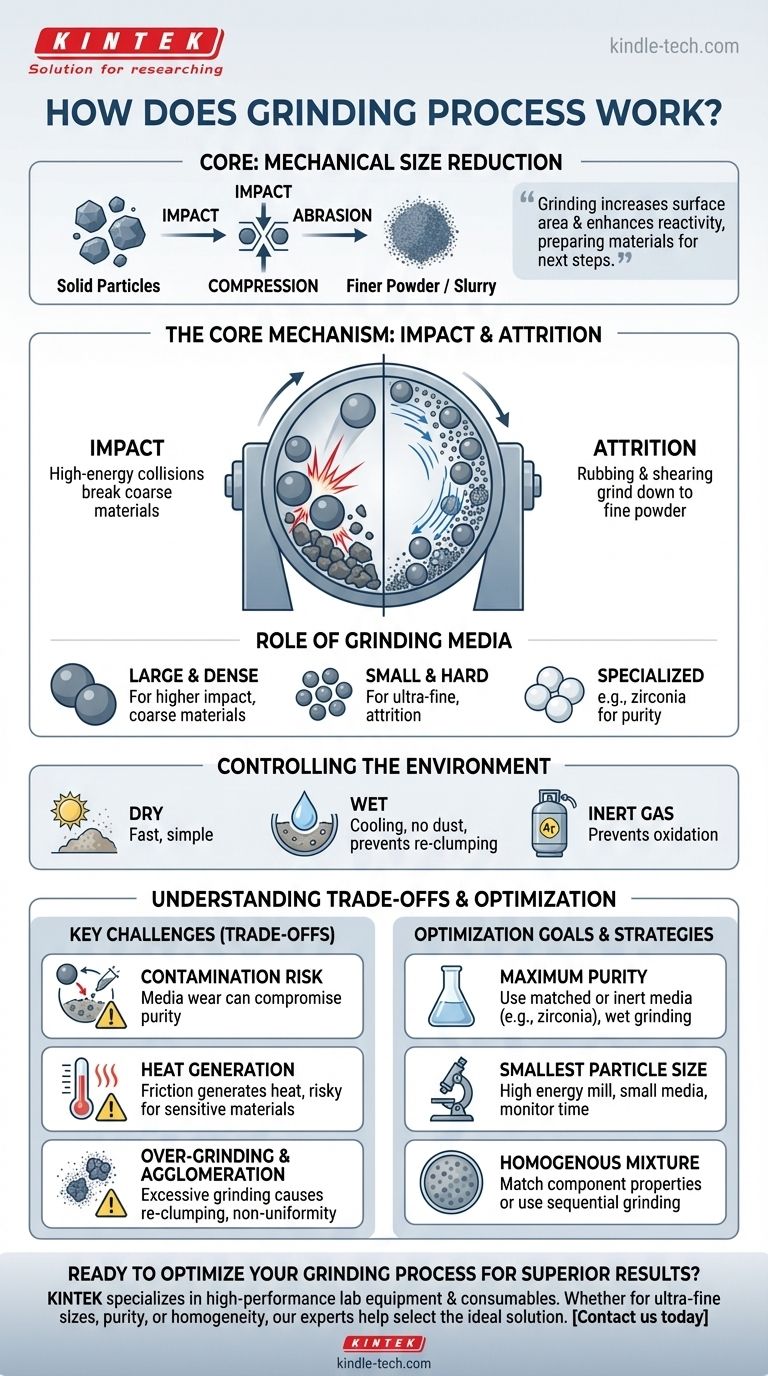
At its core, the grinding process is a mechanical method designed to reduce the size of solid particles. It operates by subjecting a material to intense physical forces—primarily impact, compression, and abrasion—which cause fractures that break larger pieces down into a finer powder or slurry.
Grinding is not merely about making things smaller; it is a fundamental process for altering a material's physical properties. By increasing surface area and creating a uniform particle distribution, grinding prepares materials for subsequent manufacturing steps and enhances their reactivity.

The Core Mechanism: How Grinding Works
The effectiveness of any grinding operation depends on the precise application of mechanical energy. This is typically accomplished within a specialized mill containing the material to be ground and a "grinding media."
Impact and Attrition
The primary forces that cause particle reduction are impact and attrition.
In a common setup like a planetary ball mill, hard grinding balls are placed in a rotating bowl with the source material. As the bowl spins at high speeds, the balls are lifted and then cascade down, colliding with the material at high energy. This is impact.
Simultaneously, the balls and particles rub against each other and the walls of the container. This rubbing and shearing action, known as attrition, grinds the material down further.
The Role of Grinding Media
The grinding media—the balls or rods inside the mill—are the instruments that transfer energy to the material. Their characteristics are critical.
Factors like the size, density, and hardness of the media are carefully selected. Larger, denser media deliver higher impact forces, suitable for breaking down hard, coarse materials. Smaller media are more effective for achieving an ultra-fine final product through attrition.
Controlling the Grinding Environment
Grinding is not always done in open air. The environment can be precisely controlled to achieve specific outcomes.
Dry grinding is often faster and simpler. However, wet grinding (in a suspension or slurry) helps dissipate heat, prevent dust, and can stop fine particles from re-clumping. Grinding in an inert gas like argon is essential when working with air-sensitive materials to prevent unwanted oxidation or chemical reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, grinding is a process that requires careful control to avoid common pitfalls. Understanding these limitations is key to achieving a successful outcome.
Risk of Contamination
The grinding media and the mill container itself are subject to wear. Over time, microscopic particles from the media can break off and mix with the material being ground. This contamination is a major concern in applications requiring high purity, such as pharmaceuticals or advanced ceramics.
Heat Generation
The immense friction and constant impacts generate significant heat. For temperature-sensitive materials, this can trigger unwanted phase transformations, decomposition, or melting. This is a primary reason for choosing wet grinding, as the liquid acts as a coolant.
Over-Grinding and Agglomeration
There is a point of diminishing returns. If a material is ground for too long, the particles can become so fine that their surface energy causes them to agglomerate, or clump back together. This negates the goal of size reduction and can create a non-uniform final product.
Optimizing the Grinding Process for Your Goal
The ideal grinding strategy depends entirely on your end goal. The process variables must be tuned to match the material's properties and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity: Choose grinding media made from the same material as your sample (if possible) or a very hard, inert material like zirconia, and consider wet grinding to minimize wear.
- If your primary focus is achieving the smallest particle size: Use a high energy density mill with smaller grinding media and carefully monitor the process time to avoid agglomeration.
- If your primary focus is preparing a homogenous mixture: Ensure the components have similar densities and hardness, or perform sequential grinding steps to achieve a uniform particle size distribution before mixing.
By controlling these forces and conditions, you can precisely engineer the fundamental characteristics of a material at the particle level.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Core Forces | Impact (high-energy collisions) and Attrition (rubbing/shearing) |
| Grinding Media | Size, density, and hardness of balls/rods are critical for energy transfer |
| Environment | Dry (fast), Wet (cooling, no dust), or Inert Gas (for sensitive materials) |
| Key Challenges | Contamination from media wear, heat generation, and over-grinding causing agglomeration |
| Optimization Goal | Match media and conditions to material properties (purity, fineness, homogeneity) |
Ready to optimize your grinding process for superior results? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including precision mills and contamination-minimizing grinding media. Whether you need to achieve ultra-fine particle sizes, maintain material purity, or create homogenous mixtures, our experts can help you select the ideal solution for your specific materials and goals. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's grinding efficiency and outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Laboratory Jar Ball Mill with Alumina Zirconia Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Laboratory Disc Cup Vibratory Mill for Sample Grinding
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
People Also Ask
- Why are zirconia milling balls preferred for P2-type layered oxides? Ensure High Purity and Grinding Efficiency
- What is the particle size of XRF sample preparation? Achieve Accurate & Repeatable Results
- In what way does a laboratory ball mill affect material properties when modifying PHBV/pulp fiber composites?
- Why is a hammer mill essential for processing raw materials in garden waste pelletization? Optimize Feedstock Sizing.
- What is the maximum speed of a ball mill? Find the Optimal Speed for Efficient Grinding
- Why is it necessary to crush or grind the samples? Ensure Accurate & Reliable Lab Analysis
- Where are hammer mills used? From Agriculture to Recycling, a Versatile Size-Reduction Solution
- What is the technical purpose of using a light ball mill for CuW30 powder? Achieve Perfect Particle Dispersion



















