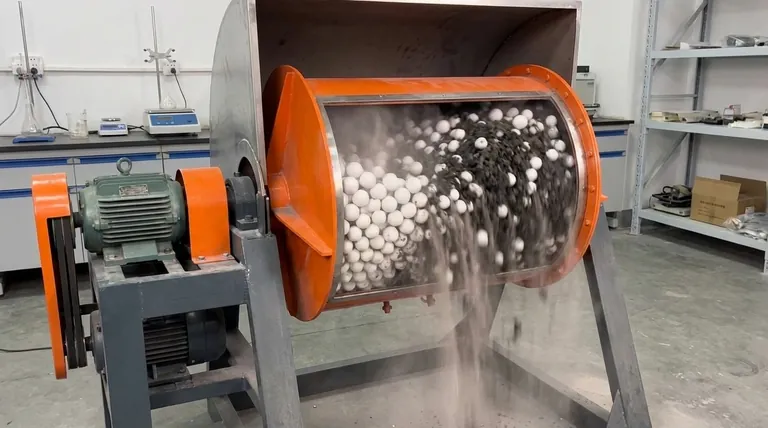
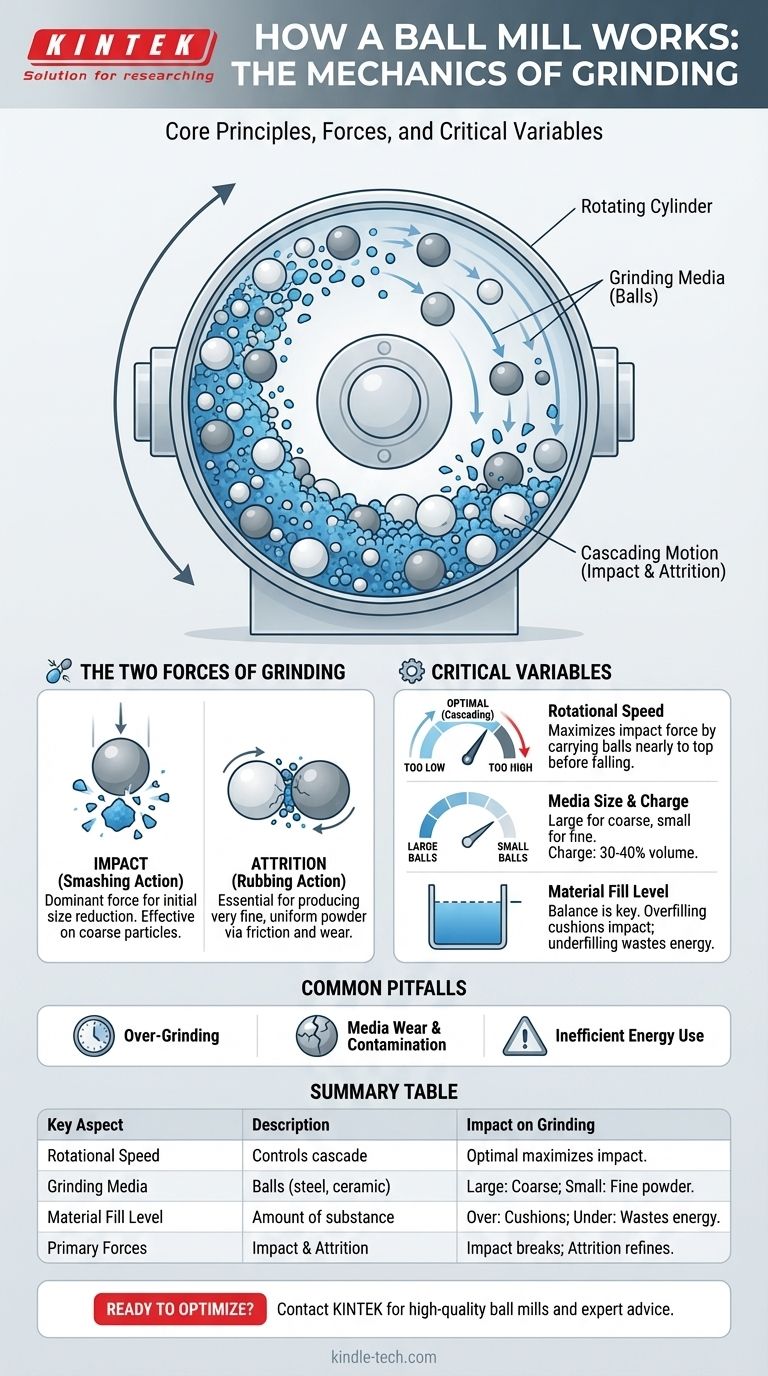
At its core, a ball mill is a grinder that reduces hard materials into a fine powder. It uses a simple and robust mechanism: a rotating, hollow cylinder is partially filled with the material to be ground and a charge of heavy grinding media, typically steel or ceramic balls. As the cylinder turns, the balls are lifted and then fall, crushing and grinding the material through a combination of impact and abrasion.
The essential principle of a ball mill is the controlled conversion of rotational energy into grinding force. The rotation doesn't just tumble the material; it lifts the grinding media, creating a continuous cascade that generates the two critical forces—impact and attrition—needed for effective size reduction.

The Core Mechanism: From Rotation to Reduction
Understanding how a ball mill works requires looking at its key components and the motion they create together. The design is straightforward, but the physics in action are precise.
The Rotating Cylinder
The main body of the mill is a horizontal cylinder or shell. It is rotated on its longitudinal axis by a motor. Material is fed in one end and, in continuous systems, discharged at the other.
The Grinding Media
Inside the cylinder is the grinding media, most commonly solid balls. These balls are the primary instrument of size reduction. They are typically made of high-chromium steel, stainless steel, or ceramic, chosen based on the material being ground and concerns about contamination.
The Cascading and Cataracting Motion
As the cylinder rotates, friction carries the balls up the interior wall. What happens next depends on the rotational speed. The balls travel upwards to a certain point and then break away, tumbling back down to the bottom of the mill in a continuous cascade. This motion is what powers the entire grinding process.
The Two Forces of Grinding: Impact and Attrition
A ball mill does not grind material in just one way. It employs two distinct physical forces simultaneously to achieve its result, making it effective on a wide range of materials.
Grinding by Impact
Impact is the force generated when the balls are lifted high enough to drop directly onto the material below. This powerful smashing action is highly effective at breaking down larger, coarse particles. It is the dominant force for initial size reduction.
Grinding by Attrition
Attrition is the grinding force created as the balls tumble over one another and against the cylinder wall. This creates a shearing and rubbing action that wears particles down, making it essential for producing a very fine, uniform powder.
Understanding the Critical Variables
The final particle size is not left to chance; it is controlled by carefully tuning several key operational variables.
Rotational Speed
This is the most critical factor. If the speed is too low, the balls will only tumble at the bottom, resulting in inefficient grinding dominated by attrition. If the speed is too high, centrifugal force will pin the balls to the cylinder wall, preventing them from falling and stopping the grinding process entirely. The optimal speed allows the balls to be carried nearly to the top of the cylinder before cascading down, maximizing impact force.
Media Size and Charge
The size of the grinding balls directly influences the final product. Large balls provide greater impact force for breaking coarse feed, while smaller balls create more contact points and promote attrition for a finer final grind. The "charge" refers to the volume of the mill filled with media, typically around 30-40%.
Material Fill Level
The amount of material being ground is also crucial. Too much material will cushion the impact of the balls, reducing grinding efficiency. Too little material means energy is wasted as the balls strike each other and the mill liner instead of the target substance.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While effective, the ball milling process involves trade-offs and requires careful management to ensure optimal and safe operation.
Risk of Over-Grinding
Running the mill for too long can produce particles that are finer than desired. In some cases, this can even lead to particle agglomeration, where the fine powders begin to stick together, negating the grinding process.
Media Wear and Contamination
The grinding media and the mill's inner lining are subject to wear over time. This wear introduces small amounts of the media or liner material into the final product. For high-purity applications like ceramics or pharmaceuticals, this contamination is a critical concern.
Inefficient Energy Use
Ball mills are energy-intensive machines. Operating outside the optimal parameters for speed and charge level leads to significant energy waste, as the rotational energy is not efficiently converted into grinding force.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The way you operate a ball mill should be directly tied to your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is coarse grinding of hard materials: Utilize larger, denser grinding balls and operate at a speed that maximizes the cataracting motion for the highest possible impact force.
- If your primary focus is producing an ultra-fine powder: Use smaller grinding media to increase surface area contact and promote attrition, often with a slightly longer grinding time.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Carefully optimize the rotational speed to just below the critical "centrifuging" speed and maintain the proper material and media charge levels to maximize grinding action per unit of energy.
Ultimately, mastering the ball mill lies in understanding and controlling the interplay between rotational speed, media selection, and the fundamental forces of impact and attrition.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description | Impact on Grinding |
|---|---|---|
| Rotational Speed | Controls the cascade of grinding balls | Too low: Inefficient. Too high: No grinding. Optimal: Maximizes impact. |
| Grinding Media | Balls (steel, ceramic) inside the cylinder | Large balls: Coarse grinding. Small balls: Fine powder. |
| Material Fill Level | Amount of substance being ground | Overfilling: Cushions impact. Underfilling: Wastes energy. |
| Primary Forces | Impact (smashing) and Attrition (rubbing) | Impact breaks large particles; attrition creates fine, uniform powder. |
Ready to Optimize Your Grinding Process?
Understanding the mechanics is the first step. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality ball mills and expert advice to help you achieve precise size reduction for your laboratory needs. Whether you're processing ceramics, pharmaceuticals, or other materials, our equipment ensures efficiency and consistency.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your lab's productivity and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why use ball milling for NMC cathode materials? Achieve Precision Particle Sizing for Composite Cathodes
- What is the key role of a planetary ball mill for IZO targets? Achieve Atomic-Level Uniformity in Material Preparation
- Why is a laboratory ball mill used in Co-Ni catalyst research? Optimize CO2 Conversion with Precise Milling
- How does a high-energy planetary ball mill facilitate the synthesis of sulfide glassy electrolytes? Achieve Amorphization
- What is the product size of a ball mill? Achieve Micron-Level Precision for Your Materials



















