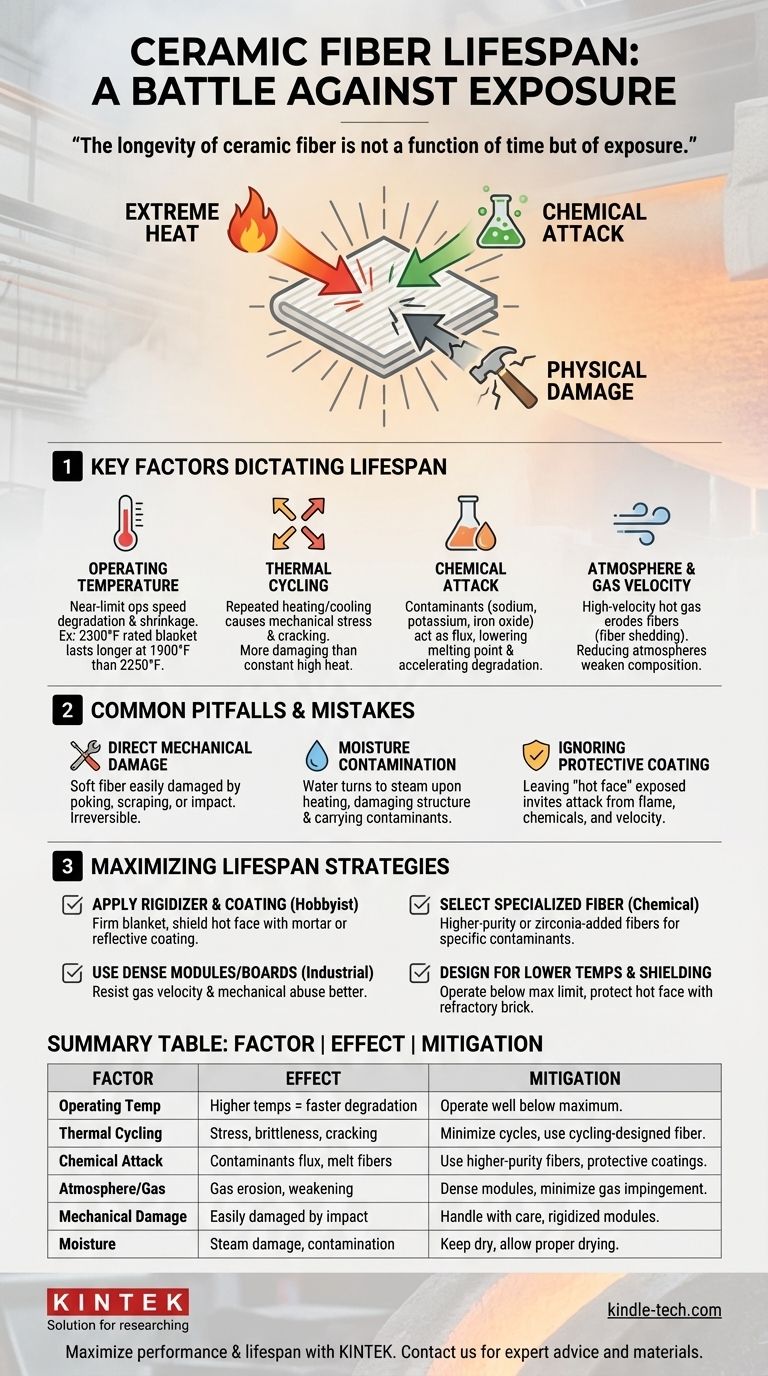
Under ideal conditions, the service life of a ceramic fiber blanket can extend beyond a decade. However, its practical lifespan is not a fixed number and is dictated entirely by its operating environment, often being reduced to mere months in demanding applications.
The longevity of ceramic fiber is not a function of time but of exposure. Its useful life is determined by a constant battle against three primary forces: extreme heat, chemical attack, and physical damage.
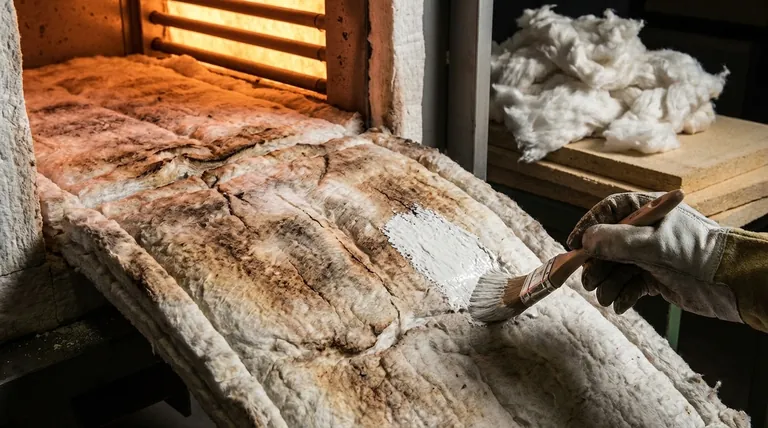

The Key Factors Dictating Ceramic Fiber Lifespan
The vast difference between a 12-year lifespan and a 6-month lifespan comes down to specific environmental stressors. Understanding these factors is the key to predicting and maximizing the material's service life.
Factor 1: Operating Temperature
The closer your application runs to the fiber's maximum service limit, the faster it will degrade. The fibers begin to vitrify (turn glassy and brittle) and shrink when held at high temperatures for extended periods.
For example, a blanket rated for 2300°F (1260°C) will last significantly longer if consistently operated at 1900°F (1040°C) than if it is pushed to 2250°F (1230°C) in every cycle.
Factor 2: Thermal Cycling
Repeatedly heating and cooling the fiber is often more damaging than holding it at a constant high temperature. This process, known as thermal cycling, causes the fibers to expand and contract.
Over time, this mechanical stress breaks down the fragile fiber structure, reducing its insulating properties and leading to brittleness and cracking. Applications like hobbyist forges or kilns that are fired up and cooled down frequently are prime examples of this.
Factor 3: Chemical Attack
Ceramic fiber is primarily composed of alumina and silica, which are vulnerable to certain chemical contaminants, especially at high temperatures. These contaminants act as a flux, lowering the melting point of the fibers.
Common culprits include sodium, potassium, iron oxide (from scale), and other alkalis. Even small amounts can dramatically accelerate degradation, turning the fluffy insulation into a shrunken, crusty shell.
Factor 4: Atmosphere and Gas Velocity
The environment inside the furnace or kiln plays a critical role. A high-velocity flow of hot gas, common in flue stacks or certain furnace designs, can physically erode the fiber surface.
This process, often called fiber shedding, literally blows the insulation material away over time. A chemically reducing atmosphere can also alter the fiber's composition and weaken it.
Common Pitfalls That Destroy Ceramic Fiber
Beyond the core environmental factors, simple operational mistakes are a frequent cause of premature failure. Avoiding these is crucial for extending the material's life.
Direct Mechanical Damage
Ceramic fiber blanket is extremely soft and fragile. Poking it with tools, scraping it with workpieces, or allowing parts to fall against it will cause immediate and irreversible damage.
Moisture Contamination
Allowing the fiber to become saturated with water or other liquids is highly detrimental. When heated, the rapid conversion to steam can damage the fiber structure. Furthermore, moisture can carry contaminants deep into the insulation.
Ignoring the Need for a Protective Coating
In many applications, especially forges and kilns, leaving the "hot face" of the fiber exposed is a major mistake. It leaves the fiber vulnerable to all forms of attack: high gas velocity, chemical contamination from flux or scale, and direct mechanical damage.
How to Maximize Lifespan in Your Application
You can significantly extend the life of your ceramic fiber insulation by proactively protecting it from the stressors that cause it to fail.
- If your primary focus is a hobbyist forge or kiln: Apply a rigidizer to firm up the blanket and then coat the hot face with a suitable refractory mortar (like Satanite) or a reflective coating (like ITC-100) to shield it from direct flame, chemical attack, and mechanical damage.
- If your primary focus is an industrial process furnace: Use dense ceramic fiber modules or boards instead of soft blankets for the hot face, as they offer superior resistance to gas velocity and mechanical abuse.
- If your application involves potential chemical contamination: Select a higher-purity or specialized fiber composition (like those with higher alumina or added zirconia) designed to resist the specific contaminants present.
- If your goal is absolute maximum longevity: Design your system to operate well below the fiber's maximum temperature rating and protect the hot face with a hard refractory brick or castable layer.
Ultimately, protecting the fiber from its environment is the single most effective strategy for extending its service life.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Lifespan | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | Higher temperatures near the limit cause faster degradation and shrinkage. | Operate well below the fiber's maximum rated temperature. |
| Thermal Cycling | Frequent heating/cooling causes mechanical stress, brittleness, and cracking. | Minimize cycles or use fiber designed for cycling. |
| Chemical Attack | Contaminants (alkalis, iron oxide) flux and melt fibers, drastically shortening life. | Use higher-purity fibers; shield with protective coatings. |
| Atmosphere/Gas Velocity | High-velocity hot gas erodes fibers; reducing atmospheres weaken them. | Use dense modules/boards; design to minimize gas impingement. |
| Mechanical Damage | Soft blanket is easily damaged by tools, scrapes, or impact. | Handle with care; use rigidized modules on hot face. |
| Moisture Contamination | Water turns to steam, damaging structure and carrying in contaminants. | Keep insulation dry; allow for proper drying before use. |
Maximize the performance and lifespan of your ceramic fiber insulation with KINTEK.
Whether you're building a hobbyist forge or optimizing an industrial furnace, the right materials and protective strategies are crucial for longevity. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab and processing equipment, offering the ceramic fiber products and expert advice you need to protect your investment.
We provide:
- High-purity ceramic fiber blankets, boards, and modules designed for specific temperature ranges and chemical resistance.
- Protective coatings and rigidizers to shield your insulation from direct flame, chemical attack, and physical damage.
- Expert consultation to help you select the right materials for your specific operating environment and maximize service life.
Don't let premature failure disrupt your operations. Contact our experts today to find the perfect ceramic fiber solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Yttria Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What is the function of alumina setter plates for LATP? Protect Material Purity & Prevent Adhesion
- What is the primary purpose of using alumina sintering plates? Ensure Purity for R1/3Zr2(PO4)3 Samples
- Which of the following is used in furnace to withstand high temperature? Key Materials for Extreme Heat
- What functions do high-purity alumina support rods serve in sCO2 experiments? Ensure High-Temp Material Integrity
- What are the typical properties of high-alumina (Al2O3) refractories? Enhance Performance with High-Temp Resilience



















